News
Sophos is proud to announce that we have been named a Leader in the 2025 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Endpoint Protection Platforms, marking our 16th consecutive report as a Leader in this category.
Sophos is recognized as a Leader among a total of 15 endpoint protection (EPP), endpoint detection and response (EDR), extended detection and response (XDR), and managed detection and response (MDR) vendors in this Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ report. The report provides readers with a comprehensive independent evaluation of the recognized solutions in this space.
In addition to this most-recent recognition, Sophos has also been named a “Customers’ Choice” vendor in the 2025 Gartner® Peer Insights™ Voice of the Customer Report for Endpoint Protection Platforms for the fourth consecutive year and in the inaugural Voice of the Customer Report for Extended Detection and Response. This makes Sophos the only vendor to be named a “Customers’ Choice” in both reports. We believe this highlights the comprehensive protection, detection and response capabilities delivered by the Sophos platform.
A Magic Quadrant Leader for the 16th consecutive report
Sophos has been recognized in the Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP) since the inaugural publication for this category in 2007. We believe this continued recognition reflects our dedication to delivering industry-leading protection for our customers and partners, and our sustained ability to keep organizations secure in the face of increasingly sophisticated threats. Achieving this recognition in the hyper-competitive endpoint security market for 16 consecutive reports demonstrates, in our opinion, Sophos’ focus on developing innovative solutions that evolve with the global threat landscape and the adversaries we are fighting every day.
Sophos and Secureworks: Unveiling the future of protection, detection, and response
Sophos completed its acquisition of Secureworks in February 2025, combining two leading and complementary portfolios to offer a comprehensive suite of solutions for small, midmarket and enterprise organizations. Secureworks Taegis XDR customers can use Sophos Endpoint powered by Intercept X to elevate their cyber defenses — at no additional charge — delivering both improved protection and return on investment. We believe the unique combination of Sophos Endpoint’s protection technologies and the powerful detection and response capabilities of our open AI-native XDR platform contributed to Sophos’ continued position as a Leader in this Gartner evaluation.
We have an exciting roadmap planned, with the further convergence of Sophos Central and Taegis XDR coming soon to provide customers with advanced detection and response tools, identity protection, an expanded range of technology integrations, and more.
The integration of Secureworks also adds a new Counter Threat Unit (CTU) to the Sophos X-Ops advanced threat response joint task force, further expanding the rich threat intelligence that informs all customers’ defenses. Backed by Sophos’ advanced security technologies and a broad network of intelligence contacts and partners, the CTU plays a critical role in identifying and tracking threat actors and analyzing anomalous activity, uncovering new attack techniques, threats, and major shifts in the threat landscape.
SecOps innovation and expertise — from our team to yours
Sophos’ technology is rooted in our unique prevention-first approach that reduces breaches, adapts defenses in response to an attack, and improves detection and response outcomes. Our commitment to innovation is, we believe, evidenced by our recognition as a Leader in this Gartner Magic Quadrant evaluation, and includes our continued focus on delivering a superior open AI-native security operations platform. Sophos has been pushing the boundaries of AI-driven cybersecurity for nearly a decade. AI technologies and human cybersecurity expertise work together to stop the broadest range of threats, with deep learning and generative AI capabilities embedded across Sophos products and services.
We extended our range of generative AI features in early 2025 with the new Sophos AI Assistant. Designed in partnership with Sophos’ frontline security analysts, Sophos’ AI-powered tools enable in-house security teams to benefit from real-world workflows and the experience of Sophos MDR experts. The Sophos AI Assistant isn’t just another AI tool — it’s expertise from the team behind the Sophos Managed Detection and Response service, distilled into an intelligent agent.
Sophos is honored to be recognized again as a Leader in this Gartner Magic Quadrant evaluation. We are committed to continuing to deliver industry-leading products and services that protect organizations from cyber threats, no matter where they are in their security journey.
Read the Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ report
To learn more about Sophos’ recognition in the 2025 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Endpoint Protection Platforms, read the full report.
Source: Sophos
This week, we’re updating Sophos Central firewall management with a couple of important updates, including a new account health check feature and enhanced scalability and performance for partners managing large groups of customers.
The new account health check capability provides a framework that will be expanded over time to perform a variety of helpful assessments across your entire estate. We’re kicking off this new account health check capability with a firewall backup assessment.
Firewall Backup Health Check
This new assessment will review your firewalls under management for backup status and will:
- Identify all firewalls in your estate that are not on a backup schedule
- Automatically add a backup schedule for those firewalls not already on a schedule
This ensures all your firewalls are backing up regularly to Sophos Central so if you ever need a configuration backup for one of your devices, it’s only a few clicks away.
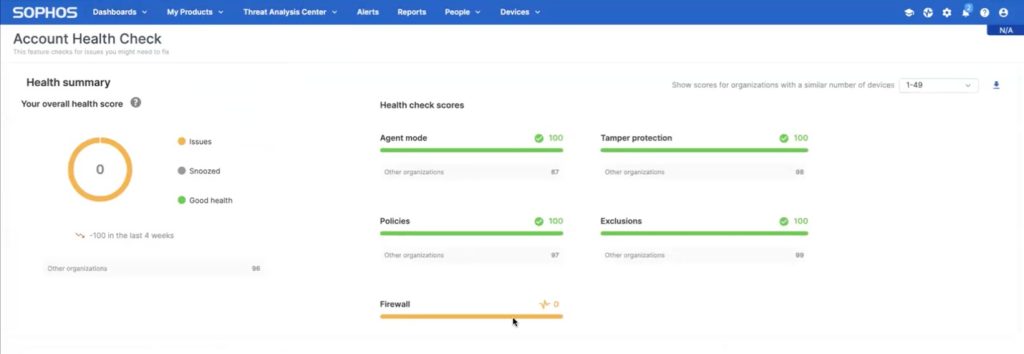
You will find a new widget for Firewalls under the Dashboards > Account Health Check area…
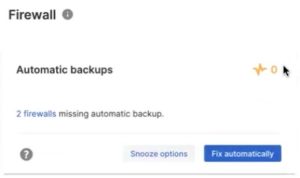
Scrolling down will show the new firewall backup assessment results, where you can choose to ignore the results, drill down to see which firewalls are missing backups, or fix them all automatically and assign a backup schedule.
You should see this new capability in Sophos Central next time you log in.
As mentioned, we will be adding more health check assessments over time for licensing, firmware, and more.
Scalability and performance enhancements for partners
Overall performance and scalability have been improved for partners managing large numbers of customers. Management should now be much easier for those partners managing thousands of firewall customers thanks to back-end optimizations and UI enhancements.
Source: Sophos
In Remote Support 25.1, BeyondTrust is reinforcing its core commitment to security, stability, reliability, and customer confidence. This release focuses on strengthening our foundation—delivering a smoother experience with enhanced stability and robust security updates.
Our top priority is to provide customers with the most secure and dependable remote access solution possible. To ensure maximum reliability, we prioritized a comprehensive security patch rollup, focused quality assurance (QA) efforts that include a full regression testing cycle, and key stability enhancements. Our goal: to empower your support teams to work with confidence, knowing they’re backed by the most secure and dependable remote access solution. These new features are designed to provide a smoother, more resilient experience, helping you operate with confidence and peace of mind.
We strongly recommend this update for all customers. Cloud customers will receive the update automatically. For on-prem deployments, the upgrade is available with just one click.
What’s New in BeyondTrust Remote Support 25.1
This release brings a series of security-forward enhancements and experience improvements, including:
- Full patch rollup and regression testing: All Remote Support updates and patches are now thoroughly tested for stability and security in both cloud and on-prem environments via a strenuous patch rollup and regression testing cycle.
- Improved version visibility: All maintenance releases and new patches are now visible in the Remote Support login window.
- Real-time dashboard access: Greater visibility with more detailed session metrics, available across both on-prem and cloud deployments.
- Jump client upgrade improvements: Smoother jump client upgrades and fewer disruptions with new reliability fixes.
- Enhanced endpoint automation: Improved filters and job organization for better proactive IT.
- UX/UI & performance refinements: A more intuitive user experience and smoother, more stable session performance.
- Certified compatibility with the BeyondTrust Pathfinder Platform: Remote support now has certified compatibility with the BeyondTrust Pathfinder platform, bringing more secure authentication to your cloud deployments and smoother integration with the BeyondTrust ecosystem.
To maximize the effectiveness and security of your Remote Support deployment, we recommend the following practices. These are aligned with our broader commitment to helping customers secure access at every layer.
1. Keep Your Deployment Up to Date
- For on-prem instances, enable “Apply Critical Updates Automatically” in the /appliance interface to simplify patching.
- Upgrade to the latest version for access to the newest security improvements.
2. Strengthen Credential Management
- Use the BeyondTrust Vault (included with every Remote Support deployment) to support discovery, rotation, and injection of credentials on up to 100k accounts.
- Use an external authentication provider (ex. SAML) over local accounts.
- Periodically review all active accounts on your appliance(s), especially those with admin privileges.
- Deactivate those not in use, and rotate passwords at recurring intervals where possible.
3. Apply Least Privilege Principles
- Use group policies and session policies when setting up user roles to enforce least privilege.
- Validate your policies and settings are being applied as intended using the Session Policy simulator.
4. Review and Harden Network Configurations
- Ensure that you are adhering to the network restriction best practices outlined in our documentation to prevent unauthorized access.
- Integrate with a SIEM using one of our various middleware for session data, and regularly review to monitor changes and detect anomalies and suspicious activity.
- Use outbound events to trigger alerts or log session activity in real-time.
- Configure syslog to send all configuration changes and authentication events to your SIEM.
In summary, at BeyondTrust, we believe security is not a one-time feature—it’s a continuous commitment. With Remote Support 25.1, we’re delivering meaningful improvements that reflect this mindset, strengthening the foundation for secure, stable, and high-performing remote support. Whether you’re a long-time customer or evaluating your remote support strategy, this release is designed to help your teams operate with greater confidence and resilience.
We encourage all customers—especially those managing on-prem deployments—to update to the latest version and take advantage of the best practices outlined above to further fortify your environment.
Source: BeyondTrust
Cyber threats continue to evolve, and organizations must stay ahead by fortifying their defenses.
While external attack surface management (EASM) identifies vulnerabilities that could be exploited from outside the network, many organizations face an internal blind spot: hidden vulnerabilities within their environments.
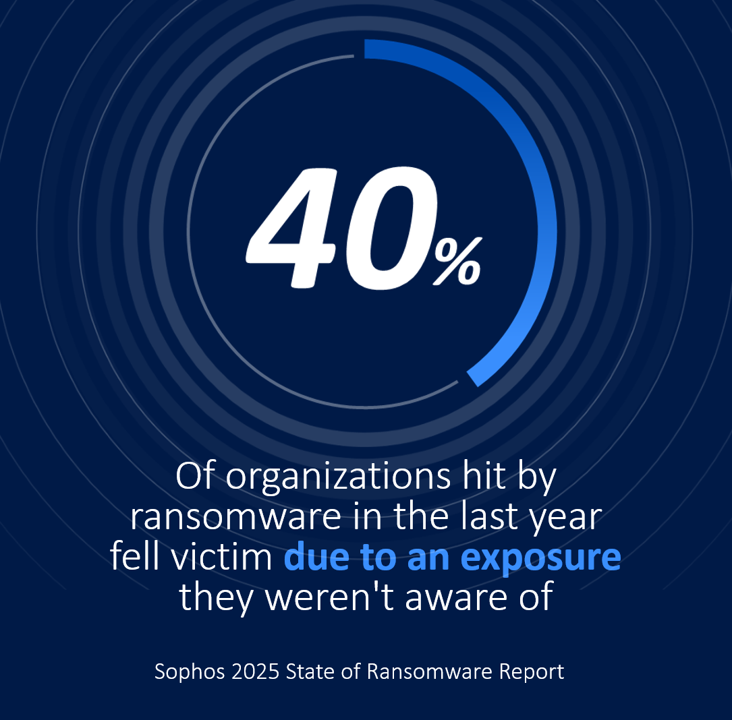
40% of organizations hit by ransomware in the last year said that they fell victim due to an exposure they weren’t aware of. To address this challenge, Sophos Managed Risk is expanding its capabilities with Internal Attack Surface Management (IASM).
