News
Sophos’ market-leading Managed Detection and Response offering continues to go from strength to strength, with over 20,000 organizations worldwide now protected by the service.
Industry analysts agree. We are delighted to announce that Sophos has been named a Leader by Frost & Sullivan in their 2024 Frost Radar™ report for Global Managed Detection and Response.
According to Frost & Sullivan, Sophos stands out as an MDR leader for:
Flexibility
Citing Sophos’ expansive integrations with both native and third-party technologies, the report also highlights the flexibility of our MDR response modes and subscription tiers.
Support for Microsoft Environments
The evaluation calls out Sophos’ ability to deliver MDR services for Microsoft environments as an advantage, with the expertise to investigate and respond to Microsoft security alerts across endpoint, cloud, and identity sources, among others.
Unlimited Incident Response
Frost & Sullivan highlights a powerful differentiator of Sophos MDR: “To go a step beyond the traditional functionalities and responsibilities of MDR platforms, Sophos delivers unmetered incident response services as part of its core offering”.
Rapid Growth
Acknowledging our success in the market, the report notes that Sophos is “growing faster than average in the already fast-growing MDR market”, thanks to our channel-best approach and thought leadership.
Download the full Frost & Sullivan Report
Continued Industry Recognition
Sophos MDR continues to garner high praise from experts across the industry. In addition to this Frost & Sullivan recognition, Sophos is proud to be:
- A Gartner Peer Insights Customers’ Choice for Managed Detection and Response
- Rated the Number 1 MDR solution by customers in the G2 Winter 2024 Grid Reports
- Named a Representative Vendor in the Gartner Market Guide for Managed Detection and Response Services
Check out our full range of independent accolades and endorsements on Sophos.com.
To learn more about Sophos MDR, or speak to your Sophos representative or partner.
Source: Sophos
We are delighted to announce that Sophos has been named a Leader in the IDC MarketScape: Worldwide Modern Endpoint Security for Small Businesses 2024 Vendor Assessment (doc #US50521424, March 2024). This recognition comes on the heels of Sophos also being named a Leader in the IDC MarketScape: Worldwide Modern Endpoint Security for Midsize Businesses 2024 Vendor Assessment (doc #US50521323, February 2024).
The IDC MarketScape study evaluates modern endpoint security vendors’ prevention, EDR, and MDR capabilities and business strategies, with a specific focus on the requirements of small businesses.
According to the IDC MarketScape evaluation, “Sophos is a strong consideration for small businesses, particularly those with large business security requirements that have little to no in-house security expertise.” Read the excerpt
“Every organization, regardless of size, suffers from resource constraints. The stakes in cybersecurity, with small businesses in particular, are massive, and many of these companies are struggling to keep up,” said Michael Suby, research vice president, Security & Trust, IDC. “Sophos, with an expansive set of protection technologies and proven MDR service offering, is a great option to help a small business improve its security posture in whatever way fits best – either with the tools to help its experts in-house or by leveraging the expertise of the dedicated MDR security team.”
Trusted Managed Detection and Response Service
Cybersecurity is becoming so complex that most small businesses cannot keep up and need every advantage. Sophos delivers superior cybersecurity outcomes by giving customers the advantages they urgently need. Our 24/7 Managed Detection and Response service enables organizations to reduce the risks and costs associated with security incidents and data breaches that could potentially be catastrophic to small businesses.
The IDC MarketScape report notes: “Sophos MDR, already in use by over 20,000 Sophos customers, is a time-tested MDR service combined with Sophos’ engagements with cyber insurance providers delivers the confidence small businesses need to attain their endpoint security objectives without being security experts.”
Innovative Protection Capabilities
Sophos delivers strong preventative security that significantly reduces the workload resource-stretched small businesses. We believe our continued ‘protection-first’ strategy is a key contributor to Sophos’ position as a Leader in this evaluation.
We are constantly innovating to stay ahead of the evolving and expanding attack landscape. The IDC MarketScape assessment references Sophos’ expansive set of protection technologies provided as standard features in our endpoint security offering, and calls out some of our most recent innovations:
“Even with the most diligent efforts to deflect attackers, there are no guarantees that all manner of attacks can be thwarted. Addressing this potential, Sophos recently added several new capabilities: adaptive attack protection, critical attack warning, and data protection and recovery.”
Get the excerpt
To learn more about why Sophos was named a Leader in the 2024 IDC MarketScape for Worldwide Modern Endpoint Security for Small Businesses, read the excerpt here.
Source: Sophos
Organizations should implement the principle of least privilege to protect their sensitive data from unauthorized access. To implement the principle of least privilege, organizations need to define roles and permissions, invest in a Privileged Access Management (PAM) solution, enforce MFA, automatically rotate credentials for privileged accounts, segment networks and regularly audit network privileges.
Continue reading to learn more about the principle of least privilege, why it is important and how your organization can implement it.
What Is the Principle of Least Privilege and Why Is It Important?
The Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) is a cybersecurity concept in which users are granted just enough network access to data and systems to do their jobs, and no more. Least privilege access applies to users, processes, applications, systems and IoT devices. It prevents users from accessing resources they do not need and limits what they can do with the resources they do have access to.
Least privilege access is important because it:
- Reduces attack surface: Attack surface refers to the possible entry points where cybercriminals can access a system and steal data. By limiting privileges, organizations can reduce the possible entry points for unauthorized access and easily prevent any potential threats.
- Minimizes insider threats: Insider threats are cyber threats originating from within an organization when current or former employees, partners, contractors or vendors heighten the risk of sensitive data and systems becoming compromised. By limiting access, organizations can minimize insider threats from compromising sensitive data, whether by accident or intentionally.
- Prevents lateral movement: Lateral movement is when cybercriminals move deeper within an organization’s network after gaining initial access by escalating their privileges. Least privilege access prevents threat actors from moving laterally throughout a network. The cybercriminal will be restricted to the systems and data of the compromised account.
- Adheres to regulatory compliance: Least privilege access helps organizations protect sensitive data and adhere to regulatory and industry compliance frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA and SOX.
6 Ways Organizations Can Implement the Principle of Least Privilege
The principle of least privilege will help organizations improve their security and protect their sensitive information from unauthorized access. Here are six ways organizations can implement the principle of least privilege.
Define roles and permissions
The first step of implementing the PoLP is to define roles and permissions. Organizations need to determine the level of access to specific sensitive data and systems – who should be accessing these resources, why they are accessing them and how long they should have access to them. They then need to define what role each member of the organization has and what permissions each member has based on their role. They should use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to help define roles and permissions.
RBAC grants specific network permissions based on a user’s defined role. Users will have limited network access to specific data and systems based on their role within the organization and what they need to do their jobs. They should not have access to any resources outside of their assigned job duties. RBAC restricts what users can do with a system or file they have access to. For example, marketing employees need access to customer data but not developer environments, and IT administrators need access to developer environments but not financial records.
Invest in a PAM solution
To help manage and keep track of privileged accounts, organizations need to invest in a PAM solution. PAM refers to securing and managing accounts with access to highly sensitive systems and data. These privileged accounts can range from local administrator accounts to non-human service accounts to privileged user accounts. With a PAM solution, organizations can implement least privilege access since they have full visibility into their entire data infrastructure and how much access users have to sensitive data. They can determine who can access privileged accounts and how much access each user should have. PAM solutions help prevent privileged accounts from being misused by insider threats and compromised by threat actors.
Enforce MFA
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security protocol that requires additional authentication. To access a privileged account protected by MFA, authorized users must provide the login credentials to the account and an extra form of verification. Organizations need to enforce MFA on all privileged accounts to add an extra layer of security and ensure that only authorized users can access them. Even if the login credentials to the privileged account were compromised, cybercriminals could not access the account because it’s protected by MFA and they cannot provide additional authentication.
Automatically rotate credentials for privileged accounts
Password rotation is a cybersecurity practice in which passwords are regularly changed on a predetermined schedule. Organizations should use automated password rotation to protect privileged accounts from unauthorized access. Since privileged accounts provide access to sensitive information, organizations need to regularly change their passwords for these accounts. This locks out users who do not need access to the accounts anymore and prevents cybercriminals from cracking the passwords. Using automated password rotation ensures that privileged accounts are protected with strong and unique passwords after every rotation.
Segment networks
Network segmentation divides and isolates parts of an organization’s network to control access to sensitive information. These segments are divided based on the type of sensitive information stored and the users who need access. Segmentation limits access to the entire network and only allows users to access resources within their respective segments. It helps prevent cybercriminals who have gained unauthorized access to an organization’s network from moving laterally across the network because the cybercriminal is limited to only the network segment they accessed. To provide better security to their network, organizations can create micro-segments which are isolated parts of the network within a segmented network.
Regularly audit network privileges
Organizations need to regularly audit network privileges to ensure the right users have the necessary access they need to do their jobs and remove any users who do not need access to specific resources anymore. Regularly auditing network privileges and access prevents privilege creep, which is when users have accumulated higher levels of access than they need. It helps prevent misuse by potential insider threats and unauthorized access by cybercriminals.
Use Keeper® To Implement the Principle of Least Privilege
The best way to implement the principle of least privilege is with a PAM solution. With a PAM solution, organizations can see who has access to their network and limit user access to sensitive data. They can secure privileged accounts by ensuring employees are protecting them with strong and unique passwords and MFA.