Why IASM matters
Without visibility into internal vulnerabilities, your organization risks leaving critical gaps in your security posture. Threat actors who gain access to the network often move laterally to exploit internal weaknesses.
The latest release of Sophos Managed Risk introduces unauthenticated internal scanning, which assesses a system from the perspective of an external attacker without user credentials or privileged access. This helps you identify and mitigate high-risk vulnerabilities, such as open ports, exposed services, and misconfigurations that are accessible and potentially exploitable by attackers.
Key features and benefits
- Comprehensive vulnerability management: Regular automated scanning to identify weaknesses affecting assets within the network.
- AI-powered prioritization: Intelligently determines which vulnerabilities pose the highest risk and need immediate attention, guiding your team to prioritize their patching and remediation efforts.
- Industry-leading technology: Sophos leverages Tenable Nessus scanners to detect vulnerabilities inside the network and determine their severity.
- The Sophos advantage: Unlike vendors that separate EASM and IASM into distinct products, Sophos provides an integrated managed service powered by leading Tenable technology and backed by the world’s leading MDR service.
Available now
The new IASM capabilities are available today for all new and existing Sophos Managed Risk customers, with no changes to licenses or pricing. Customers can immediately benefit from the extended coverage by deploying Tenable Nessus scanners and scheduling automated scans in their Sophos Central console.
Learn more
As the cybersecurity landscape grows more complex, internal visibility is essential to achieve a more resilient security posture. With Sophos Managed Risk, you can now close security gaps affecting internal and external assets and take a proactive approach to vulnerability management. Learn more at Sophos.com/Managed-Risk or speak with a security expert today.
Source: Sophos
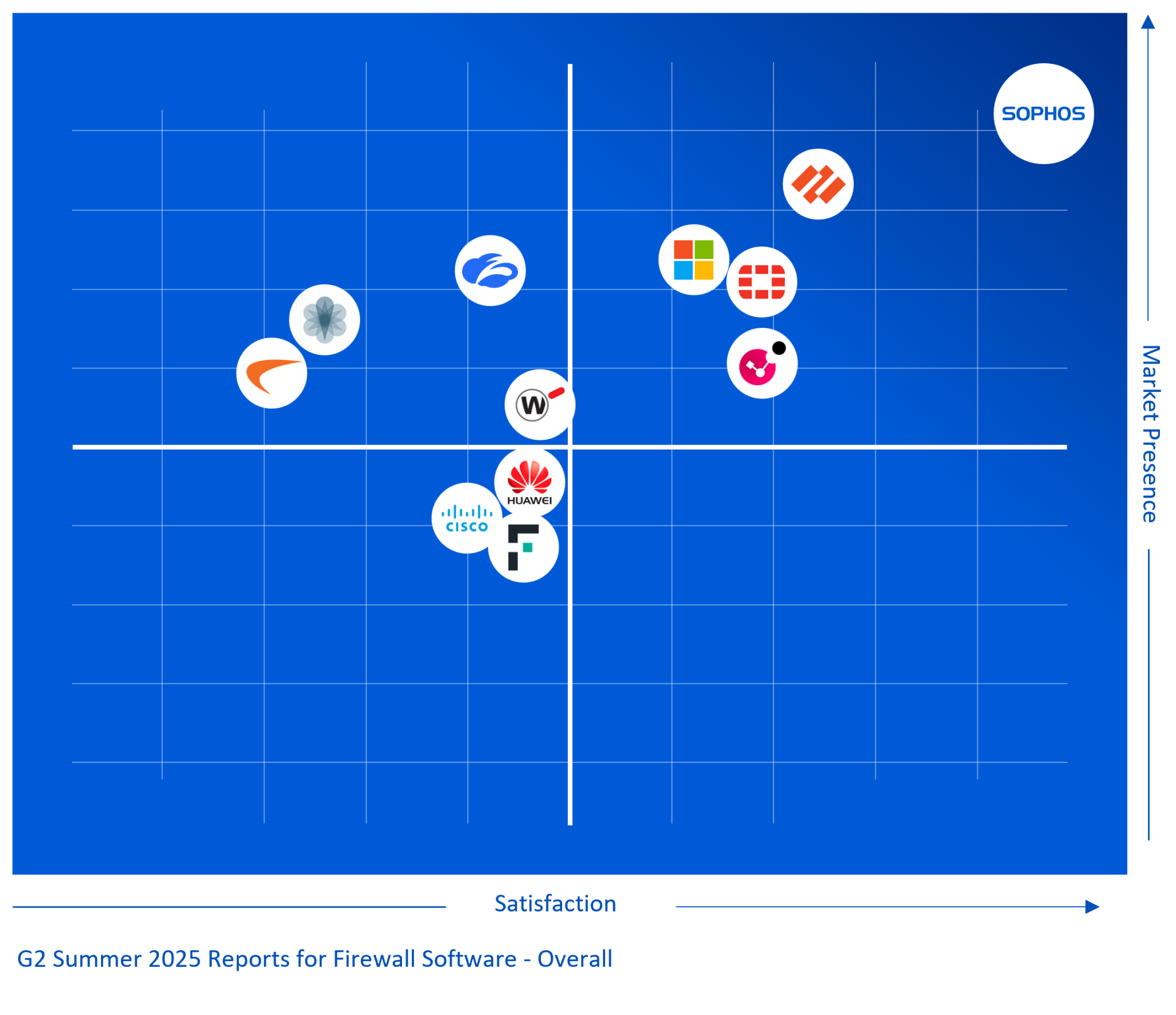
Customers have spoken, and the results are in. G2, a major technology user review platform, has just released their Summer 2025 Reports, where Sophos Firewall was rated the #1 Firewall in the Overall Firewall Grid. This marks the 10th consecutive G2 Seasonal Report where Sophos Firewall is the top-ranked Firewall, dating back to G2’s Spring 2023 Reports.
G2 rankings are based on independent, verified customer reviews on G2.com, the world’s largest software marketplace and peer-review platform. Additionally, Sophos Firewall was rated the #1 firewall in the Enterprise and Mid-Market grids.
What Sophos customers are saying
“The real time communication between endpoint and firewall allows automatic isolation of compromised devices, significantly reducing threat response time.” said a user in the Enterprise segment
“What I like best about Sophos Firewall is its intuitive web interface and deep visibility into network traffic. The Security Heartbeat feature, which integrates with Sophos endpoints, provides real-time health status of connected devices” said a user in the Mid-Market segment
“I am absolutely thrilled with the Sophos Firewall! It offers outstanding performance and security that far exceeds my expectations. The user interface is intuitive and easy to use, making management and configuration a breeze” said a user in the Mid-Market segment
“The best thing about [Sophos Firewall is that it simply works. It’s been bombproof for us for years and years” said a user in the Small Business segment
“We’ve been using Sophos Firewall for just over 10 years across multiple sites, and it has consistently delivered outstanding performance, visibility, and security. What makes Sophos stand out is its perfect balance of robust protection and user-friendly design” said a user in the Enterprise segment
“Sophos Firewall offers a wide range of security features, including advanced threat protection, web filtering, VPN management. Sophos Firewall is a well-regarded solution for businesses looking for a robust and easy-to-manage security platform” said a user in the Mid-Market segment
Why customers love Sophos Firewall
Customers love that they get much more than a firewall, that allows them to consolidate their cybersecurity products and services with a single vendor and a single management console. This allows them to simplify and save on their cybersecurity: on products, services, licensing, support and management.
They also love that Sophos Firewall gets better and faster with every release. Our latest release introduces a new Network Detection and Response capability that’s a first in the industry and helps detect active threats operating on the network – before they can become a real problem. We’re also improving performance and protection with every release – at no extra cost. Check it out today.
Source: Sophos
BeyondTrust continues to raise the standard for privileged access security. Version 25.1 of BeyondTrust Privileged Remote Access (PRA) delivers critical behind-the-scenes upgrades, doubling down on BeyondTrust’s mission to deliver the most dependable, secure privileged remote access platform on the market. This maintenance release focuses on providing stronger security, improved reliability, and more seamless control of privileged sessions.
Version 25.1 rolls up recent security patches, runs them through an exhaustive regression test suite, and layers in targeted stability improvements and key performance refinements for both cloud and on-prem environments.
This update is available whether you run a cloud or on-prem deployment of Privileged Remote Access. Cloud users receive updates automatically. On-prem customers can download and apply version 25.1 from the appliance console.
What’s New in Privileged Remote Access 25.1
This release brings a series of security-forward enhancements and experience improvements to Privileged Remote Access, including:
- Security patch rollup + rigorous testing: All PRA updates and patches have been thoroughly tested for stability and security in both cloud and on-prem environments. A strenuous patch rollup and regression testing cycle ensures consistency and delivers dependable performance across deployments.
- Improved version visibility: Admins can now view a complete list of installed maintenance releases directly from the PRA login window, boosting visibility and compliance readiness.
- Real-time dashboard access: Gain deeper insight into usage patterns, session activity, and system health across cloud and on-prem PRA deployments.
- Smoother Jump client upgrades: Bug fixes and upgrade process refinements improve reliability during endpoint and Jump Client updates.
- Enhanced endpoint automation: New filter and job organization options help streamline privileged task automation and improve proactive IT workflows.
- Refined UX/UI & performance enhancements: Enjoy smoother performance and usability improvements that reduce friction across daily workflows.
Certified Pathfinder compatibility: PRA now officially integrates with the BeyondTrust Pathfinder platform, delivering more secure, seamless authentication across hybrid access environments and smoother integration with the BeyondTrust ecosystem.
Even the strongest tools benefit from smart configuration. Use these best practices to maximize the protection and control offered in Privileged Remote Access 25.1:
1. Patch Smart & Stay Current
- On‑prem? Toggle “Apply Critical Updates Automatically” in /appliance to streamline patching.
- Always run the latest build to inherit the newest hardening measures.
2. Lock Down Credentials
- Use the built-in BeyondTrust Vault for secure credential discovery, rotation, and injection.
- Prioritize SAML and other external identity providers.
- Regularly audit admin accounts, disable any unused accounts, and rotate passwords proactively.
3. Apply Least Privilege with Precision
- Set strict session and group policies to limit access to only what’s required.
- Test policy configurations with the Session Policy Simulator before rollout.
4. Harden Your Network (Access) Layer
- Follow the network restriction checklist to minimize external exposure and block unauthorized access.
- Route session data to your SIEM via middleware and set up syslog and outbound event hooks for real-time monitoring.
- Enable outbound event hooks for real-time alerts, and forward syslog data for every config change or auth event.
Why This Release Matters
Security never stands still, which is why BeyondTrust is committed to delivering secure, intelligent remote access, where control is precise, visibility is clear, and protection is always evolving. Privileged Remote Access 25.1 reinforces BeyondTrust’s continuous improvement model by delivering practical, behind-the-scenes enhancements that translate into tangible confidence for your technicians and your auditors alike. Whether you’re defending internal infrastructure or enabling third-party access, PRA 25.1 delivers the trust and control modern security teams demand.
Already a customer? Upgrading keeps you on the safest, most stable footing. Upgrade now to benefit from the latest security and performance advancements.
Source: BeyondTrust
As organizations hurry to embrace AI and its many benefits, one challenge weighs heavily on CISO and security teams’ minds: how do you quickly and effectively secure these new capabilities?