KeeperPAM™ is a privileged access management solution that helps simplify privilege management by combining Keeper Enterprise Password Manager (EPM), Keeper Secrets Manager (KSM) and Keeper Connection Manager (KCM) into one, unified solution. With KeeperPAM, organizations can achieve complete visibility, security and control over every privileged user on every device.
Source: Keeper
Some of the benefits of using passphrases are that they’re easy to remember, difficult for cybercriminals to crack and they’re considered to be more secure than traditional passwords because of poor password habits. Some of the disadvantages of using passphrases are that some websites and apps may have low character limits, it’s impossible to remember passphrases for every single one of your accounts and they’re still vulnerable to being exposed in public data breaches.
Continue reading to learn more about passphrases and when you should use them to secure your online accounts and apps.
What Is a Passphrase?
A passphrase is a type of password that is created using a random combination of uncommonly used words. Since passphrases are created using words, they are generally longer, easier to remember and are considered to be more secure than using traditional passwords. Traditional passwords are often weak and are reused across multiple accounts because it’s difficult for individuals to remember multiple strong passwords.
While passphrases are considered to be more secure, there are still rules users should take into account when creating strong passphrases. A strong passphrase should have the following characteristics.
-
- Contains at least four words that are four or more letters each
- Is made up of at least 16 characters
- Contains uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols
- Doesn’t contain personal information
- Doesn’t contain words that relate to one another
- Isn’t being reused across multiple accounts
The Benefits of Using a Passphrase
Here are three benefits to using passphrases over traditional passwords.
Easy to remember
Because passphrases are made up of different words, they’re typically easier for users to remember, especially when you compare them to traditional passwords. For a traditional password to be strong, it has to be made of a variety of characters and be at least 16 characters long. A long, complex password isn’t as easy to remember as a long passphrase that contains a mix of characters.
Difficult for cybercriminals to crack or guess
The longer a passphrase is, the longer it takes for cybercriminals to guess or crack it. This is due to its password entropy. Password entropy is a mathematical equation that is used to determine whether it would be easy or hard for a cybercriminal to crack a password. Password entropy takes into account the variation of character length used in the password. Because passphrases are longer due to multiple words, their password entropy is greater, meaning they’re more difficult for cybercriminals to crack.
More secure than traditional passwords
As mentioned above, when creating traditional passwords, many people resort to using weak passwords because they want to be able to remember them for multiple accounts. This often leads to password reuse, which places multiple accounts at risk of being compromised if a cybercriminal cracks just a single password that’s being reused. Using passphrases as passwords removes this risk since they’re both strong and easy for users to remember.
The Disadvantages of Using a Passphrase
Here are three primary disadvantages to using passphrases.
Some websites and applications have low character limits
The longer a passphrase is, the more secure it’s considered to be. However, using passphrases may not be possible on some websites and applications that have low character limits. This means users should instead use traditional strong passwords on these websites and apps to ensure that the password they’re creating cannot be easily guessed or cracked by cybercriminals. We suggest using a password generator to help you create these strong passwords.
You can’t remember passphrases for every single account
While passphrases are easier to remember than long, complex passwords, you won’t be able to remember them for every single account. The average person has 100 accounts, ranging from bank accounts to social media accounts, so even if you choose to use passphrases to protect every single one of them, it’ll be impossible to remember 100 passphrases on your own.
Still vulnerable to data breaches
While passwords – like passphrases – are meant to secure your online accounts from unauthorized access, they’re still vulnerable to data breaches. This is especially true for users who fail to also enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) on their accounts. MFA adds an extra layer of security to your online accounts by requiring that a user verify who they are before being able to access their account. The more MFA methods enabled on an account, the more secure that account will be.
When public data breaches occur, whether or not a user’s password is strong doesn’t matter – all that matters is how that organization protects user information, which includes their credentials. If a user’s credentials aren’t secured, then their password is vulnerable to being exposed in a data breach.
When To Use a Passphrase
Passphrases are great to use in any instance where you only need to create passwords for a small number of accounts. The more accounts you use a passphrase on, the more passphrases you’ll have to rely on yourself to remember. Many people choose to use passphrases when creating a master password for an account, such as a password manager.
Password managers are tools that aid users in creating, managing and securely storing their sensitive data, such as the logins to their online accounts, credit card details and sensitive files. Password managers remove the need for users to remember multiple passwords and instead, users only have to create and remember one master password. This password should be both strong and easy for the user to remember, so it’s the perfect instance to use a strong passphrase.
Passphrases Are Easy To Remember and Secure
Passphrases are a great way to create passwords that are both strong and easy to remember. However, even though you’ll be able to remember one or two passphrases easily, it’ll be impossible to remember a passphrase for every single one of your accounts. A password manager like Keeper® can help. Keeper helps users create, store and manage the logins for every one of their accounts. Keeper also stores Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) codes, to make securing accounts with MFA a lot easier.
Ready to see how Keeper Password Manager can help you secure your online accounts? Start a free 30-day trial today.
Source: Keeper
Cybersecurity professionals are a core element of an organization’s cyber defenses. While much has been written about the shortage of skilled cybersecurity staff, far less focus has been given to how to enable these professionals to make the greatest impact. In short, how best to set them up for success.
Our recent analysis aims to advance this area of understanding by exploring the question: Does organizational structure affect cybersecurity outcomes? The findings will hopefully prove useful for anyone considering how to structure a cybersecurity function to achieve the best outcomes. Download the report
Approach
Our starting point was an independent survey commissioned by Sophos into the experiences of 3,000 IT/cybersecurity professionals working in mid-sized organizations (between 100 and 5,000 employees) across 14 countries. The research was conducted in the first quarter of 2023 and revealed the realities of ransomware, cyber risk, and security operations for security professionals operating at the frontline. The findings formed the basis of the Sophos State of Ransomware 2023 and State of Cybersecurity 2023 reports.
This analysis looked at those cybersecurity experiences through the lens of the organizational structure deployed. The goal was to identify if there is any relationship between structure and outcomes and, if so, which structure reported the best results.
Survey respondents selected one of the following models that best represented the structure of the cybersecurity and IT functions in their organization:
- Model 1: The IT team and the cybersecurity team are separate organizations (n=1,212)
- Model 2: A dedicated cybersecurity team is part of the IT organization (n=1,529)
- Model 3: There is no dedicated cybersecurity team; instead, the IT team manages cybersecurity (n=250)
Nine respondents did not fall into any of these models and so were excluded from the analysis. Organizations that fully outsourced their cybersecurity, for example, to an MSSP, were excluded from the research.
Executive summary
The analysis revealed that organizations with a dedicated cybersecurity team within a wider IT team report the best overall cybersecurity outcomes (model 2) relative to the other two groups. Conversely, organizations where the IT and cybersecurity teams are separate (model 1) reported the poorest overall experiences.
While cybersecurity and wider IT operations are separate specializations, the relative success of model 2 may be because the disciplines are also intrinsically linked: cybersecurity controls often have a direct impact on IT solutions while implementing good cyber hygiene, for example, patching and locking down RDP, is often executed by the IT team.
The study also made clear that if you lack essential cybersecurity skills and capacity, how you structure the team makes little difference to many of your security outcomes. Organizations looking to supplement and extend their in-house capabilities with specialist third-party cybersecurity experts (for example, MDR providers or MSSPs) should look for flexible partners who demonstrate the ability to work as an extension of the wider in-house team.
Analysis highlights
The analysis compares the reported experiences of the three groups across a number of areas, revealing some thought-provoking outcomes.
Root cause of ransomware attacks
Interestingly, the reported root cause of ransomware attacks varied by organizational structure:
- Model 1: Almost half of attacks (47%) started with an exploited vulnerability, while 24% were the result of compromised credentials.
- Model 2: Exploited vulnerabilities (30%) and compromised credentials (32%) were almost equally likely to be the root cause of the attack.
- Model 3: Almost half of attacks (44%) started with compromised credentials, and just 16% with an exploited vulnerability.
Ransomware recovery
Model 1 organizations were far more likely to pay the ransom than the other groups, and reported the lowest rate of backup use to recover encrypted data. In addition to being the group most likely to pay the ransom, model 1 organizations also reported paying much higher ransoms, with their median payment more than double that of models 2 and 3.
Security operations
The biggest takeaway from this area of analysis is that while model 2 organizations fare best in security operations delivery, most organizations find it challenging to deliver effective security operations on their own. Essentially, how you structure the team makes little difference if you lack essential capacity and skills.
Day-to-day cybersecurity management
There is a lot of common ground in this area across all three groups, and all experience similar challenges. More than half of respondents in all three models report that cyberthreats are now too advanced for their organization to deal with on their own (60% model 1; 51% model 2; 54% model 3).
All models also share similar worries around cyberthreats and risks. Data exfiltration and phishing (including spear phishing) feature in the top three cyber concerns for all three groups, and security tool misconfiguration is the most common perceived risk across the board. Essentially, everyone has the same top concerns, independent of organizational structure.
Important note
While this analysis provides unique insights into the correlation between IT/cybersecurity structure and reported outcomes, it does not explore the reasons behind these results i.e., causation. Every organization is different, and the structure of the IT/cybersecurity function is one of many variables that can impact propensity to achieve good security outcomes, including industry sector, the skill level of team members, staffing levels, the age of the organization, and more. These learnings should be used alongside other considerations to identify the best approach for an individual organization.
Learn more
To learn more and see the full analysis, download the report.