Today, Silverfort introduces AI Agent Security, our latest innovation designed to empower CISOs to lead secure AI adoption by treating AI agents as identities—governed, visible, and protected with the same rigor applied to human users.
The emerging risk: AI agents left to their own devices
Gone are the days when only the most experimental companies adopted AI. Now, as executives across industries demand AI integration, it’s a business-critical priority. But while productivity soars, so do new risks.
One area these risks abound is with the use of AI agents: software programs that perform tasks autonomously or on behalf of a human, often making decisions and taking actions based on context or input data. To perform these tasks, AI agents require a level of access to systems, resources and data—just like human users.
And that’s where the problem lies. AI agents exist in the grey area between human and non-human identities. They need a different type of protection, because current identity and access management (IAM) solutions simply weren’t built for machines who could make their own decisions. They lack visibility and effective governance capabilities for AI agents, leading to a substantial risk of misuse by threat actors, not to mention potential compliance violations and limited auditability.
This creates a visibility and control vacuum. CISOs, developers, identity teams, urgently need solutions that seamlessly connect AI agents’ identities and privileges to the human actors behind them to ensure full visibility, compliance, and risk management at the speed of innovation. Yet they are expected to secure a rapidly expanding AI ecosystem using tools that were never designed for it.
Against a backdrop where expertise is still emerging, the pressure to move quickly is high, and AI agent behavior is evolving every day, it’s easy to see why the task at hand might feel impossible.
Our vision: Securing AI agents starts with treating them as an identity
Luckily, there’s a way forward. Our method for securing AI is built on a simple premise: AI agents must be treated as identities and they should be tied to a person. At the core of this is a new definition of “who is doing the action”: not just a username or token, but the combined identity of the human and the AI agent acting on their behalf.
With this identity-first approach, we can automatically discover, classify and monitor AI agent identities before applying dynamic access policies to each of them and, crucially, tying them to their human initiators. This means we can protect all involved with robust, real-time security controls and prevent attackers from using AI agents in lateral movement.
This allows you to put governance and boundaries around autonomous agents and pull humans into the loop when appropriate, while protecting all involved with robust security controls. Even better, our unique identity-first architecture allows for a single, end-to-end view of every AI agent and MCP server in action in your environments while being quick to deploy and implement. This means Silverfort can limit AI agent misuse, privilege escalations, and unauthorized actions in your environments within hours of deployment.
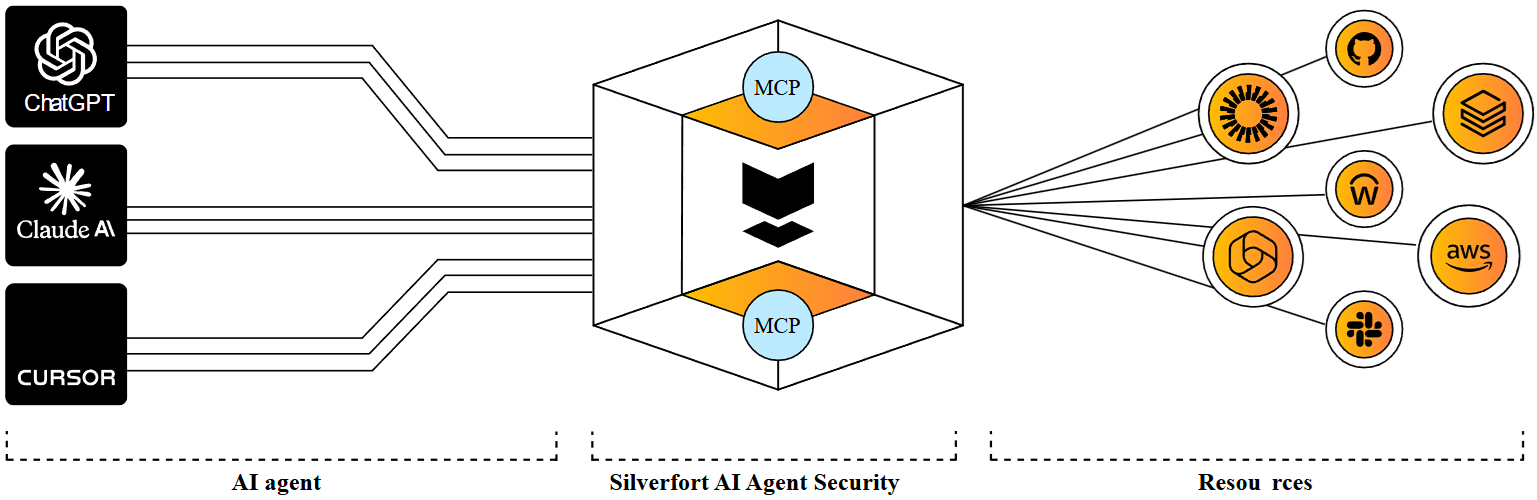
In short, Silverfort’s AI Agent Security product:
- Discovers, classifies and monitors AI agents based on real-world behavior
- Ties every action to a responsible human to ensure accountability
- Enforces dynamic, least-privilege access policies tailored to each AI agent’s role
- Provides comprehensive auditability, enabling compliance in a shifting regulatory landscape
- Empowers organizations to securely adopt AI agents without requiring them to be AI experts
- Deploys rapidly to prevent key identity security threats in your environment with minimal effort
It’s the first solution that uses this unique architecture to reimagine identity security specifically for AI, significantly reducing the complexity and time required to safely and compliantly adopt AI technologies. With AI Agent Security, AI adoption is no longer a security compromise, but a secure, scalable strategy.
Built for businesses, backed by Silverfort
We’re just getting started. As the landscape evolves, Silverfort will continue to lead the way in pioneering technologies that help security leaders stay ahead of the curve.
We’re actively inviting Silverfort customers to become design partners and help shape the future of AI identity security. If you’re leading AI adoption and need to secure it fast, we want to work with you. Find out more and get a demo.
Source: Silverfort
The sixth annual Sophos State of Ransomware report provides fresh insights into the factors that led organizations to fall victim to ransomware and the human and business impacts of an attack.
Based on insights from a vendor-agnostic survey of 3,400 IT and cybersecurity leaders across 17 countries whose organizations were hit by ransomware in the last year, the report combines year-on-year insights with brand new areas of study, including why ransom payments rarely match the initial demand, and the downstream impact of ransomware incidents on in-house teams.
Download the report to get the full findings and read on for a taste of some of the topics covered.
Why organizations fall victim to ransomware
It is rarely a single issue that leaves organizations exposed to ransomware; rather a combination of technological and operational factors contributes to organizations falling victim to attack.
Technical root causes
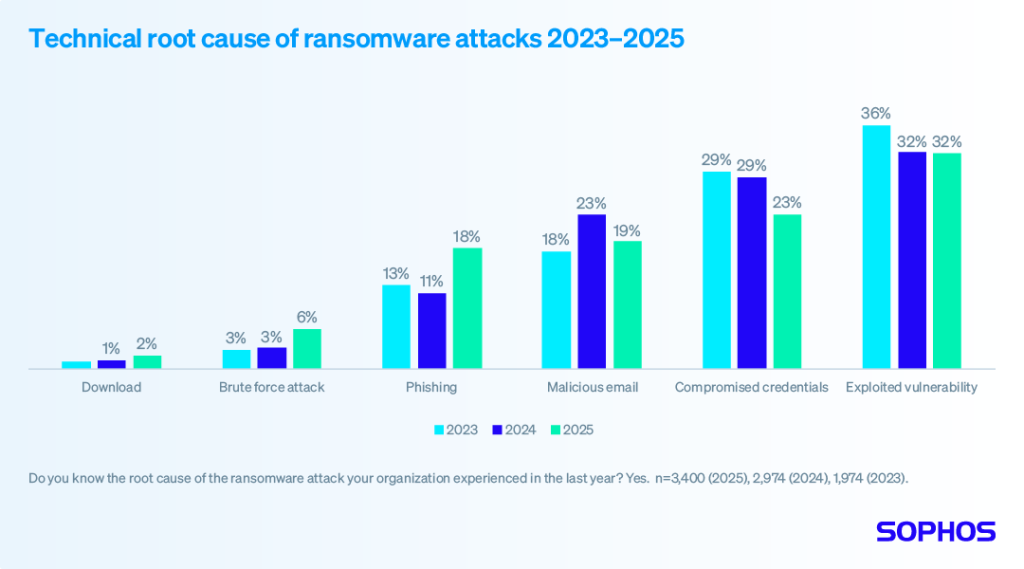
For the third year running, victims identified exploited vulnerabilities as the most common root cause of ransomware incidents, used to penetrate organizations in 32% of attacks overall. This finding highlights the importance of identifying and patching security gaps before adversaries can take advantage of them.
Compromised credentials remain the second most common perceived attack vector, although the percentage of attacks that used this approach dropped from 29% in 2024 to 23% in 2025. Email remains a major vector of attack, whether through malicious emails (19%) or phishing (18%).
 Read the full report for insights into how attack vectors vary based on organization size.
Read the full report for insights into how attack vectors vary based on organization size.
Operational root causes
For the first time, this year’s report explores the organizational factors that left companies exposed to attacks. The findings reveal that victims are typically facing multiple operational challenges, with respondents citing 2.7 factors, on average, that contributed to them being hit by ransomware.
Overall, there is no single stand-out source, with the operational causes very evenly split across protection issues, resourcing issues, and security gaps.
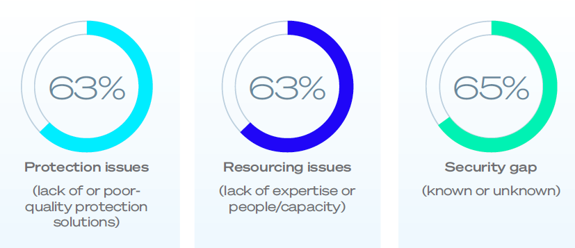
Download the full report for a deeper dive, including insights into the individual factors behind these numbers, as well as a breakdown of operational challenges by company size and industry sector.
Recovery of encrypted data
The good news is that 97% of organizations that had data encrypted were able to recover it. Less encouraging is that data recovery through backups is at its lowest rate in six years.
Just under half (49%) paid the ransom and got their data back. While this represents a small reduction from last year’s 56%, it remains the second highest rate of ransom payments in the last six years.
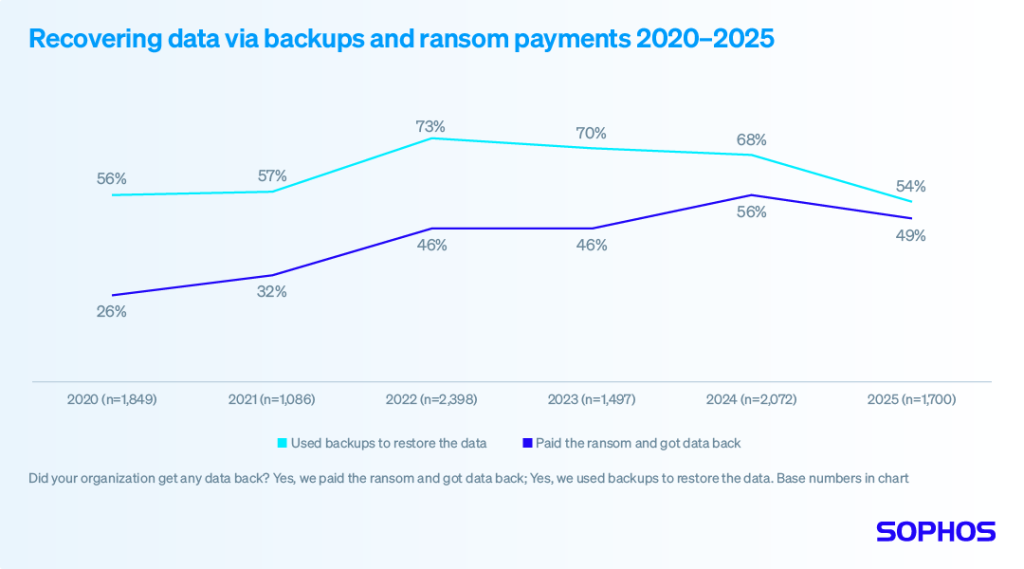
Read the report to learn more about both data encryption rates and data recovery.
Ransoms: Demands and payments
There is good news on this front: both initial ransom demands and actual ransom payments dropped over the last year – largely driven by a reduction in the percentage of demands/payments of $5 million or more. While encouraging, it’s important to keep in mind that 57% of ransom demands and 52% of payments were for $1 million or more.
826 organizations that paid the ransom shared both the initial demand and their actual payment, revealing that they paid, on average, 85% of the initial ransom demand. Overall, 53% paid less than the initial ask, 18% paid more, and 29% matched the initial demand.
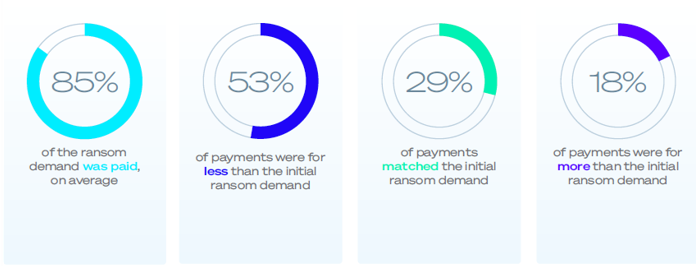
Read the full report to learn more, include details of why some organizations pay more than the demand and others are able to pay less.
The business and human consequences of ransomware
The data reveals that organizations are getting better at responding to attacks, reporting lower costs and faster recovery.
The average (mean) cost to recover from a ransomware attack (excluding any ransom payment) dropped by 44% over the last year, coming in at $1.53 million, down from $2.73 million in 2024. At the same time, over half of victims (53%) were recovered within a week, a significant jump from the 35% reported in 2024.
Having data encrypted in a ransomware attack has significant repercussions for the IT/cybersecurity team, with all respondents saying their team has been impacted in some way.
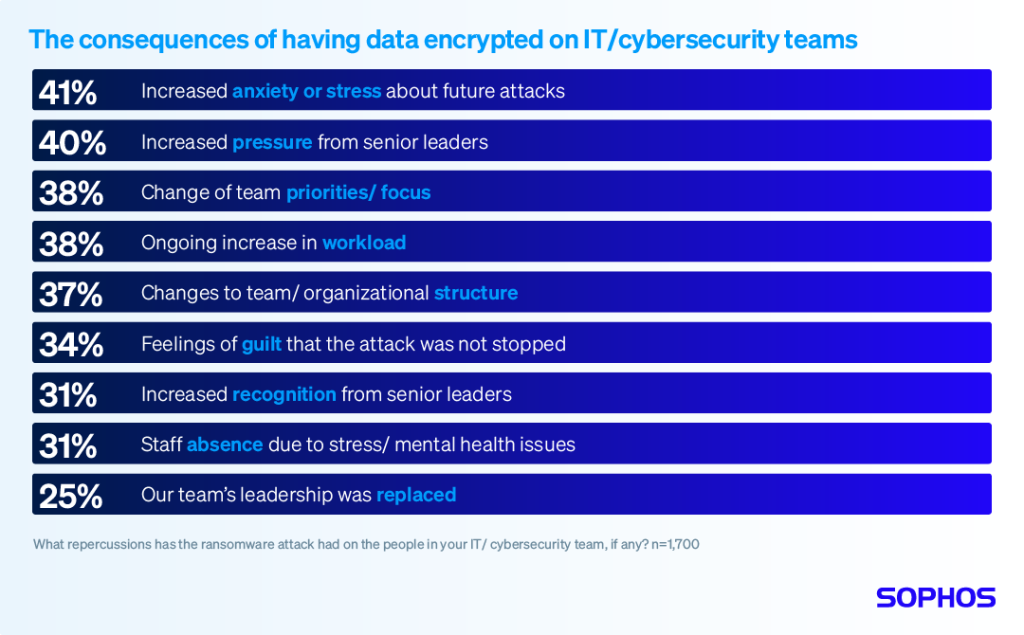
Read the report
Download the report to get the full findings together with recommendations on how to elevate your ransomware defenses based on the learnings from 3,400 organizations that fell victim in the last year. To learn more about how Sophos MDR and Sophos Endpoint Protection deliver world-leading ransomware protection, visit our website or speak with your Sophos adviser.
Source: Sophos
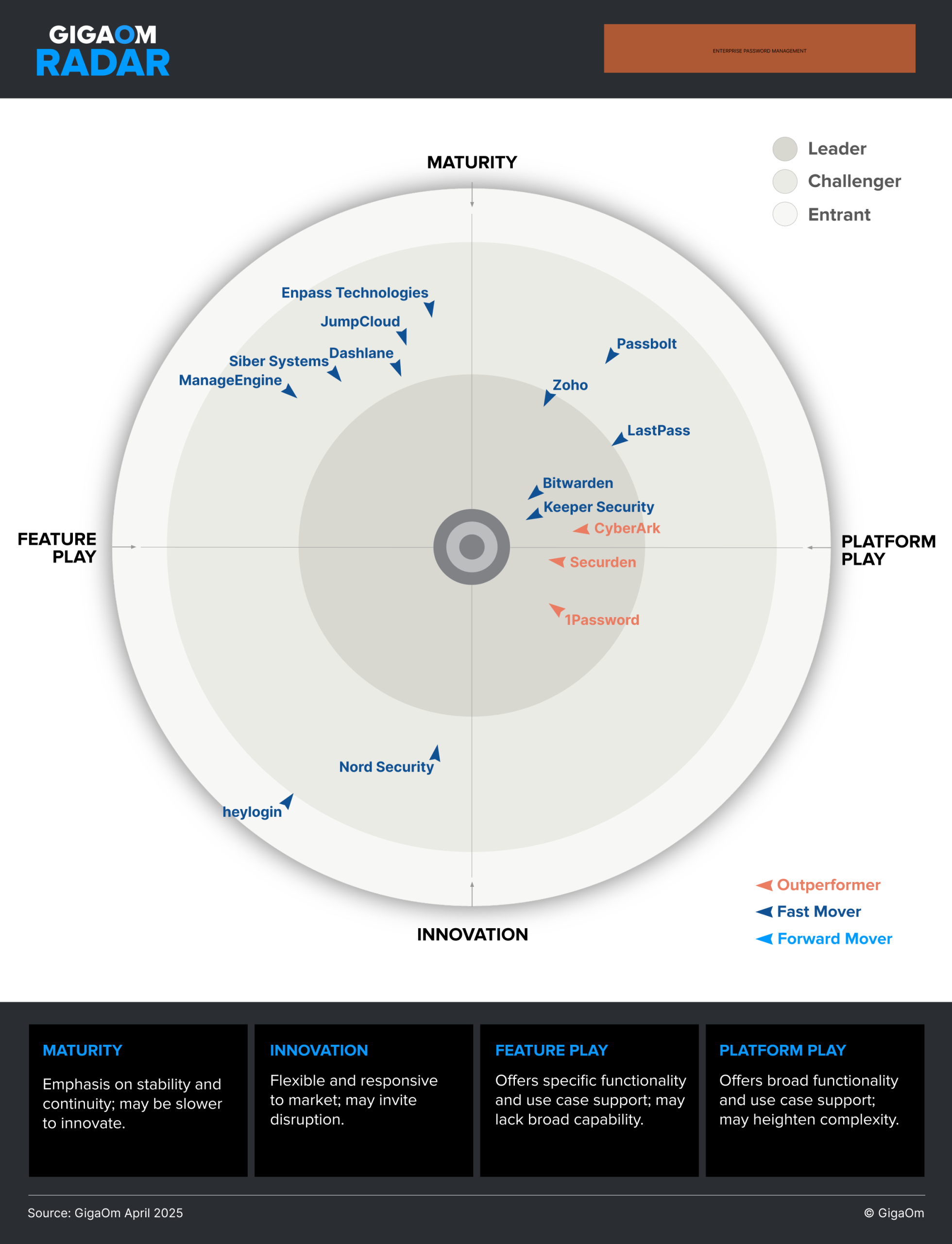
GigaOm, a renowned technology analyst firm, has recognized Keeper Security as the Overall Leader in Enterprise Password Management for the fourth year in a row. The GigaOm 2025 Radar Report for Enterprise Password Management highlights Keeper’s Privileged Access Management (PAM) solution, KeeperPAM®, which helps organizations secure passwords, credentials, secrets and connections to mitigate cyber risks and defend against internal and external threats. The report also highlights Keeper’s password protection capabilities and user-friendly software.
Report overview and key highlights
This GigaOm Radar report examines 15 of the top enterprise password management solutions and compares offerings against the capabilities (table stakes, key features and emerging features) and non-functional requirements (business criteria) outlined in the companion Key Criteria report. Together, these reports provide an overview of the market, identify leading enterprise password management offerings and help decision-makers evaluate these solutions so they can make a more informed investment decision.
This is the fourth year that GigaOm has evaluated the enterprise password management space, and it is also the fourth year that Keeper Security has been named the Overall Leader. The report builds on previous analysis while considering how the market has evolved over the past year.
What sets Keeper apart
Unlike fragmented tools or limited vault-only solutions, Keeper delivers a zero-trust, zero-knowledge security architecture that secures all credentials – user and machine – from a single platform. Key advantages include:
- Compliance-ready architecture with best-in-class security: FedRAMP and GovRAMP Authorized, FIPS 140-3 validated, with the longest-standing SOC 2 and ISO certifications in the industry.
- Cross-platform compatibility: Access Keeper on desktop, mobile and browsers from any location on any device.
- Fine-grained access controls and secure record sharing: Including time-limited access, one-time share and self-destructing record capabilities.
- Seamless security integrations: Keeper works out of the box with passwordless authentication, SSO, SIEM, SDK, MFA and CI/CD applications.
Since the release of last year’s GigaOm report, Keeper has introduced a series of updates and new features for its platform. These include features such as Remote Browser Isolation and the Risk Management Dashboard, along with the official release of KeeperPAM, the next generation of Keeper’s Privileged Access Management (PAM) platform.
Additionally, Keeper has expanded both passkey and passwordless authentication functionalities, along with continuous UI/UX improvements to provide a cleaner, more accessible experience designed to reduce friction and increase productivity. These innovations reflect Keeper’s commitment to user-centric security, combining usability with powerful administrative controls.
Keeper evolves with the cyber landscape, integrating solutions and adding capabilities based on customer feedback and questions. Whether deployed as a standalone enterprise password manager or as part of Keeper’s broader security suite, the KeeperPAM platform adapts to meet the growing needs of organizations of all sizes.
Why password management matters
GigaOm’s 2025 report makes it clear: Passwords remain a critical vulnerability in today’s cybersecurity landscape. With users and organizations managing thousands of credentials, the risk of compromise through weak or reused passwords continues to rise. A modern enterprise password management platform like Keeper addresses these challenges by:
- Enforcing strong password practices and visibility across the organization.
- Protecting machine identities and secrets in developer and DevOps environments.
- Enabling passwordless authentication to reduce risk and streamline access.
- Offering centralized management and auditing for compliance and security teams.
As organizations mature their security posture, password management becomes a pillar that supports zero-trust frameworks, regulatory compliance and proactive risk reduction. Enterprise password management is more than just storing passwords; it’s about protecting access at scale, on every device, in every location.