As stated, this analysis focuses on correlation rather than causation, and further research is needed to understand the reasons behind these outcomes. In the face of today’s cybersecurity challenges, any gain for defenders is important and we hope this analysis will spur further study into how organizations can leverage their internal structure to help optimize their defenses.
In the past fifteen years, at least 5,887 large healthcare data breaches have been reported to the U.S. Office for Civil Rights (OCR). With so much sensitive personal data housed in one place, it is no wonder the healthcare sector is a prime target of attack.
The State of Cybersecurity in Healthcare
According to the HIPAA Journal, healthcare-targeted data breaches have been trending upwards over the past few years, with nearly 46 million breaches in 2021 turning into nearly 52 million in 2022. However, 2023 “smashed all previous records with an astonishing 133 million records exposed, stolen, or otherwise impermissibly disclosed,” the Journal states.
According to the Verizon 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report, 35% of healthcare data breaches stem from internal bad actors, while 66% come from outside. What motivates attackers targeting this sector? Per the same report: money, espionage, fun, and ideology, in that order.
There are several key factors that make healthcare a highly targeted industry:
- Vast amounts of sensitive data
With swaths of personal health information (PHI) and other forms of personal identifiable information (PII) in their databases, healthcare organizations are a jackpot of data wealth to criminals. - Slow digitization
A slow-moving tech update culture leaves many medical groups still transitioning to digital records and, consequently, still learning to secure them. - Third-party risks
The global healthcare supply chain is so vast that the healthcare supply chain management market size is expected to more than double in the next six years and is already valued at nearly 3 billion dollars worldwide. That’s not even mentioning the software supply chain, and with ubiquitous digitization, cyber threats can lurk anywhere among those upstream vendors.
Additionally, the most common cyber threats and vulnerabilities resulting in data breaches are:
- Ransomware attacks
- Email phishing
- Electronic health records vulnerabilities
- Insider threats
- Lost, stolen, or misplaced devices
- Identity fraud
- DDoS attacks
Diving into just a few, ransomware attacks on hospitals have changed for the worse, becoming more sophisticated and evolving into a matter of life or death, as hacked devices could include defibrillators, surgical technology, and life support machines. When it comes to social engineering, phishing is not only the leading cause of healthcare data breaches, but seems to be increasing, with 57% of healthcare cybersecurity professionals stating that their most severe security incident involved phishing.
And since the Electronic Medical Records (EMR) Mandate took effect in 2014, healthcare groups with no prior experience creating digital health documents now have had to secure them — with varying levels of success. A report by Critical Insight noted that EHR-related breaches accounted for a full 7% of all data breaches to the healthcare sector within a six-month period.
The Main Industry Challenges
Although attack rates may be high, it is safe to say that the healthcare sector has its share of troubles when securing their patient data. The main industry challenges include:
- Increasing costs
Rising costs associated with healthcare and tight security budgets make it nearly impossible for healthcare organizations to effectively manage the vast amount of data flowing through their systems and storage spaces. - Complex technologies
Newer technologies like smartphones, tablets, and even medical IoT devices can throw people and processes for a loop, and legacy healthcare security systems have a hard time keeping up. As organizations move to the cloud and otherwise diversify their digital landscapes, it is challenging for security leaders to ensure medical device security. Medical devices like X-rays and MRIs are also potent vector of attack for hackers. - Intertwined systems and omnichannel interactions
The complexity of EHR systems, increased cloud usage, the rising number of health-related apps, and remote work (even doctor’s visits) expand the medical attack surface, introducing more opportunities for endpoint attacks.
Solutions on the Horizon
Notwithstanding the challenges, there are also solutions coming to the forefront. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS)’s Cybersecurity Strategy for the Healthcare Sector is one such example. It is a framework put forth by the federal government to help protect the healthcare sector against cybersecurity threats. Its tenants include:
- Establishing voluntary security goals within the healthcare industry
- Incentivizing the accomplishment of these security goals
- Implement an HHS-wide strategy for greater enforcement and accountability
- Expand and mature the HHS’ “one-stop shop” for healthcare cybersecurity
Government strategy and involvement is an encouraging step to developing mature healthcare cybersecurity regulations. However, it is one that must be coupled with the right security technology.
Cybersecurity Best Practices for Healthcare and How Fortra Can Help
When crafting their security strategy, it is important for organizations to prioritize prevention, not simply the cure. Prevention goes a long way to protect PHI and PII from being exposed in the first place and save medical groups from damage to their systems and reputation.
Here are a few tips for developing a preventative security approach:
- Choose a multi-layered data security solution that will help you classify data, detect and prevent leaks, and encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest, as well as provide next-generation data loss prevention (DLP) for healthcare.
- Monitor for changes to your EHR so you know when an unauthorized party is trying to make changes without the owner’s consent.
- Perform risk assessments on your network, technologies, software, and applications to close security gaps. Regularly patch software to ensure all systems are up to date.
- Invest in a robust identity governance and administration (IGA) solution to help you properly manage access to medical devices, hospital rooms, and applications.
- Pick an identity and access management (IAM) platform that features a managed file transfer (MFT) solution and a zero-trust methodology as standard components. HIPAA secure file transfer solutions enable your team to work with confidence and focus on what matters — all while keeping patients, the organization, and the industry safe.
- Find a trusted email security solution that can identify good email behavior from bad.
- Closely manage and monitor third-party vendors who have access to your systems and data.
- Maintain a detailed incident detection and response plan at all times. While prioritizing prevention, it’s vital to always be ready for the crisis.
- Share your experiences. Team up with healthcare security experts and government agencies to share your expertise and find innovative solutions to emerging threats.
And remember, good healthcare cybersecurity software solutions deliver effective compliance, helping you keep up with standards such as:
- HIPAA and HITECH
- PCI DSS, CCPA, GDPR, SOX
- NIST Framework
- CISA Healthcare Mitigation Guide
Source: Fortra
Sophos NDR can now be deployed in AWS AMI for all NDR and XDR/MDR customers with a licensed integration pack that requires a log collector.
Sophos NDR in AWS offers several advantages for threat detection and response:
What you get
Cloud-native security monitoring:
- AWS-native NDR sensors can now efficiently provide visibility into the network traffic and security events within AWS environments. This is crucial for monitoring and securing cloud-based workloads.
- If the NDR sensor is external to the AWS environment, then the network traffic has to be routed to the external NDR sensor at a significant data transfer cost.
Scalability:
- Deploying an NDR sensor as an AMI allows you to scale your security monitoring capabilities based on the growth of your AWS infrastructure. You can easily launch multiple instances of the sensor to cover larger environments or increasing workloads.
- Each deployed sensor can support 1GBS network traffic via a span/rspan configuration.
Real-time threat detection and response:
- Sophos NDR monitors both encrypted and un-encrypted network traffic in real time, detecting and alerting on potential security incidents.
- Combining Sophos NDR and XDR/MDR with Sophos Firewall in AWS provides real-time Active Threat Response to block active adversaries dead in their tracks.
How it works
Amazon Machine Image (AMI) is a pre-configured virtual machine image used to create Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances within the Amazon Web Services (AWS) environment. An AMI contains the necessary information to launch an instance, which includes the operating system, application server, and any additional software required to run your application. The AWS AMI also supports log collectors for third-party integrations, as well as NDR.
Getting started
Check out the video, documentation, and links to AWS on the Sophos NDR community for information on how to get started quickly.
Source: Sophos
You can avoid social media identity theft by setting strict privacy settings, securing your social media accounts with strong passwords, vetting every friend and follower request, keeping an eye out for phishing attempts and limiting what you share on social media. With almost every person having at least one social media account, cybercriminals are leveraging this by targeting these accounts to carry out various cyber attacks, including identity theft.
Continue reading to learn more about what social media identity theft is, how it happens and the dangers of oversharing on these platforms.
What Is Social Media Identity Theft?
Social media identity theft is when cybercriminals use social media platforms such as Instagram and Facebook to steal your Personally Identifiable Information (PII). Some cybercriminals will even go as far as gaining access to your social media accounts so they can gather even more information about you.
When a cybercriminal has just enough information about you, they can use it to steal your identity. Identity theft can not only be costly to recover from, but it can also be time-consuming, as well as mentally and emotionally draining.
How Social Media Identity Theft Happens
Social media identity theft can happen in different ways, but one of the most common ways is through Account Takeover (ATO) attacks. An ATO attack is when a cybercriminal takes over one of your online accounts and locks you out of it by changing your password. Since you no longer know the password to your account, you’re unable to log in to it until you reset your password or get in contact with customer service.
While a cybercriminal has access to your account, they can do anything on it such as make posts or scam your friends and followers. For some cybercriminals, taking over one of your accounts is just the beginning and they may even attempt to take over other critical accounts like your bank account.
Most people tend to overshare on social media making them targets for cybercriminals. For individuals who have larger followings, you’re an even bigger target because cybercriminals can attempt to scam your followers by pretending to be you. Because your followers are unaware of the account takeover attack, they may unwittingly share sensitive information.
Steps To Avoid Social Media Identity Theft
Here are five steps to avoid becoming a victim of social media identity theft.
Set strict privacy settings
All of your social media accounts should have strict privacy settings set. Here’s how to make your Instagram, Facebook and X (formerly known as Twitter) accounts more private.
- Instagram: Go to Settings and privacy > Click Who can see your content > Toggle Private Account > Click Switch to private to confirm.
- Facebook: Go to Settings > Under Audience and visibility click Followers and public content > Customize these settings to be more private. We recommend not having any of these settings set to public.
- X: Click your profile icon on the upper right-hand corner > Click Settings and privacy > Click Privacy and safety > Click Audience and tagging > Toggle the buttons where it says Protect your posts and Protect your videos.
The stricter your privacy settings are on your social media accounts, the more secure they’ll be from prying eyes.
Strengthen your social media accounts with strong and unique passwords
To prevent account takeover attacks, each of the passwords to your online accounts should be strong and unique. This means they shouldn’t be reused or use common dictionary words and phrases. Each of your passwords should integrate the following password best practices:
- Be at least 16 characters long
- Include uppercase and lowercase letters
- Include numbers
- Include symbols (e.g. $, &, #)
When creating strong passwords, it’s best to have a password generator create them for you to ensure that they are always long and complex. If you find yourself having trouble remembering multiple passwords, it’s worth investing in a password manager to help you create, manage and securely store your strong passwords for you.
Vet every friend and follower request
Having a large number of followers isn’t always good, especially if most of those followers are strangers you don’t know. Rather than accepting every friend and follower request you receive, check to see if it’s worth giving them access to your social media accounts.
Some cybercriminals go as far as creating fake social media accounts just so they can follow you to see what you post, so you’ll want to be extra cautious about which friend requests you’re accepting.
Be on the lookout for phishing attempts
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack that aims to get victims to disclose sensitive information by pretending to be someone the victim knows or a company they have an account with. Phishing attempts leverage malicious links and attachments and when victims click on these links or attachments, malware is installed on their device or they’re led to a spoofed website. Spoofed websites are made to look legitimate so victims are inclined to enter their sensitive information such as their login credentials or credit card numbers.
Cybercriminals may use phishing attempts to commit social media identity theft, so it’s important to learn how to spot them. Here are a few phishing attempt indicators.
- Use of urgent language
- Offers that seem too good to be true
- Requests for personal information
- Urging you to click on unsolicited links or attachments
- Threats of serious consequences if you don’t follow their instructions
Limit what you share on social media
It can be tempting to share information about an upcoming trip or event on your social media, but you should limit what you share on these platforms, especially when it comes to your whereabouts. Cybercriminals and cyberstalkers look to your social media accounts for information like this so they can use it against you.
The Dangers of Oversharing on Social Media
Oversharing on social media such as posting where you are while you’re at that location, and posting intimate details about your personal life, can jeopardize your online privacy. Cybercriminals look for personal details about your life so they can use them to carry out all types of social engineering attacks. Social engineering is a technique used by cybercriminals to psychologically manipulate victims into doing things or revealing sensitive information. The more a cybercriminal knows about you, the easier it is for them to manipulate you using social engineering tactics.
Oversharing too much information on your social media accounts not only places you at risk of account takeover attacks, but also places you at a greater risk of being a victim of identity theft.
Don’t Fall Victim to Social Media Identity Theft
Social media identity theft can place you at risk of losing access to your accounts and losing money. To keep yourself protected from social media identity theft, implement the steps mentioned above to make your accounts more secure and private.
To learn more about how you can keep your social media accounts secure, here are a few more of our tips. To see how a password manager like Keeper® can help you keep your accounts secure with strong passwords, start a free 30-day trial of Keeper Password Manager today.
Source: Keeper by Aranza Trevino
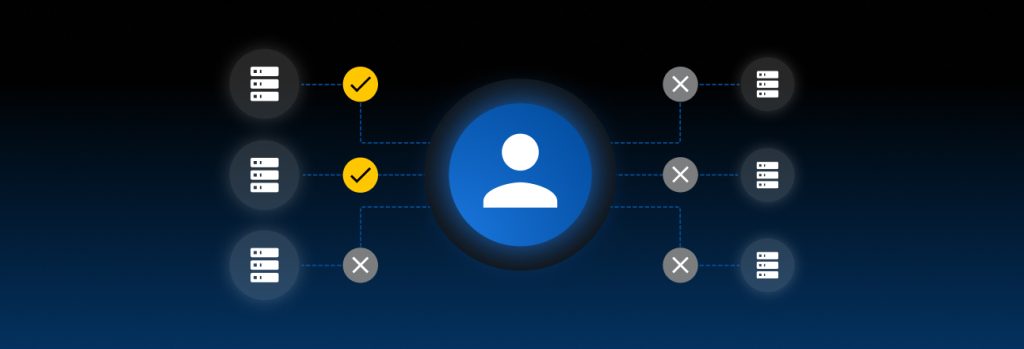
Organizations using Veeam Backup and Replication can now strengthen their defenses against ransomware with Sophos MDR and Sophos XDR. Read on to learn how Sophos’ new integration with Veeam delivers better visibility to detect and stop threats targeting backup data.
Backup and recovery are integral parts of a holistic cybersecurity strategy. Adversaries attempt to tamper with backup solutions to prevent recovery from ransomware attacks – early detection of this malicious activity is critical.
 Sophos’ new integration with Veeam seamlessly exchanges security information when a threat emerges, extending visibility to help detect, investigate, and respond to active attacks.
Sophos’ new integration with Veeam seamlessly exchanges security information when a threat emerges, extending visibility to help detect, investigate, and respond to active attacks.
This powerful new partnership provides peace of mind that backup data is always available and protected, enabling organizations to detect threats, investigate suspicious activity, and ultimately recover data quickly.
With Sophos and Veeam, organizations can ensure the integrity and availability of backups, reducing the risk of data loss due to malware, accidental deletion, internal security threats, and other data loss scenarios.
- The Sophos MDR service provides 24/7 security monitoring, filters out redundant alerts, and investigates threats to Veeam environments, like attempts to delete backup repositories, disable multi-factor authentication, delete encryption passwords, and more.
- Organizations using the Sophos XDR solution for in-house investigation and response can also integrate Veeam telemetry to identify potentially malicious activity, combined with threat detections from other sources in a single unified platform and console.
The strongest protection against ransomware attacks
The Sophos XDR solution and the Sophos MDR service include industry-leading CryptoGuard technology that universally detects and stops ransomware before it impacts customers’ systems, including new variants and local and remote encryption.
Sophos’ superior prevention, detection, and response capabilities, combined with immutable backups and versioning provided by Veeam, ensure backup data remains secure and recoverable.
Elevate your defenses with Sophos’ new Veeam integration
The new Veeam integration is now available as an add-on for Sophos MDR and Sophos XDR subscriptions via a new “Backup and Recovery” Integration Pack license.
To learn more and explore how Sophos MDR and Sophos XDR can help your organization better defend against active adversaries, including attacks that target your backup repositories, speak with a Sophos adviser or your Sophos partner.
Already a Sophos MDR or Sophos XDR customer? Activate the Veeam integration in your Sophos Central console today.
Source: Sophos
It’s not news that most enterprises operate in the cloud. Migration to the cloud leads to better collaboration, data storage, and lower costs compared to on-premises resources. Odds are your organization is currently enjoying the conveniences of the cloud.
The cloud has reshaped the way organizations operate, but with the migration comes new obstacles in email security, and the cloud has its own vulnerabilities. Relying on Microsoft’s add-on security features is simply not enough at stopping advanced threats. According to Gartner, Microsoft lacks the ability to detect and eradicate 20% of the advanced email threats. This is why Gartner recommends a multi-tier architecture for cloud email security.
Has Your Email Security Kept Up with Your Capabilities?
Email remains a prominent target for phishing attacks. Verizon’s Data Breach Investigation Report (DBIR) states that the three primary ways in which attackers access an organization’s data include phishing, stolen credentials, and exploitation of vulnerabilities.
Traditionally, a secure email gateway has been at the center of email security platforms. However, as cloud adoption continues, the existing capabilities offered by secure email gateways and native cloud service providers fall short in providing adequate protection.
Business Email Compromise (BEC) and phishing dominate the email threat landscape and chances are, your current traditional email security solution is struggling with the challenges posed by these sophisticated threats. According to the FBI’s Internet Crime Report, BEC attacks reported in end user inboxes grew more than 43% between 2021 to 2022.
Email security struggles to detect BEC because it doesn’t contain any malicious links or attachments and completely relies on social engineering tactics. The spoofed content is enhanced for legitimacy making them look believable to recipients – including your email security platform.
Why Frontline Email Security Is Insufficient
Keeping up with email security can often feel like running on a treadmill. As soon as you feel good about your email security solution, new threats emerge causing the circle of spending more on layers of protection with multiple vendors and environments to manage. Frontline tools were not designed to solve the targeted, social engineering-based attacks.
In fact, a Fortra 2023 study found that the leading cloud email provider missed 625 threats annually for every 1,000 users!
Fortra’s Cloud Email Protection
I believe keeping digital information safe and advocating for proactive measures to protect sensitive information through email is vital to an organization. As a former senior principal analyst at Gartner, I helped clients address email security issues such as phishing protection and unstructured data protection. Which is why I am thrilled to be a part of Fortra’s team. The launch of Fortra’s Cloud Email Protection encompasses an array of advanced features like AI/ML-driven detection, threat intelligence, and security awareness training and much more. I eagerly anticipate leading initiatives that drive innovation within this dynamic product landscape at Fortra.
Fortra combined capabilities from Agari, Clearswift, and PhishLabs, creating a new cloud email security platform that delivers multi-faceted defense against advanced email threats in a single solution.