Try Keeper for free
Protect your organization’s passwords, credentials and secrets with zero-trust and zero-knowledge security. Sign up for a free 14-day trial or reach out to our team to learn more.
Looking to secure your organization beyond password management? Learn more about KeeperPAM®
Strengthen your organization’s security posture by investing in a privileged access management solution that supports a zero-trust strategy. KeeperPAM is both zero trust and zero knowledge, which helps prevent unauthorized access and ensures that only the right users have the appropriate level of access. With features like endpoint privilege management, role-based access control, Just-in-Time (JIT) access and detailed auditing, monitoring and session recording, KeeperPAM helps your organization secure critical data and maintain tight controls over all infrastructure.
To learn more about how KeeperPAM can secure your organization with its zero-trust strategy, request a demo today.
Source: Keeper Security
Threat actors remain on the offensive, constantly expanding how they infiltrate organizations’ environments and inflict financial, operational, and reputational harm. Turning to a proven incident response provider for emergency services is essential when a threat actor strikes your business.
Sophos and Secureworks have built industry-leading incident response services designed to help customers in their hour of need with a rapid response to cyberattacks.
We are delighted to announce the general availability of Sophos Emergency Incident Response, the first service to combine the strengths of these two robust incident response practices into one converged offering.
Rapid remote and onsite support
When a cyber emergency strikes, there isn’t time to waste. You need quick action by experienced incident response personnel to assess and contain the threat, specialized skills to neutralize and eject the adversary, and an understanding of what happened and how to prevent it moving forward.
Sophos Emergency Incident Response delivers remote and onsite assistance to organizations experiencing a cyberattack or who believe they are a victim of threat actor activity. This service focuses on executing responses throughout all stages of the incident response lifecycle, from initial contact and investigation through iterative forensics and threat analysis, attack surface reduction, remediation activities, improvement recommendations, and detailed post-incident summary.
Fueled by threat intelligence and vast security expertise
Sophos Emergency Incident Response experts provide digital forensics, malware analysis, threat intelligence from the Counter Threat Unit research team – now part of Sophos X-Ops – and threat hunting to find and eliminate threats. We use cross-disciplinary subject matter experts (such as penetration testers and threat researchers) to ensure comprehensive risk mitigation and recovery, as well as fortification against future strikes.
Key features and benefits
- Deploy vast expertise: The combined power of the Sophos and Secureworks incident responders – now part of one team – provides you with seasoned and accredited global incident responders experienced in common and uncommon cyber threat scenarios.
- Reduce attack impact: Using our combined experience responding to attacks of all types, Sophos rapidly triages, contains, and neutralizes active threats and ejects adversaries from your environment to prevent additional damage.
- Holistic incident response capabilities: Emergency Incident Response engagements include a range of capabilities and options, including remote and onsite technical support, incident command and advisory leadership, expert ransom negotiations, incident-specific threat intelligence, and threat hunting to dig out hidden details of the attack.
- Understand the root cause and how to prevent it: You receive a detailed post-incident report that includes a root cause analysis, actions taken by our responders, an enriched summary of threat actor tactics, and recommendations to fortify resiliency, plus an executive summary for non-technical audiences.
Available now
Being able to respond to a cyberattack is critical. Sophos Emergency Incident Response replaces the existing Sophos Rapid Response service and is available now to help. Learn more at Sophos.com/Emergency-Response or contact the Sophos Emergency Incident Response team for immediate assistance.
Source: Sophos
Keeper Security, the leading cybersecurity provider of zero-trust and zero-knowledge Privileged Access Management (PAM) software protecting passwords, passkeys, privileged accounts, secrets and remote connections, today announces that its zero-trust and zero-knowledge PAM solution, KeeperPAM, has won the Fortress Cybersecurity Award in the zero-trust security architecture category.
Presented by the Business Intelligence Group, the Fortress Cybersecurity Awards program honors the industry’s leading companies and professionals who are going beyond compliance to build and maintain secure systems and processes. Winners are selected based on innovation, measurable impact and commitment to security best practices.
Keeper adopted zero trust and zero knowledge as foundational design and architecture principles from day one, ensuring all contents of a user’s vault are protected with multiple layers of safeguards and encryption. KeeperPAM unifies enterprise password, secrets and connections management with endpoint privileged management, zero-trust network access and remote browser isolation in one platform. By combining these critical identity and access management components, Keeper delivers unparalleled visibility, security and control, while ensuring that compliance and audit requirements are easily met.
“The volume and complexity of threats facing organizations today is growing by the minute,” said Russ Fordyce, CEO of the Business Intelligence Group. “The winners of this year’s Fortress Cybersecurity Awards are not only keeping up – they’re setting the pace. We’re proud to honor Keeper Security for providing a platform that makes us all more secure.”
Recent high-profile breaches have demonstrated the devastating consequences of compromised privileged access, with attackers using these accounts to infiltrate networks and steal sensitive data. KeeperPAM addresses this challenge head-on by incorporating a zero-trust approach to validate every access request, ensuring only those with explicit authorization can access critical systems and resources.
“This recognition from the Business Intelligence Group demonstrates our team’s dedication to providing best-in-class cybersecurity software that empowers our customers to stay ahead of modern threats,” said Darren Guccione, CEO and Co-founder of Keeper Security. “We are honored to receive this award and remain committed to leading the future of privileged access management – delivering superior visibility, security, compliance, reporting and control across the entire enterprise.”
Trusted by leading federal agencies and thousands of organizations of all sizes, KeeperPAM’s zero-trust and zero-knowledge security architecture is unmatched in safeguarding information and mitigating the risk of cyber attacks and data breaches. KeeperPAM is compliant with a broad range of industry standards and regulations, including FedRAMP and GovRAMP Authorization, SOC 2 Type I and Type II attestation, FIPS 140-3 validation, ISO 27001, 27017 and 27018 certifications, as well as HIPAA and PCI-DSS, reducing the administrative burden of audit tracking and access management.
To learn more about Keeper’s award-winning PAM platform, please visit: https://www.keepersecurity.com/.
Source: Keeper Security
Keeper Security, the leading cybersecurity provider of zero-trust and zero-knowledge Privileged Access Management (PAM) software protecting passwords, passkeys, privileged accounts, secrets and remote connections, today announces an update to its password management platform. Keeper’s upgraded One-Time Share feature enables bidirectional, single-use encrypted sharing between Keeper users and non-users, providing customers with a secure way of exchanging confidential information with their customers, vendors and partners.
The new bidirectional sharing feature builds upon the functionality of Keeper’s existing One-Time Share (OTS) feature. OTS is designed to securely share credentials and files with a selected recipient for one-time use. These shares are protected in transit by Keeper’s elliptic-curve and AES-256 cryptography and can only be decrypted locally on the recipient’s device. Once received, shared records automatically expire based on the sender’s specified time. Additionally, each share is restricted to a single device, allowing the recipient to access the shared data multiple times until it expires or the sender terminates the share — whichever occurs first.
“Bidirectional One-Time Share is the latest step in our commitment to ensuring that all customers can simply and securely exchange confidential information with end-to-end encryption,” said Craig Lurey, CTO and Co-Founder of Keeper Security. “By adding bidirectional editing support, we add yet another layer of security to our users’ cyber defenses. We’re proud to be the first in the industry to add this capability and continue supporting our customers, first and foremost.”
The bidirectional functionality update allows easier sharing between users and non-users of Keeper’s platform. Previously, users were able to send view-only external shares. Now, non-users can also exchange data with Keeper customers, offering end-to-end encryption for both parties. This powers the secure collection and exchange of confidential information such as documents and credentials – without having to use insecure email, text messages or instant messaging channels.
Users share records by selecting the desired record from their Keeper Vault and initiating a one-time share. The user can then customize the access settings and generate a secure, time-limited link. The recipient clicks the link to view the content, where they can upload, modify or comment as needed. Once the time limit is reached or access is revoked, the session ends permanently and the record is no longer accessible.
Organizations can use the bidirectional one-time share to facilitate operations such as:
- Collaboration: Securely collect signed documents, feedback or sensitive files from clients, contractors and partners without needing them to create an account.
- Vendor Requests: Request compliance documents or private credentials from third parties securely.
- Internal Audits: Temporarily share and retrieve information with auditors or legal teams.
To learn more about Keeper’s new One-Time Share functionality, please visit our documentation portal.
Source: Keeper Security
Delivering world-class security solutions is our top priority at Sophos. The true measure of our success is the satisfaction and feedback of the customers who rely on our products every day to protect their organizations. We are delighted that our user feedback led Sophos to be recognized as a Customers’ Choice vendor in the 2025 Gartner® Peer Insights™ Voice of the Customer Reports for Endpoint Protection Platforms and Extended Detection and Response. This makes Sophos the only vendor to be named a Customers’ Choice in both reports, highlighting the comprehensive, robust protection of the Sophos platform.
In the 2025 Voice of the Customer for Endpoint Protection Platforms, Sophos received a 4.8/5.0 rating based on 361 reviews, as of 31 Jan 2025. This marks the 4th consecutive time customers have recognized Sophos as a Customers’ Choice vendor in this market.
The 2025 Voice of the Customer for Extended Detection and Response is this category’s inaugural report. Sophos is the highest-rated vendor with a 4.8/5.0 rating and has the most reviews in the report (257 reviews, as of 31 Jan 2025). Additionally, Sophos has the highest rating in all four categories covering specific aspects of the experience with the vendor – customers rated Sophos a 4.9/5.0 in Product Capabilities, Sales Experience, and Deployment Experience, and a 4.8/5.0 in Support Experience (based on 257 reviews as of 31 Jan 2025).
Customer reviews
Here are some examples of what customers had to say about Sophos Endpoint and XDR:
Sophos Endpoint offers robust protection with advanced threat detection leveraging AI and deep learning to identify and block malware, ransomware and other attacks.
- IT SAP Consultant in the Manufacturing industry, $50M-250M
- Review link
[Sophos Endpoint] is very mature and offers great protection against light and heavy security attacks on our infrastructure.
- IT Specialist in the Healthcare and Biotech industry, $500-1B
- Review link
[Sophos Endpoint] merges technologies such as deep learning, AI, and endpoint detection & response to provide a holistic endpoint security software.
- IT Associate in the Education industry, <5000 employees
- Review link
Sophos XDR is a next-generation endpoint protection software that uses a combination of advanced techniques to defend against a wide variety of cyber threats.
- IT Manager in the Retail industry, $500M-1B
- Review link
Sophos XDR makes detecting and responding to threats easy. It is AI-equipped and is fast and accurate and we no longer have to worry about endpoint threats.
- Structural Engineer in the Construction industry, $250M-500M
- Review link
The [Sophos XDR] platform employs cutting-edge machine learning models to identify and block even zero-day threats and advanced persistent threats that traditional signature-based systems might miss.
- IT Associate in the Retail industry, $50M-250M
- Review link
From fast detection to investigating threats and offering amazing threat response, Sophos XDR has it all. Its reliability has kept cyber threats at bay.
- IT Manager in the IT Services industry, $250M-500M
- Review link
Sophos XDR is an excellent product. This is not just an analytical tool that is helping us with enhancing our detection and response capabilities as a team but also helping us with day-to-day IT operations.
- Customer Service & Support Associate in the IT Services industry, $250M-500M
- Review link
Πηγή: Sophos
One of the most fundamental — and often overlooked — processes of a strong security posture is vulnerability management (VM). VM is much more than just running a vulnerability scan; it’s at the core of all the layers that make up solid cybersecurity.
Whether your organization has a simple infrastructure or consists of thousands of globally distributed endpoints, VM is essential. With networks becoming increasingly complex and dynamic, it’s critical to assess and remediate vulnerabilities on a regular basis.