The foundation of Fortra’s Cloud Email Protection encapsulates data science, global inbox threat intelligence, and automated remediation. This foundation makes Cloud Email Protection the only integrated cloud email security solution that combines these features into a single cloud-native platform – stopping threats that bypass traditional defenses.
Data Science: Through data science and AI, Cloud Email Protection applies machine learning models, large language models and neural networks to stop unknown threats.
Global Inbox Threat Intelligence: By crowdsourcing malicious indicators from user inboxes worldwide, Cloud Email Protection can stop emerging threats.
Email Threat Operations: Cloud Email Protection mines threat data across millions of user inboxes and develops countermeasures for novel attack patterns.
Continuous Detection and Response: At enterprise scale, Cloud Email Protection automatically finds and eradicates threats throughout the email environment.
Fortra’s distinctive product portfolio features capabilities like AI/ML-driven advanced detection, threat intelligence, security awareness training and much more. All these capabilities are part of Fortra’s Cloud Email Protection product which perfectly embodies my vision of a comprehensive email security solution. I am thrilled to be part of the team contributing to Cloud Email Protection and eagerly anticipate leading initiatives that drive innovation within this dynamic product landscape at Fortra.
Source: Fortra
Why should the financial services sector adopt a data classification strategy?
Because more than nine out of ten (95%) of data breaches are financially motivated, according to this year’s Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report. Within the finance and insurance sector specifically, the rates were as high as 97% — no surprise there.
However, what may be surprising is that most of these attacks were easy to do.
One of the top two attack patterns was misdelivery, or in other words, sending the wrong document to the wrong person. This can result in de facto data breach, or simply supply a threat actor with just enough information to leverage another (bigger) breach down the road.
In either event, protecting data starts with sorting it properly. That’s where data classification comes in. You can’t secure what you don’t understand, and last week’s webinar deserves a different level of security than snippets of the company’s source code.
The finance sector is losing too much ($5.9 million this year) to data breaches when data classification helps get to the root of the issue. Here’s why, how, and what financial firms have to gain.
Why Financial Data Protection Is Critical
Every year, thousands of pilfered records hit the dark web. Stolen data can go for up to $1,000 a piece, and there were no less than 153.3 million records negatively impacted by financial service data breaches between 2018 and 2022. At least 79 U.S. financial firms reported data breaches affecting upwards of 1,000 people in 2022.
While the impact to consumers is paramount, we can’t ignore the effect on the financial services industry. Finance firms lose approximately 28% more than the global average per data breach, according to the IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023. And since most estimates place the financial sector at roughly a quarter (20-25%) of the global economy, it isn’t hard to see that what happens here can inflict the status quo at large.
Financial data is at a premium, and if there is any time for solutions that work, it is now. Data protection in the financial services industry requires not only next-generation solutions, but primarily, a foundation of accountability for all digital assets.
What Is Data Classification?
As this year’s DBIR notes, it’s the little things that impact financial breaches the most. That’s why, when considering cybersecurity solutions for financial services, a data classification tool should be at the top of the list.
Data classification is the process of using predefined criteria to organize and label assets by type, business value, and sensitivity. The four common levels of data classification are:
- Public: No restrictions on access or usage; press releases, brochures, public research
- Internal: For internal employees who are granted access only; memos, internal emails, marketing research
- Confidential: Access by permission only and contained within the business or third parties: personally identifiable information (PII), personal health information (PHI)
- Restricted: Need-to-know basis: trade secrets, intellectual property, federally protected data
Classifying your data in this way is foundational to creating policies that will then protect that data and protect it accurately. Each classification warrants its own level of security and makes policy creation methodical and more effective. This, along with other ways of streamlining financial data security, can help companies in the industry protect against threats at scale and with intention.
Challenges of Financial Data Protection
With the acceleration of hybrid models, cloud-based networks, increasing regulation, and advanced threats, the industry has faced some significant obstacles to smoothly meshing finance and cybersecurity. Data classification solutions help to alleviate these challenges in the following ways:
- Data Visibility: Know which data is sensitive customer banking information and which is publicly available policy information — and know where all that sensitive information resides. If data gets lost in the network, it is both unprotected and likely uncompliant, landing you on the wrong side of data protection requirements.
- Addressing Workforce Gaps: The cyber talent shortage is expected to grow in the banking industry, and SOCs need a way to do more with less. Data classification lifts the burden of overwhelm as data is neatly arranged and easier to create policies and protections around.
- Data Privacy Regulations: Stay compliant with financial data privacy regulations like SOX, PCI DSS, GDPR, and more. You can’t securely maintain data you are unaware of, and data classification makes data easy to pull in an audit.
- Emerging Threats: Classifying data helps defend finance firms against this year’s emerging threats — from RaaS to supply-chain exploitation — by providing context to partner tools like endpoint detection and response (EDR), user/entity behavior analytics (UEBA), and more. It not only helps determine where the breach occurred and how severe it is, but what response action should be prioritized first.
Benefits of Data Classification in Finance
Besides identifying and protecting data wherever it is located within the enterprise, benefits of finance data classification include:
- Preventing missends. One of the top two most prominent sources of financial data loss, missent information can be prevented with data classification tools. Email classifiers sort information within an email client to prevent sensitive data from being sent to the wrong person.
- Global data protection regulations like GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, CMMC, ITAR, and CUI to help you stay compliant. Categorizing information gives organizations more control and granularity, making data easier to retrieve when needed for risk management and compliance purposes.
- Metadata that presents context to otherwise general alerts. Data classification augments downstream data security solutions like encryption, data loss prevention (DLP), and digital rights management (DRM). It does this, in part, by reducing the number of false positives stirred up by the high-level scans of DLP tools, improving responses with better, more accurate information.
Knowing not only where, but what data is lets companies make better choices about how to protect, manage, and share it both inside and outside the organization.
Advancing Data Classification with Fortra
When it comes to financial data protection, Fortra’s Data Classification Suite offers financial institutions around the world a way to structure data, secure it in place, improve DLP via automation, and make users more aware of the data they use. Talk to a Fortra expert today and start the conversation.
Source: Fortra
The IDC MarketScape study evaluates endpoint security vendors’ prevention, EDR, and MDR capabilities and business strategies.
We are delighted to announce that Sophos has been named a Leader in the IDC MarketScape: Worldwide Modern Endpoint Security for Midsize Businesses 2024 Vendor Assessment.
This IDC MarketScape evaluates vendors based on how their endpoint prevention, EDR, and MDR capabilities meet the needs of organizations with 100 – 2,499 employees.
According to the IDC MarketScape evaluation, “Sophos should be a strong consideration for midsize businesses seeking to reduce their number of core security vendors without sacrificing security efficacy”. Read the excerpt
“With their professional and managed security services, expanded product set, and ability to integrate with existing security investments, it’s clear that Sophos understands the needs and challenges of a midsize business,” said Michael Suby, research vice president, Security & Trust, IDC. “Sophos’s comprehensive approach from prevention through recovery places Sophos on the shortlist of midsize businesses looking for an established and effective partner for security.”

Protection-first approach
We believe our continued focus on preventative security is a key contributor to Sophos’ position as a Leader in this evaluation. It provides a robust foundation for the Sophos XDR solution and the Sophos MDR service. Sophos delivers strong threat protection to significantly reduce the detection and response workload for IT admins and security analysts.
The IDC MarketScape notes, “Sophos recently added several new capabilities: adaptive attack protection, critical attack warning, and data protection and recovery. Adaptive attack protection, introduced in early 2023, is a demonstration of Sophos’ means to disrupt hands-on-keyboard attackers while minimizing potential disruption to legitimate operations.”
The report also notes, “Sophos includes an expansive set of protection technologies (host-based firewall and IDS/IPS, device control, DLP, and encryption) as standard features in its endpoint security offering.”
Extensive and compatible security platform and ecosystem
The Sophos security platform combines an expansive portfolio of products and managed security services with compatibility with an extensive suite of third-party solutions. Organizations can detect and respond to threats using a single unified platform, leveraging the technology they need from Sophos or connecting their existing cybersecurity technologies.
“For the many midsize businesses and VARs serving midsized business that are struggling with SecOps staffing and maturity, Sophos offers the means to overcome this challenge without forcing a full vendor swap.”
We continue to expand and diversify strategic and technology partnerships to enable organizations to reduce cyber risk further. Recognizing this approach, the IDC MarketScape refers to our expanded partnerships with cyber insurance providers, helping midsize businesses address potential challenges in seeking insurance coverage.
Get the excerpt
To learn more about why Sophos was named a Leader in the 2024 IDC MarketScape for Worldwide Modern Endpoint Security for Midsize Businesses, read the excerpt here.
Additional Sophos customer and analyst validation
Sophos’ recognition as a Leader in this IDC MarketScape comes on the heels of multiple customer endorsements and third-party validations, including:
- Sophos named a Leader in the Gartner MQ for EPP for the 14th consecutive report
- Sophos named a Leader for Endpoint Protection, EDR, XDR, Firewall, and MDR in G2’s Winter 2024 (December 2023) Reports
- Sophos earning a 100% Total Protection score in SE Labs’ Q4 2023 Enterprise Endpoint Security and Small Business tests
- Sophos named Gartner Customers’ Choice for EPP for the second consecutive year
- Sophos named Gartner Customers’ Choice for MDR in Gartner’s first-ever report in the segment
Source: Sophos
Your data that’s stored with an organization you trusted could become exposed due to a targeted cyber attack or data breach. If your data was part of a public data breach, you need to change any compromised passwords, monitor your accounts for suspicious activity, freeze your credit and notify any relevant parties of the data breach.
Continue reading to learn more about data breaches, how to recover from a data breach and how to prevent future data breaches from happening.
What Is a Data Breach?
A data breach is when sensitive data of a user or organization is accessed, stolen and used by unauthorized users. Cybercriminals can access sensitive data when it is accidentally exposed due to human error or through vulnerabilities in data infrastructure. They can also steal sensitive data by targeting a user or organization with a cyber attack. Data breaches can lead to identity theft in which threat actors steal a victim’s Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and impersonate them to commit fraud.
Data breaches are often the result of data leaks, targeted cyber attacks or malicious insider threats.
- Data leaks: Sensitive data unintentionally exposed from within an organization. Data leaks are often the result of human error and can be the result of accidentally revealing sensitive information to the public, an internal user having unauthorized access to sensitive data or improperly storing sensitive data.
- Targeted cyber attacks: Attacks on computers, networks or systems by cybercriminals in an attempt to steal sensitive information. Cybercriminals exploit a user or organization’s security vulnerabilities such as software bugs or weak cybersecurity practices. They exploit these vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access and steal sensitive data.
- Malicious insider threat: A cyber threat that happens within an organization. They occur when current or former employees, partners, contractors or vendors intentionally expose or steal sensitive data for malicious purposes.
How To Recover From a Data Breach
If you received a notification that your sensitive data has been exposed in a data breach, you need to act quickly to identify the impact of the data breach and mitigate the impact. The first step is to identify what information of yours was exposed in the data breach. Once you have identified the information that was exposed, you can take the necessary steps to contain the damage and mitigate the effects of the data breach. Here are the steps to recover from a data breach.
Change any compromised passwords
When you have determined what sensitive information was revealed in a data breach, you need to change any compromised passwords for the accounts associated with it. You should create new and unique passwords that are difficult to guess. To easily change compromised passwords, you should use a password manager.
A password manager is a tool that securely stores and manages your personal information, such as your passwords, in a digital encrypted vault. With a password manager, you have access to all of your passwords and can use it to help change them with the built-in password generator.
Monitor accounts for suspicious activity
After you have changed the compromised passwords, you need to monitor your accounts for any suspicious activity to determine if cybercriminals still have access. Look for any suspicious activity such as:
- Fraudulent charges
- Additional debt
- Unknown logged-in devices
- Changes in security settings
- Failed login attempts
- Unfamiliar messages
- Unauthorized applications for loans
Freeze your credit
Cybercriminals can use your sensitive information to apply for loans or open lines of credit under your name, which can hurt your credit and leave you with large amounts of debt. If your sensitive information was exposed in a data breach, you need to individually freeze your credit with each of the three credit bureaus – Experian, TransUnion and Equifax. If you fail to contact all three of the credit bureaus, then a cybercriminal can still apply for a loan under your name.
If you are afraid your leaked information could lead to identity theft, you should apply for a fraud alert. A fraud alert is a free notice that you can add to your credit report that requires you to verify your identity before you’re able to take out a loan under your name. It protects you from identity theft and helps to ensure that only you can take out loans or open lines of credit under your name. To place a fraud alert, you would need to contact one of the credit bureaus.
Notify any relevant parties
Depending on the sensitive information revealed in the data breach, you need to notify any relevant parties of the data breach. For example, if your credit card information is exposed, you should contact the bank to cancel the card and get a new one. Contact your social network if your online accounts were compromised as they can be used for phishing attacks. If your company’s data was exposed, contact your company to inform them, so they can take the proper steps to handle the security breach.
How To Prevent Future Data Breaches
Although you may have taken the right steps to recover from a data breach, cybercriminals may try to retarget you for future cyber attacks to steal your information. You need to take precautionary measures to prevent future data breaches. Here are the ways to prevent future data breaches.
Use strong and unique passwords
You need to use strong and unique passwords to protect your online accounts from cybercriminals. By using unique passwords for each of your accounts, you can prevent cybercriminals from executing credential stuffing attacks and compromising multiple accounts. Strong passwords make it difficult for cybercriminals to guess and crack your passwords.
Strong and unique passwords protect your accounts that hold sensitive information. You should create passwords that are at least 16 characters long. Each password should have a unique and random combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers and special characters. You should avoid including personal information, sequential numbers or letters and commonly used dictionary words when creating passwords.
Enable MFA
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security protocol that requires users to provide additional forms of authentication to gain access to their accounts. With MFA enabled, you need to provide your login credentials along with an additional form of identification to access your accounts. MFA provides an extra layer of security by ensuring only authorized users are allowed access to your accounts. Even if your login credentials were compromised, cybercriminals would not be able to access your accounts since they wouldn’t be able to provide the additional authentication.
Keep your software up to date
Cybercriminals will try to exploit security vulnerabilities of outdated software that allow them to bypass security measures and install malware. You should regularly update your software to patch any security flaws and add security features that better protect your device. Keeping your software up to date will help prevent cybercriminals from accessing your data.
Reduce your attack surface
An attack surface refers to all of the possible entry points where cybercriminals can access a system and steal data. A large attack surface makes it harder to manage the various points where a cybercriminal can attack you and gain unauthorized access to your sensitive information. Reducing your attack surface will limit the opportunities a cybercriminal has to attack you. You can reduce your attack surface by deleting inactive accounts, getting rid of unnecessary applications, strengthening login credentials and updating your software.
Stay educated about cyber attacks
Cybercriminals are always finding new ways to attack users and steal their sensitive data. You need to stay educated about new cyber attacks to recognize and avoid them. Take precautionary measures to prevent cyber attacks from successfully impacting you or your organization.
Keeper® Helps Prevent Future Data Breaches
The best way to implement cybersecurity best practices and prevent future data breaches is by using a password manager. With a password manager, you can store and protect your personal information such as your login credentials, Social Security number, passport, IDs and other sensitive data. It will help you strengthen your accounts with access to sensitive data and help you change any compromised passwords if you suffer a data breach.
Keeper Password Manager uses zero-trust and zero-knowledge encryption to protect your personal information. This ensures that only you have access to your digital vault. Sign up for a free trial to protect your sensitive information from data breaches.
Source: Keeper
A password breach is when a cybercriminal has your password and is able to use it to get into your account. Password breaches can occur due to social engineering and insider threats, but most often, weak password habits are the culprit.
Keep reading to learn more about how passwords get breached, what can happen if your passwords are breached and how to prevent password breaches from happening.
How Do Passwords Get Breached?
Passwords are the keys meant to safeguard your online accounts and the data they contain. They should never be accessed by someone who is unauthorized to do so. Cybercriminals take advantage of individuals who reuse passwords, use weak passwords, click on phishing scams and insecurely store their passwords in order to launch their attacks.
Reusing passwords
One way passwords get breached is through password reuse. Password reuse is extremely common. In fact, 52% of people use the same password for multiple accounts because it’s easier for them to remember one password or several versions of the same password, instead of strong and unique passwords for each separate account. However, this poses a serious risk, because if a cybercriminal gets hold of that one password, they are able to access all of the accounts that you use it for. If a company that you have an account with were to be breached and your password is exposed, cybercriminals can then launch credential stuffing attacks to see if they can access multiple accounts with the same password.
Using weak passwords
Passwords also get breached because they are weak. Any password that is easy to guess or uses a small number of characters that password-cracking software can easily crack is likely to be compromised by cybercriminals. Weak passwords are those that are too short, repeat letters or numbers and use personal information like the year you were born. Avoiding weak passwords, and creating strong and unique passwords for each account, is simple with the help of an online password generator that will create them for you.
Phishing scams
Phishing scams are emails, text messages or phone calls from cybercriminals portraying themselves to be someone they’re not, like a company or family member, to get you to reveal sensitive information. A cybercriminal uses phishing scams to solicit information they can use to compromise your online accounts.
For example, a cybercriminal might send you a phishing email saying to immediately change your password because your account has been compromised. The email may even urge you to click on a link, but clicking that link could take you to a spoofed website that looks legitimate. If you enter your credentials into the spoofed website, you’re essentially handing them over to the cybercriminal.
Insecurely storing passwords
Anytime you store your passwords insecurely, like in a spreadsheet or the notes feature on your phone, you’re placing your accounts at risk of becoming compromised. Storing login credentials in an unencrypted format means cybercriminals can easily gain access to your accounts and any data stored within them.
Insecure password-sharing methods
Password sharing is meant to give others secure access to your account with your approval. However, insecure password-sharing methods like sharing through text messages and email can be easily intercepted by cybercriminals. Furthermore, if a bad actor has physical access to your device, they can see the password in plain text.
It’s important that when you choose to share your passwords, you do so with full end-to-end encryption to prevent your password from being breached. A secure password manager can facilitate this type of secure credential sharing.
What Happens if My Passwords Get Breached?
If any of your passwords get breached, it can lead to a variety of privacy and financial issues that can have serious impacts on your day-to-day life. Data stolen by a cybercriminal can be used to access other accounts, especially if you reuse passwords or variations of them. Password breaches can also lead to cybercriminals blackmailing you or stealing your identity.