What Is Enterprise-Grade VM?
Basic vulnerability scanners may identify threats, but they often lack the intelligence to help you act on them. The best VM solutions regularly identify, evaluate, report, and prioritize vulnerabilities in network systems and software in dynamic environments.
No matter how simple or sophisticated your IT environment is, having a centralized view of vulnerabilities across your entire network is vital. An enterprise VM system will have the flexibility to handle on-premises, cloud, or hybrid assets, and provide not just data, but context as well, so your team can focus on what truly matters.
Enterprise-grade VM programs include:
- Scanning local systems as well as the entire global network
- Segmenting reports into different locations, specific IT teams, and departments
- Correlating vulnerability data on dynamic assets
- Seamlessly integrating with other enterprise IT and security tools
- Creating efficiencies by being simple to deploy, learn, and maintain
Why Risk-Based VM Is Necessary
All IT environments have vulnerabilities, but not all of them pose equal risk. When it comes to VM, you need a solution that not only tells you whether a security alert actually represents a threat or not, but also helps you understand the level of risk to your unique network.
A risk-based solution will help you use the three pillars of information security: confidentiality, integrity, and availability (the CIA Triad). Risk-based VM evaluates vulnerabilities using real-world threat intelligence and takes into account how exploitable a vulnerability is.
Pro Tip: Look for a solution that combines this intelligence with real-world threat activity and industry-standard severity scores to rank vulnerabilities.
Other Functionality to Consider
Understanding the need for an enterprise-grade, risk-based VM tool is the first step. But what should you look for when choosing the right platform?
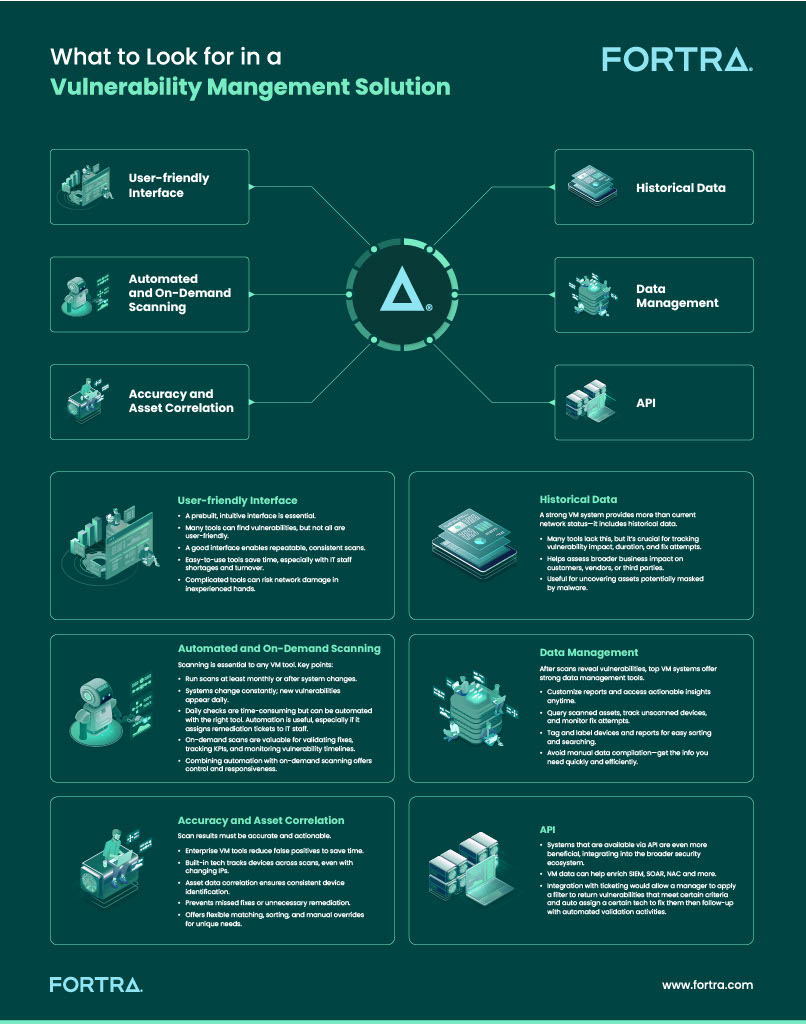
Platform Interface
As IT departments face turnover and staff shortages, there’s no time to waste learning or trying to use a complicated, unintuitive tool. While scans can be automated, not all fixes can. Technicians still need to interact with your VM solution to address the vulnerabilities. That’s why a prebuilt, intuitive interface is important.
Historical Data
A good system will also deliver far more than just the current state of your network. For example, historical data isn’t available on many VM tools in the marketplace. Historical data shows which assets were vulnerable, for how long, and what was done to address them.
Automated and On-Demand Scanning
Best practice says VM scans should be run monthly at a minimum, or anytime there’s a change to the system. Sometimes it makes sense to automate. Other times, you need on-demand scanning to validate issues that have been addressed or demonstrate how long vulnerabilities were on the system, track KPIs, and more.
Accuracy and Asset Correlation
Scan results need to be accurate and actionable. Enterprise VM solutions can distill results, reducing false positives that could otherwise waste your team’s time. Enterprise VM systems ensure accurate asset tracking, even when IP addresses or configurations change. Look for built-in asset correlation that ensures consistent visibility.
Data Management
Your VM solution should let you query against all scanned assets, see which devices haven’t been scanned in a certain period, devices where fix attempts have been made, and more. While some systems require you to compile data from various reports and figure out how to create a spreadsheet or other report to pull all the data together, enterprise-grade VM will let you tag and label devices as well as reports so you can search and sort to deliver exactly the results you need.
API
VM systems that support API integration can become a seamless part of your broader security stack. VM data can help enrich SIEM, SOAR, NAC and more. Integration with ticketing would allow a manager to apply a filter to return vulnerabilities that meet certain criteria and auto-assign a certain tech to fix them then follow up with automated validation activities.
Source: Fortra
As language learning models (LLMs) continue to advance, so do the security threats and risks that accompany them. With the plethora of news and information out there regarding generative AI, Fortra has conducted in-depth threat analysis to cut through the noise and identify the most pressing AI threats to watch out for as 2025 rolls along. Although it’s imperative to remain vigilant in the face of the ever-evolving threat landscape and all the other possible risks it may expose us to, these are the threats that stand out as the most pressing for both defenders and users alike.
1. Prompt Injections
What is a prompt injection?
Prompt injections occur when an AI input command allows the user to manipulate the model’s behavior through bypassing the developer’s original instructions for that prompt. This threat is similar to input injections in traditional application security attacks. However, prompt injections are a consistent threat in generative AI because LLMs tend to process the input command as one single text and may not be able to separate or validate these inputs, unlike typical software inputs.
Why worry about prompt injections?
The threat of prompt injections can pose several risks to organizations, especially those who have integrated generative AI into their IT environments. There are a few risks:
- Data leakage. This is where a command can be injected to prompt the AI model to reveal sensitive information or to even leak sensitive data from a previous session that the current user may not be authorized to access.
- Trick the LLM into revealing API keys. Threat actors can then exploit to gain unauthorized access to cloud environments and other valuable digital assets, maliciously configure access controls such as turning off multi-factor authentication (MFA) to bypass IAM defenses and even carry out data breaches to compromise personally identifiable information (PII).
- Poisoning the language model to spread false information through commands that inject bogus data and even running malicious code that can increase exposure to malware infections.
2. Romance Scams and Deepfakes
What are romance scams?
Romance scams occur when a scammer develops an online romantic relationship with the victim to gain their trust and exploit them, often financially. Scammers typically hide under a false identity by setting up fake online profiles to lure in potential victims, especially through dating and social media sites, and ask for money from the victim upon gaining their trust.
Why worry about romance scams?
- GenAI. Romance scammers have begun weaving generative AI into their malicious tactics. For example, a common telltale sign of a romance scam is that the scammer relies on text messaging to communicate with the victim and avoids phone calls or meeting in person as their voice can reveal their true identity or location. However, AI-generated voices can now allow scammers to impersonate many different voices, including accents from various locations, ages, and genders.
- Deepfakes. Another example of how generative AI poses a threat in romance scams is using deepfakes to conduct video calls with the victim. As deepfakes continue to advance in quality, scammers can use this technique to make their fake online personas seem more realistic and further manipulate the victim as video calling can carry more emotional weight than regular text messaging.
3. Improved Spear Phishing
What is spear phishing?
Spear phishing, a form of phishing that is personalized towards its targeted victim, has gained a new lethal potency in targeting victims through the assistance of LLMs.
When Fortra’s 2025 Email Threat Intelligence Report revealed that a staggering 99% of email threats were social engineering attacks or contained phishing links, it is no surprise that attackers are amping up their email attacks by incorporating AI to strengthen their phishing attempts. Recent warnings and research about email AI attacks have revealed that AI crafted attacks are now beating traditional human attacks.
Why worry about spear phishing?
Threat actors can leverage AI to target the victim’s LinkedIn account to identify their workplace information and carry out business email compromise (BEC) attacks against them or even target their social media and other public profiles to gather as much information as possible to craft highly advanced and personalized spear phishing attacks. This poses a particular challenge to both organizations and users as spear phishing attempts can be difficult to identify due to their personalized nature which adds an element of realism to the lure. Additionally, unlike traditional human threat actors or cybersecurity red teams, these AI generated attacks can be conducted at a large and unlimited scale which further exasperates this threat.
4. Bypassing Linguistic Barriers
What are linguistic barriers in cybersecurity?
LLMs have unlocked improved translation capabilities as AI-generated translations continue to produce more natural-sounding texts that better capture slang and human conversational cues. Attackers can harness this capability to expand the geographical horizon of their targets.
Why worry about smarter translations?
Scams and other social engineering attacks that have proven to be successful in one language can now be effectively translated into other languages to reach victims from new locations around the world.
Not only does this allow threat actors to expand their geographic outreach and bypass linguistic barriers, but this can also increase the success rate of attacks because the newly targeted regions are often less familiar with these scams and users may lack the awareness needed to identify the signs of these attacks.
For example, financial scams that tend to attract a lot of victims in North America, such as payroll diversions, can be translated into other languages to target other continents that were not victimized by these threat actors before.
Fortra’s monthly BEC Global Insights Report revealed that the average amount requested in wire transfer attacks was a staggering $81,091 in April 2025, putting them at the forefront of one of the most effective financial scams to target victims. Organizations can expect to see such effective and widespread scam tactics translated into different languages, especially in never seen before languages and regions, as attackers continue to identify new tricks to maximize the efficacy and reach of their lures.
5. Shadow AI
What is shadow AI?
Shadow development, the use of software development practices that has not been approved by an organization, has historically been one of the most prominent end user risks when it comes to employee non-compliance with IT policies. However, we can now add Shadow AI to the list of end user risks that IT and cybersecurity professionals worry about. Shadow AI refers to the unsanctioned or unauthorized use of AI tools and resources.
Why worry about shadow AI?
When almost 60% of employees have entered high-risk information into generative AI technologies, the threat of shadow AI is rampantly on the rise. This can expose organizations to the risk of data leakage because LLMs can be trained on user input, which can then be included in the output of newer AI model versions.
For example, an employee can accidentally leak sensitive personally identifiable information (PII) or an organization’s proprietary software code if it were unintentionally included as input in their AI prompts. This privacy breach can expose organizations to the risk of various damages such as regulatory fines, reputational damages, legal breaches of NDAs, and other consequences.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence, like any other innovative tool or technology, can be used to accomplish both the bad and the good depending on who is wielding it. Attackers will always find a way to exploit these tools. Although it can seem overwhelming to defend against such an easily scalable tool such as AI, Fortra can help you fight fire with fire by offering various machine learning-based solutions that keep pace with the threat landscape and integrate AI to fortify your threat detection capabilities.