Suppose a cybercriminal were to breach your email password and you did not have multi-factor authentication enabled on the account, they may be able to reset the passwords of your other accounts that use the same email address.
How To Know if Your Password Is Breached
The best way to know if your password has been breached is with a dark web monitoring tool. Keeper Security offers a free dark web scan that allows you to check if your data has been stolen and published on the dark web. The dark web is a hidden part of the internet that allows transactions and information to be shared and sold anonymously. It is notoriously used for unlawful purchases, including the selling and purchasing of stolen personal information.
How To Prevent Your Passwords From Being Breached
You can prevent your password from being breached by using a password manager, enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and avoiding public WiFi.
Use a password manager
The best way to prevent your passwords from getting breached is by using a password manager. A password manager is a tool that helps you generate, manage and securely store your passwords. Password managers help you ensure that your passwords are always following password best practices and are never being reused across your accounts.
One way passwords get breached is by using personal information when creating a password. For example, using a pet name or the street you live on in your password makes it easy for cybercriminals to guess and gain access to your account. Of course, remembering passwords that have no significance to you can be hard, but that’s where using a password manager helps. With a password manager, the only password you’ll have to remember is your master password.
Enable MFA
Another essential step in increasing your overall online security is to enable multi-factor authentication whenever possible. MFA requires you to use one or more additional methods of authentication to log in to your accounts. Having MFA enabled keeps your confidential information safeguarded from unauthorized access. Even if your passwords were to become breached, a cybercriminal would still be unable to access your account if MFA was enabled, because they wouldn’t be able to authenticate who they are.
Avoid using public WiFi
Avoiding public WiFi can also help prevent your passwords from being breached. When using public WiFi, your data is vulnerable to being intercepted through a Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack. A MITM attack is when data being sent between two individuals is intercepted by a cybercriminal. Avoiding public WiFi will mitigate the risk of a MITM attack happening to you.
Stay Safe From Password Breaches
Remember to always use strong, unique passwords that are not easily guessable. To ensure you’re always using strong passwords, use a password manager like Keeper Password Manager. As the world’s most trusted password manager, Keeper can keep your passwords protected from breaches. The user-friendly interface ensures it’s as simple to use and seamless across all of your devices. Start a free 30-day trial today.
Source: Keeper
Protect your Google Workspace productivity tools with Sophos.
Organizations with distributed workforces are increasingly reliant on cloud-based productivity platforms like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace for email, file sharing, and collaboration. Read on to learn how Sophos’ new integration with Google Workspace can help defend against advanced attacks against your business-critical productivity tools.
Detect and respond to threats targeting your Google Workspace environments
Google Workspace (formerly known as G Suite) includes some built-in security controls, but investigating, validating, and responding to threats can be challenging for under-resourced security teams.
Security teams need granular visibility across their entire IT environment to defend against active adversaries. The Sophos Extended Detection and Response (XDR) solution and the Sophos Managed Detection and Response (MDR) service leverage a connected tech approach that correlates data from a broad ecosystem of products and technologies, providing full visibility across your applications, tools and security components.
Sophos has launched a new integration that extends this ecosystem by collecting security data and telemetry from the Google Workspace productivity suite, giving Sophos MDR analysts and Sophos XDR users better visibility to detect and stop threats.
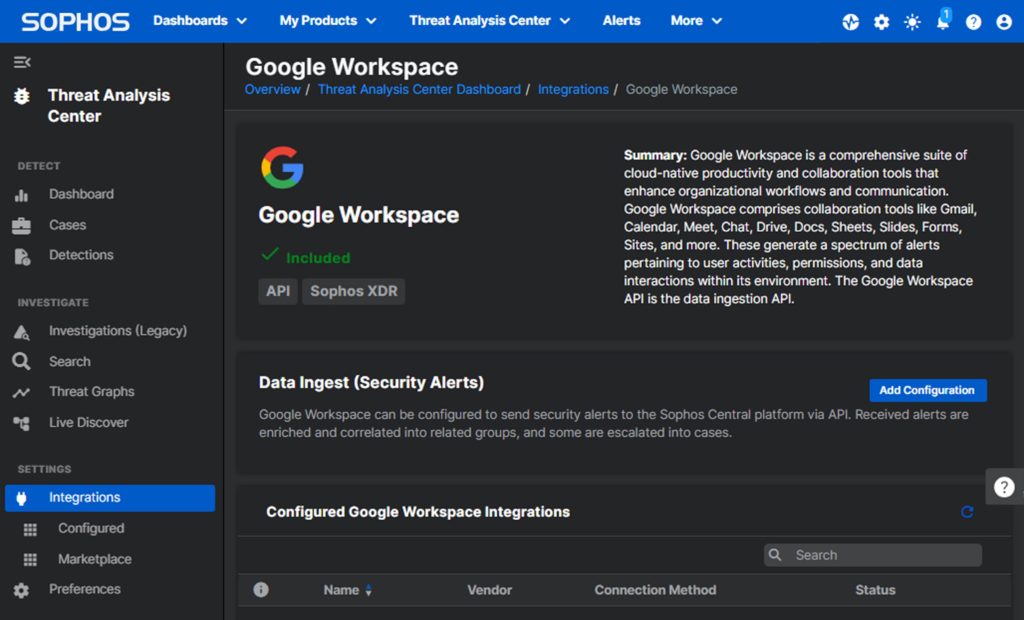
The Sophos MDR service provides 24/7 security monitoring, filters out redundant alerts, and investigates threats to your Google Workspace environment, like unauthorized Google Account access and malicious Gmail activity.
Organizations using the Sophos XDR for in-house investigation and response can also integrate Google Workspace telemetry to identify potentially malicious activity including suspicious logins, activity associated with suspended user accounts, and anomalous changes to administrator settings – combined with threat detections from other sources in a single unified view.
Available to Sophos MDR and Sophos XDR customers at no additional charge
Sophos includes a range of turnkey integrations with both Sophos and third-party technologies in Sophos MDR and Sophos XDR subscriptions. Integrations with productivity tools including Microsoft 365, and now Google Workspace, are available to all new and existing Sophos MDR and Sophos XDR customers at no additional charge.
Elevate your defenses with the new Google Workspace integration
To learn more and explore how Sophos MDR and Sophos XDR can help your organization better defend against active adversaries, including attacks that target your productivity tools, speak with a Sophos adviser or your Sophos partner.
Already a Sophos MDR or Sophos XDR customer? Activate the Google Workspace integration in your Sophos Central console today.
Source: Sophos
ZTNA, Sophos Central, DNS protection, and more.
The Network Security Product Team has several important Sophos Firewall related news items to share with you.
Sophos Firewall v20
As you know, we launched Sophos Firewall v20 late last year, with several exciting new enhancements. Many of you have already upgraded your firewalls, but for those that haven’t, now is the time!
You will see the update waiting for you in Sophos Central, or in the web admin console as soon as you log in. Make sure you update your firewalls soon, not just to take advantage of the many new features, but also to ensure you have the latest security, performance, and reliability fixes that are in every release.
Check out what’s new in this short video overview:
Sophos ZTNA is now on Sophos Firewall
That’s right! In case you didn’t know, Sophos Firewall v20 integrates a ZTNA gateway directly into the firewall, making ZTNA deployments easier than ever.
 It’s a simple decision to switch from remote access VPN to ZTNA. ZTNA provides better security, easier management, and a much smoother and more reliable end-user experience. And with a ZTNA gateway integrated into Sophos Firewall, customers don’t need to deploy anything extra on site to enable secure remote access to systems and applications hosted behind the firewall.
It’s a simple decision to switch from remote access VPN to ZTNA. ZTNA provides better security, easier management, and a much smoother and more reliable end-user experience. And with a ZTNA gateway integrated into Sophos Firewall, customers don’t need to deploy anything extra on site to enable secure remote access to systems and applications hosted behind the firewall.
To learn more about ZTNA and how it can help you secure your applications and remote access, check out Sophos.com/ZTNA. It’s easy to try for free.
Sophos Central management updates
The January update for Sophos Central firewall management is now live, which contains several new features and fixes:
SD-WAN enhancements allow “*” wildcard characters in any IP address for the remote end of route-based VPN tunnels. Ideal for use with remote sites that frequently or rapidly change dynamic IP addresses.
Configurable suppression of repetitive alerts changes alert priorities and sets limits on how frequently repetitive alerts should be raised. Use this to suppress normally noisy alerts, keeping them from cluttering your inbox and alert counts in Sophos Central.
Automatic rollback of firmware detection. SFOS v20 and up now supports automatic firmware rollback when it detects that an update was not completely successful. Sophos Central will now detect and alert on firmware rollback events, should they occur.
Plus: other cosmetic changes to match ATP feature naming changes in SFOS v20. Review the full release notes.
Sophos DNS protection early access
The Sophos DNS protection early access program (EAP) kicked off in December and has been one of our most popular early access programs ever, with over 3 billion queries served across several hundred customer sites world-wide.
If you haven’t already joined, now is a great time to get started using it as we’ve recently added new reporting, dashboarding, and safe search features. Review the full details and get started today!
New Sophos Firewall security posture assessment report
The team is pleased to announce that a new security posture assessment (SPA) report is being added to Sophos Central firewall reporting later this week.
 This customizable report provides a management-level overview of firewall protection activity that makes an excellent tool for showing the value and protection Sophos Firewall delivers. An all-new inventory report is also included that provides a snapshot of your firewall inventory, health status, and license details.