Source: Fortra
Keeper’s Enterprise Password Manager is the only solution that uses Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) in its encryption, making it the most secure password management solution available.
ECC is a public-key cryptography method based on the mathematics of elliptic curves. First proposed in 1985, it recently rose to prominence with modern cryptography as it provides a higher level of security compared to traditional encryption methods, such as RSA.
Considered by the InfoSec community to be the most secure level of encryption for information security, ECC provides many advantages including:
- Best-in-Class Security: The difficulty of solving elliptic curves provides an added level of protection against complex cyber attacks such as quantum computing.
- Efficiency: ECC uses smaller key sizes compared to other encryption algorithms, such as RSA. This makes it more efficient in terms of computation and storage requirements as it uses limited resources.
- Fast Computation: ECC is faster than other encryption algorithms, making it an ideal choice for applications that require fast encryption and decryption.
Keeper’s encryption model documentation compares the strength of 256-bit elliptic curves against vaults encrypted with password-derived keys.
No Master Password Needed
The deployment of Keeper through a Single Sign-On (SSO) identity provider eliminates the need for a master password. Instead, Keeper uses ECC to encrypt and decrypt data, allowing for a seamless login experience with SSO and passwordless technology.
A local ECC-256 (secp256r1) private key is used to decrypt the Data Key at the device level, which unwraps the individual folder keys and record keys for the latter to decrypt each of the stored record contents.
The Encrypted Data Key is then transmitted between the devices through a push system or key exchange service called Device Approval, which is managed by the admin to preserve zero knowledge.
Without a master password to prey on, the threat of brute force attacks against stored data is eliminated.
Keeper Complements SSO to Cover Any Security Gaps
SSO’s ease-of-use and ease-of-access have made it a preferred solution to remedy password-related issues, but it still presents serious security gaps as a single point of failure.
For instance, users automatically get locked out of multiple sites and apps versus only one if they forget their password. Should a user’s account get hacked, cybercriminals would be able to gain access to all associated sites and apps, compromising the entire layer of security SSO was tasked with providing in the first place.
Even with SSO, privileged access users still need one secure location to safely store non-SSO passwords, SSH keys, API keys, etc. that – just like SSO assets – require role-based access, configurable control of policies and sharing capabilities.
Keeper integrates with all major SSO solutions and is a perfect complement for the legacy applications and other use cases that SSO doesn’t cover. IT Admins and IT Security professionals love using Keeper for its:
- Rapid Deployment: No upfront equipment or installation costs. Easy Active Directory and SSO integration.
- Ultimate Cybersecurity Protection: Zero-knowledge architecture means there is nothing to hack.
- Pervasive Employee Adoption: Intuitive UI, automated password generation and autofill makes the transition a breeze.
- Mitigate Password-Related Support: No more forgotten or lost passwords.
Request a demo of Keeper Enterprise Password Manager today to see how an elliptic curve level encryption can protect your organization’s passwords, credentials and secrets with zero-trust and zero-knowledge security.
Source: Keeper Security
Businesses of all sizes are increasingly reliant on productivity tools like Microsoft 365 — and attackers are using this to their advantage.
Business email compromise and account takeover attacks are prevalent, with adversaries accessing M365 environments using techniques that may evade detection by technology alone.
Organizations need 24/7 visibility and a fully staffed security operations center (SOC) to effectively defend against such attacks — which is a major challenge for many resource-constrained businesses.
Sophos MDR provides the people, processes, and technology to detect, investigate, and effectively respond to threats targeting Microsoft 365.
Our turnkey integrations and proprietary detection rules identified and thwarted almost 5,000 attacks on our customers’ Microsoft 365 environments last quarter alone.
We continually innovate and enhance Sophos MDR to extend and fortify your defenses. And now, the service is getting even stronger with the introduction of new response capabilities.
New analyst response actions for Microsoft 365
The ability to respond quickly to a cyber incident is crucial — the faster the attack can be detected, contained, and neutralized, the less damage the attacker can inflict.
This includes minimizing financial losses, reputational damage, and disruptions to business operations. A swift response can help prevent further data breaches and limit the exposure of sensitive information.
When an attack is detected in your Microsoft 365 environment, Sophos MDR analysts can now execute a range of response actions on your behalf — rapidly containing the threat and freeing up your team to focus on your business.
Microsoft 365 response actions now available
Block/enable user sign-in
Sophos MDR analysts can lock down a user’s account to prevent an adversary from accessing Microsoft 365 services and Azure resources using stolen credentials. Following clean-up, access to the user’s account can be restored in seconds.

Terminate current user sessions
By immediately revoking all currently active sessions for a specific user, Sophos MDR analysts can quickly eject an attacker who has already gained access to an account and remove their ability to reuse any stolen session tokens.

Disable suspicious inbox rules
Attackers routinely set up inbox rules in Microsoft 365 for business email compromise attacks in order to move, obfuscate, or delete emails that could otherwise alert the user. Sophos MDR analysts can disable specific inbox rules to regain control.
Easy setup and flexible response modes
The Sophos MDR service is customizable to meet your needs, with different service tiers and threat response modes. We can execute full-scale incident response on your behalf or collaborate with you to manage security incidents with detailed threat notifications and guidance.
The new response capabilities for Microsoft 365 are included with all Sophos MDR service tiers at no additional cost and enabled through a simple setup wizard in the Sophos Central cloud management console.
Choice of threat response modes
Sophos MDR lets you control how our team will interact with you when a cyber incident requires a response. Simply select your preferred threat response mode based on your organization’s needs and desires:
- “Authorize” mode: Our experts perform threat response on your behalf without your active involvement — and notify you of the actions taken. Once the new Microsoft 365 response actions integration is enabled, Sophos MDR analysts will immediately execute those actions when needed to provide the most efficient response.
- “Collaborate” mode: Our experts conduct investigations, but do not perform response actions without your prior consent or active involvement. Once the new Microsoft 365 response actions integration is enabled, Sophos MDR analysts will execute those actions on your behalf — once consent has been obtained. You can also choose to allow Sophos MDR to operate in “Authorize” mode if we are unable to reach you for consent.
The most robust MDR service for Microsoft environments
Sophos MDR services protect over 30,000 organizations worldwide – more than any other MDR service provider. In Gartner’s 2024 Voice of the Customer Report for Managed Detection and Response Services, Sophos once again had the highest number of reviews among all vendors and scored a 4.9/5.0 rating based on customer reviews.
Many of these businesses have also invested in Microsoft tools, leveraging Sophos MDR to defend against sophisticated attacks that technology alone can’t stop.
Get greater ROI from your Microsoft investment today with Sophos MDR:

Microsoft Certified experts
Extend your team with Microsoft Certified Security Operations Analysts specializing in detecting and responding to cyberattacks using custom Microsoft response playbooks.

Microsoft-specific threat detections
Sophos uses proprietary threat detection rules and world-class intelligence to identify and stop threats that could bypass Microsoft security solutions. We can accurately identify suspicious inbox rules, unauthorized user access patterns, and more.

NEW Analyst response actions for Microsoft 365
Sophos MDR analysts can now execute a range of additional response actions on your behalf, enabling rapid containment of threats with no action required by you. Disable user sign-in, terminate active user sessions, and more.

Comprehensive support for Microsoft solutions
Included at no additional cost, our turnkey integrations support a broad range of Microsoft solutions. Data from Microsoft 365, Defender for Endpoint, Defender for Identity, Defender for Cloud Apps, and more, is collected, analyzed, correlated, and prioritized.
To learn more about Sophos MDR and how it can strengthen your Microsoft defenses, visit our website or speak with a security expert.
Source: Sophos
As with every Sophos Firewall release, v21.5 includes several quality-of-life enhancements that make day-to-day management easier.
Watch this video for an overview of what’s new or read on for more details:
VPN enhancements
User interface and usability enhancements: Connection types have been renamed from “site-to-site” to “policy-based,” and tunnel interfaces have been renamed to “route-based” to make these more intuitive.
Improved IP lease pool validation: Across SSLVPN, IPsec, L2TP, and PPTP remote access VPN to eliminate potential IP conflicts.
Strict profile enforcement: On IPsec profiles that exclude default values to ensure a successful handshake, eliminating potential packet fragmentation and tunnels failing to establish properly.
Route-based VPN and SD-RED scalability: Route-based VPN capacity is doubled with support for up to 3,000 tunnels. Sophos Firewalls now support up to 1,000 site-to-site RED tunnels and up to 650 SD-RED devices.
Other management enhancements
DHCP prefix delegation relaxation: Now supports /48 to /64 prefixes, improving interoperability with ISPs.
Router advertisements (RA) and the DHCPv6 server: Now enabled by default.
Resizable table columns: A long-requested feature, many firewall status and configuration screens now support resizable column widths that are retained in browser memory for subsequent visits. Many screens such as SD-WAN, NAT, SSL, Hosts and services, and site-to-site VPN, all benefit from this new feature.
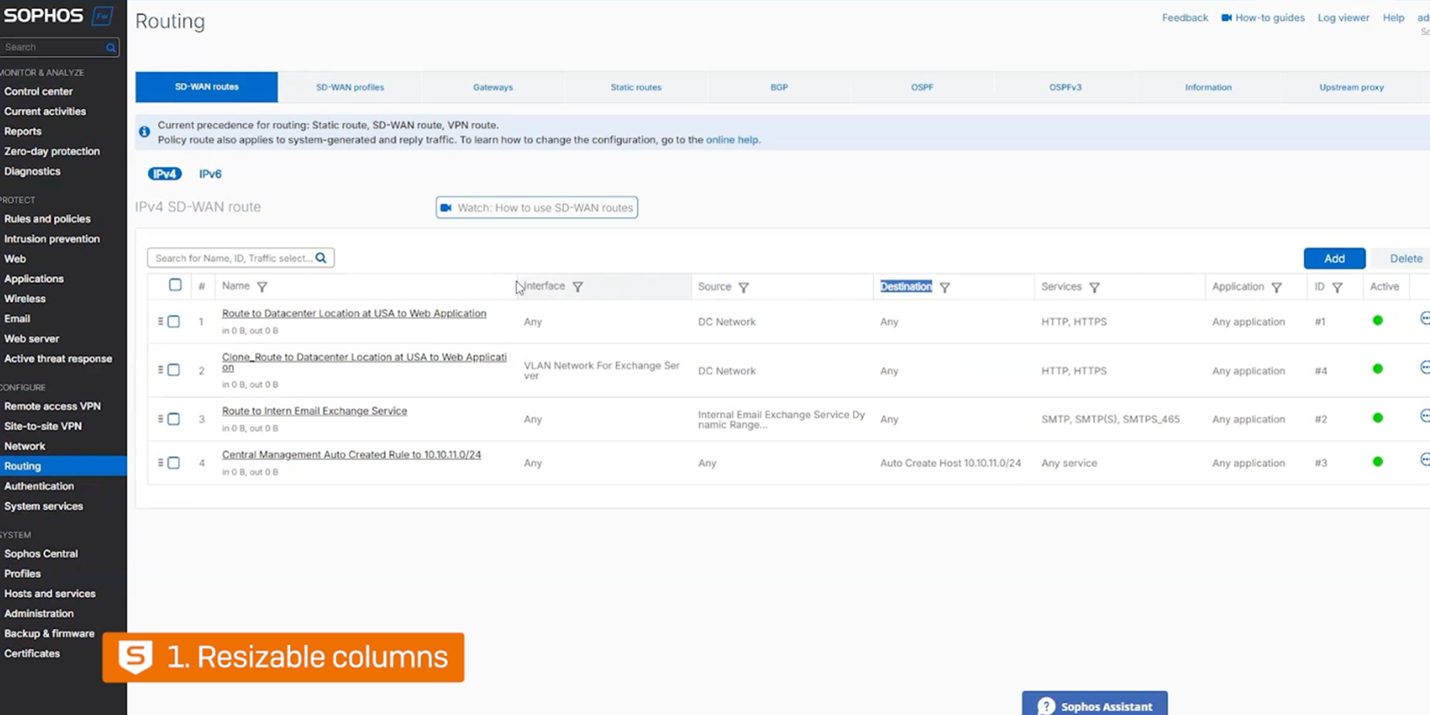
Extended free text search: SD-WAN routes now enable searching by route name, ID, objects, and object values like IP addresses, domains, or other criteria. Local ACL rules also now support searching by object name and value, including content-based search.
Default configuration: By popular demand, the default firewall rules and rule group previously created when setting up a new firewall have been removed, with only the default network rule and MTA rules provided during initial setup. The default firewall rule group and the default gateway probing for custom gateways are both set to “None” by default.
New font: The Sophos Firewall user interface now sports a new lighter, cleaner, sharper, font for added readability and improved performance.
Get the What’s New Guide
Check out the What’s New Guide for a full overview of all the new enhancements in v21.5.
Get started today
Start taking advantage of this great new capability in Sophos Firewall v21.5 by participating in the early access program. Simply register for the program, click the link in your email to download the firmware update package, and install it on your Sophos Firewall.
Πηγή: Sophos
When it comes to password managers, there are a few common misconceptions, such as them being too risky to trust, vendors being unable to handle outages, the risk of device-side attacks and them being considered a single point of failure. High-profile security incidents have brought into question the security of using password managers; however, cybersecurity experts, organizations and government agencies continue to recommend them as a best practice.
In this article, we’ll debunk four common misconceptions about using password managers and share best practices to help you get the most security out of your password management solution.
Misconception 1: Password managers are too risky to trust
A common concern about password managers is that they are too risky to trust, particularly after the LastPass data breach. While it’s understandable to have these concerns, it’s important to remember that not all password managers are the same. In fact, password managers still provide far stronger security than traditional methods, like writing passwords down or reusing the same password across multiple accounts.
Debunked
The misconception that password managers are too risky to trust is based on isolated security incidents. When choosing a password manager, it’s important to thoroughly research its security and reputation to ensure you’re selecting the most secure solution to protect your data.
The best password managers are zero-knowledge, meaning no one but the user has access to their stored data – not even the vendor. Additionally, choosing a zero-trust solution will prioritize security by assuming no user or device is trustworthy. This means continuous verification is needed before granting access to your stored passwords. For example, Keeper has a feature called device-level approval. With device-level approval, each new device attempting to access your Keeper Vault must be explicitly approved before gaining access. If you or someone else attempts to access your vault on a new device, that device must be approved by either the account owner, an existing trusted device or an administrator (in enterprise environments). Features like Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) and biometric authentication further protect your vault from being compromised.
Misconception 2: Password manager vendors can’t handle outages
The misconception that password manager vendors can’t handle outages likely stems from a recent 12-hour outage experienced by LastPass. This raised concerns about service availability and the idea that if a cloud-based password manager goes down, users might be locked out of their accounts. While it’s true that many password managers are cloud-based, the best ones have built-in features to handle outages and ensure that users can still access their passwords.
Debunked
Reputable password manager vendors offer offline access mode, which enables users to access their vaults on any device during an outage or when they do not have internet access. Offline access works by creating an encrypted copy of your vault on your local device. Your vault data is stored in an encrypted format, so the only way to access your local backup is by providing your master password or using biometric authentication. While offline access provides a solid fallback, choosing a vendor with high service reliability is also important to minimize the need for it in the first place. For example, Keeper maintains 99.99% uptime, which can be verified on our status page.
Misconception 3: Password managers increase the risk of device-side attacks
There is a misconception that password managers increase the risk of device-side attacks because some, like LastPass, run device-side components, which increases the attack surface. However, it’s important to understand that not all password managers function this way.
Debunked
The best and most secure password managers are zero-knowledge and do not run device-side components that sync and store data locally, such as cached credentials. For example, Keeper prevents device-side attacks by using a zero-knowledge architecture, in which all data is encrypted locally on your device before being uploaded to the cloud. This ensures that even if a cybercriminal gains access to your device, they can’t access your stored data because it’s stored in an encrypted format. Keeper doesn’t store unencrypted data locally or sync cached credentials. By not relying on device-side components that could be exploited, Keeper significantly reduces the attack surface and keeps your data safe at all times.
Misconception 4: Password managers alone aren’t enough
Some critics argue that even when passwords are stored in password managers, it’s still not enough to keep your accounts protected. While it’s true that strong passwords can still be compromised, they remain important for account security. This is why it’s important to use strong, unique passwords for each of your accounts, enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and switch to passkeys when given the option.
Debunked
We agree that passwords alone aren’t enough to protect your accounts, but this doesn’t mean using a password manager is insufficient to keep your accounts protected. Password managers like Keeper support phishing-resistant MFA and passkeys to further reduce reliance on passwords alone. While transitioning to passwordless authentication is ideal, password managers like Keeper still play a critical role in securely storing and managing credentials. They help ensure that even if passwords are compromised, they are used in combination with additional layers of security like MFA. Additionally, with passkey support, users can eliminate the risks of traditional password-based attacks altogether while still benefiting from the convenience and security of password management solutions.
Best practices for using password managers
To get the most security out of your password manager, it’s important to follow these best practices:
- Choose a password manager with strong encryption and a proven track record: Before choosing a password manager, research the kind of security and encryption the vendor uses to protect consumer data. Additionally, check whether the vendor has a proven track record of reliability and has not been hacked.
- Use a strong, unique master password and enable 2FA: When using a password manager, you’ll need to create a master password to protect your vault. Make sure your master password is strong and unique, and enable 2FA on your vault for an extra layer of security.
- Enable MFA whenever possible for accounts: While password managers help you create strong, unique passwords, it’s still important to enable MFA to further protect your accounts and prevent them from being compromised.
The bottom line
It’s completely understandable to be concerned about the security of your data. That’s why it’s important to research and choose the most reliable and secure password management solution. At Keeper, we prioritize transparency regarding our security model and the measures we take to secure our users’ data.
Curious why Keeper is the best and most secure password manager on the market? Start a free trial today.
Source: Keeper Security
Sophos is delighted to announce the launch of Sophos MSP Elevate, a new business-accelerating program for managed service providers (MSPs). With the new program, Sophos enables MSPs to expand their business with high-value, differentiated cybersecurity offerings that elevate their customers’ cyber defenses and rewards growth with additional investment to fuel further success.
With the increasing complexity and sophistication of today’s cyberattacks, organizations are increasingly turning to MSPs for 24/7, human-led monitoring and management of their cybersecurity environments. This has made Managed Detection and Response (MDR) a major focus for MSPs with 81% currently offering a MDR service, according to the Sophos MSP Perspectives 2024 report. MSP Elevate helps MSPs to differentiate themselves as a high-value provider to customers by delivering unique business-enhancing benefits, including an exclusive high-value Sophos MDR service offering.
Managing multiple cybersecurity platforms is a major overhead for MSPs and consumes valuable billable hours. MSPs estimate that consolidating on a single platform would slash their day-to-day management time by 48%*. MSP Elevate includes Network-in-a-Box bundles that enable MSPs to manage the full network stack through the unified Sophos Central platform, freeing-up staff for business generation activities. Furthermore, the single biggest perceived risk to MSP’s businesses is the shortage of in-house cybersecurity expertise*. Sophos’ network solutions respond automatically to threats across the customer environment, enabling MSPs to elevate their customers’ defenses without adding workload.
As Chris Bell, senior vice president of global channel, alliances and corporate development, Sophos, says:
“MSP Elevate is the first of many business-driving MSP programs following the powerhouse union of Sophos and Secureworks. As a channel-first organization that defends more than 250,000 customers of MSPs, we are constantly looking for opportunities to reward our partners and invest in their success when they grow their business with us. MSP Elevate fuels long-term growth for our partners by providing MSPs with exclusive solution access, discounts, rebates and training to deliver the best possible value to customers.”
Sophos MSP Elevate program benefits include:
- Exclusive Access to the Sophos MDR Bundle for MSP: Includes access to Sophos MDR Complete premium service tier with 24/7 incident response, 1 year data retention, Sophos Network Detection and Response (NDR), and all Sophos integration packs, enabling defenders to leverage all available telemetry from across the customer environment to accelerate threat detection and response.
- Simplified Sales Process: Speeds up time to deployment and reduces MSP overhead. With the new MDR Bundle for MSP, partners can quickly and easily allocate a single SKU to the customer for all their current and future MDR needs.
- Discounted Network-in-a-Box Hardware Bundle: Access to Sophos’ advanced network security solutions, including Sophos Firewall, Sophos Switch and Sophos Wireless Access Points at a significant discount. These products work together to automate threat response and are managed through Sophos Central.
- Growth-Based Rebates: As part of our commitment to grow with and invest in our partners, the program will recognize and reward MSPs that increase their Sophos MSP monthly billings.
- Architect-Level Training Courses: Equip MSPs to increase their in-house services delivery capabilities with trainings on Sophos Endpoint and Sophos Firewall.
- Invite-Only Access to Sophos Summits: Gain exclusive access to hands-on training and enablement, Ask the Experts sessions, attend exclusive Sophos events and meet with Sophos executive leadership to influence the Sophos roadmap and MSP strategy.
- Future benefits – Introduction of new program benefits to increase MSP’s profitability, customer defenses and overall value as a service provider.
MSP Elevate enables MSPs to quickly deploy a comprehensive MDR service that eliminates blind spots by leveraging all available telemetry from across the customers’ environment. This enhanced visibility accelerates threat detection and response while delivering improved return for customers on their existing technology investments. Furthermore, the service adapts seamlessly as the technology environment evolves over time, future-proofing customers’ defenses and providing both commercial and cybersecurity peace of mind.
MSP Elevate is a non-exclusive commitment to sell Sophos’ best-in-class cybersecurity solutions available on the Sophos Central platform, including Sophos MDR, Sophos Endpoint powered by Intercept X, and Sophos Firewall. To access the program benefits, MSPs need to commit to a minimum monthly spend for a 12-month period. As a pre-requisite to joining MSP Elevate, partners need to be part of the MSP Flex program, which enables MSPs to offer Sophos solutions on a monthly billing basis.
Feedback on the program from Sophos MSPs has been tremendous, with Craig Faiers, sales director, Arc, commenting:
“Joining MSP Elevate is a no-brainer. This new program adds further rocket fuel to the MSP growth trajectory we’ve enjoyed with Sophos over the last 17 years. Not all MDR offerings are the same, and I’m excited to be able to offer a superior service based around value and quality of outcomes that will elevate my customers’ defenses and differentiate my business in this increasingly crowded market.”
With 80% of MSPs offering MDR through a specialist vendor for delivery*, partners can choose to have Sophos fully deliver the MDR service or to use Sophos to augment in-house teams, including for the provision of out-of-hours coverage. This is particularly important considering 88% of ransomware attacks start outside of standard business hours, according to Sophos’ Active Adversary report.
Sophos MDR is the service most trusted by MSPs to secure their clients and currently defends more than 18,000 MSP-managed customer environments against advanced threats, including ransomware. This unmatched breadth of customer coverage delivers unparalleled insights into attacks on MSP-managed environments that are continually leveraged to update customers’ defenses in real-time, optimizing their protection from ever-evolving attacks.
To learn more about MSP Elevate, visit www.sophos.com/elevate. Sophos partners can sign up for the MSP Elevate Program on the Sophos Partner Portal at https://lp.sophos.com/msp-elevate.
Source: Sophos