This customizable report provides a management-level overview of firewall protection activity that makes an excellent tool for showing the value and protection Sophos Firewall delivers. An all-new inventory report is also included that provides a snapshot of your firewall inventory, health status, and license details.
Source: Sophos
Feeling good about sending your business-critical files securely via managed file transfer (MFT)? You should. It’s a secure, streamlined way to get sensitive information from one place to another, with encryption embedded into the solution, automation features to help goofproof the process, and robust security applied to files both while they are in motion and at rest. But do you know what happens to those sensitive files after they’ve reached their intended recipients? Your singular file transfer solution may not be enough to secure your files post-send.
Your MFT solution protects your organization’s valuable data in transit, but that does not mean that the files are immune to security issues once they arrive at their destination. For example, the recipient may forward the file to an unauthorized user, opening the data up for possible malware.
You can further protect your organization’s data throughout its entire lifecycle by bundling your MFT solution with a zero-trust solution. Zero-trust is a verification model that helps to address concerns such as insider threats, malware, ransomware, and human error. And bundled security solutions are an effective way to drive processes to align with the ‘trust no one and verify everything’ stance at the heart of zero trust.
Bundling Security Solutions Can Help Minimize Post-Send File Worries
In today’s cybersecurity environment, a single solution may not be enough to achieve your organization’s security goals, especially if those goals include migrating towards a zero-trust architecture. Adopting a zero-trust position around file security should include layering or bundling security solutions like MFT, secure gateways, encryption, and secure collaboration. “Taking advantage of bundled solutions that integrate and bolster security around data and how it’s handled gives IT teams a tested security combination to help move an organization closer to a zero-trust stance,” said Chris Bailey, Senior Product Manager, SFT, Fortra.
A Zero-Trust Strategy Benefits from Bundled Solutions
At its most basic, zero-trust is a ‘never trust, always verify’ model, an updated version of what tech circles used to call the ‘trust but verify’ mode of operation. This zero-trust model assumes any device or communication can be subject to fallout from malicious and criminal intentions or even by users forwarding files to non-authorized recipients. Zero trust requires a continual approach to authentication and authorization of users and systems on an organization’s network to address threats.
There are three basic pillars to zero-trust:
- Always assume a breach is possible
- Trust no one
- Verify everything
Achieving zero trust is a process, and to repeat a cliché, it’s a journey not a race. According to Gartner just 10% of large enterprises will have a solid zero trust program in place by 2026. It’s a goal well-worth striving for to protect your most sensitive data from prying eyes. Organizations that are making progress towards a zero-trust stance are in good company. The Pentagon plans to implement a zero-trust architecture by 2027 across the enterprise. And there are government-wide goals around zero trust as well.
Progressing towards this zero-trust stance, whether at a government organization, retail, healthcare, or any other type of organization is more easily achieved with vetted and layered security. “A security solutions bundle can make exchanging data more secure and more controlled at a granular level with automatic file sharing, scanning of files for malware or viruses, and encryption to deliver persistent control over files no matter where they travel. And adopting solutions from a single provider that have been tested as integrated can streamline this process further,” added Bailey.
Layered or bundled security can work proactively to reduce the attack surface as well as support compliance for organizations needing to abide by NIST, PCI DSS, and HIPAA requirements. And zero trust is not only about protecting the organization’s perimeter, rather its policies provide access control in a cloud environment as well. Zero trust policies apply no matter if your organization’s data is primarily on-prem or resides in the cloud.
Security Solutions Integrate for Zero Trust File Transfers
The solutions that comprise Fortra’s Zero Trust File Transfer bundle not only help ensure files are protected in transit and at rest with secure file transfer, they also add content inspection to scan for malware or viruses, encryption, data loss prevention, and persistent control for secure collaboration. Sensitive, business-critical files stay protected from any unauthorized access or use, even after they land at their intended destination.
“This post-send control is so vital today, as more collaboration is being done outside an organization’s walls or perimeter. Once a file lands, without a secure collaboration tool in place, you could otherwise lose all control over who is accessing or using that data,” added Bailey. “This security combination gives organizations access to their data in real time throughout its entire life cycle, no matter where that data travels or is stored to help move the file transfer process into a zero-trust position.”
Source: Fortra
Microsoft Outlook users have various options at their disposal for archiving emails. The quickest of these is the archive button as it is built into Outlook’s menu bar and can be accessed without having to call the administrator.
Have you ever used the archive button? Have you ever clicked on it by mistake when trying to delete an email? Or have you made a conscious decision to use it? Some do find it useful, but we reckon it can lead you astray. Because you don’t need to be an expert in email archiving to know that the archive button doesn’t come close to meeting the requirements expected of a professional archiving product when it comes to processing emails.
Archiving Emails with the Outlook Archive Button – How It Works
So, what does the archive button do? Essentially, it lets you move an email from your inbox to an archive folder. But since this folder is also in Outlook, all you’re actually doing is changing the storage location for your emails. So, while Microsoft may call this option “archiving”, it doesn’t satisfy the criteria a professional email archiving solution should. By definition, an archive is the final storage place of documents at the end of a chain of prior usages; as such, it must be capable of retaining this material permanently, e.g. via special safeguards. Today, the EU GDPR and other such legal requirements mean that email archiving has become quite a complex matter in everyday corporate practice. At the same time, an archive’s job is to ensure that all its records – in this case, emails – remain available at all times.
The Downside of Using the Outlook Archive Button
If you want to archive your emails professionally or are obliged to do so for legal reasons, using the archive button does entail certain risks.
The archive button is not suitable for
- guarding against data loss, as it does not safeguard emails from manipulation or deletion;
- potentially reducing the volume of data in a mailbox, as the archive folder is located within the Outlook mailbox;
- ensuring that email data remain permanently available, as emails will no longer be accessible if Outlook fails.
The archive button is only suitable for keeping an inbox visually lean. When you use the archive button, you are moving old emails out of your field of vision into an archive folder. You can use Outlook’s search function to find old emails, including those that you have moved to the archive folder.
What Other Mail Archiving Options Does Microsoft Offer?
The primary objective of any professional email archiving solution is to ensure that email data remain retrievable and, thus, permanently available over time. To do this, the archiving solution stores copies of all emails in a central archive, thus guaranteeing the availability and security of data over many years.
So, although Microsoft does provide various applications in its Outlook, Exchange Server and Microsoft 365 products in connection with email “archiving”, they either do not – or only partially – fulfill the objectives of a professional email archiving solution.
- Archiving PST Files / AutoArchive (Outlook)
Users can move emails to PST files and store them locally on their own computer or in the cloud.
- Archive Mailbox without Exchange Online Archiving
The archive mailbox is a separate mailbox with its own storage to which emails can be moved. This archive mailbox must be set up by an administrator.
- Archive Mailbox with Exchange Online Archiving
With Exchange Online Archiving (EOA), users can move their emails to a separate archive mailbox to which administrators can apply their own archiving and retention policies.
Why You Should Use an Independent Email Archiving Solution
At first glance, it may seem beneficial to have email archiving functions and the email client on the same platform. Generally, however, the email archiving options available in Microsoft do not satisfy the requirements of a professional email archive.
PST files or the archive button offer no real protection against data loss when it comes to storing emails in a safe and secure environment. Likewise, the separate archive mailbox possible in M365 (when not using Exchange Online Archiving) does not fully meet the criteria of a professional email archiving solution. Only the archive mailbox that comes with Exchange Online Archiving (EOA) has the functions and features required for professional email archiving, such as retention policies, legal holds and eDiscovery options. But since Exchange Online Archiving is included only in the more expensive Business Premium and Enterprise M365 plans, this is not normally an option for small or medium-sized companies due to their financial constraints.
A professional, independent email archiving solution, on the other hand, offers a wide range of functions at a reasonable price and is, therefore, more suitable for SMEs.
Below are some of the key benefits of an independent email archiving solution.
Independence from Microsoft
Without an external email archive, users will not be able to access their emails if the Microsoft 365 service fails. Using an external email archive will ensure that a vendor lock-in is avoided and that the company’s emails remain accessible even if M365 fails.
Self-Service for the End User
Users not only have a fast and efficient archive search function at their disposal – they can also restore archived mails quickly and simply without having to call on the services of a system administrator.
Protection Against Data Loss and Manipulation
Emails, once in the archive, cannot be deleted or modified by the user. Only an administrator can define how long emails should be retained within the system. Journaling ensures seamless archiving.
Compliance with Privacy Laws
When used appropriately, certified email archiving solutions ensure that emails are processed in line with the pertinent data privacy laws. Especially since the EU’s DSGVO came into force, data privacy has become a key focus of public attention.
Reasonable Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
An independent email archiving solution offers a wide range of functions at a reasonable price. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), in particular, can benefit from this and do not have to resort to expensive enterprise solutions.
Takeaways – The Outlook Archive Button Cannot Archive Emails Professionally
The archive button delivers much less than its name suggests. In certain circumstances, it could save time by eliminating the need to manage numerous subfolders in an inbox; but it cannot satisfy the criteria expected of a professional email archiving solution. Our two free white papers explain in detail which email archiving options are available in Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Exchange Server, and which are the most suitable for your needs.
Source: MailStore
We are delighted to announce that Sophos has been named a Leader in the 2023 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP), marking our 14th consecutive recognition as a Leader in this category.
A Leader for the fourteenth consecutive time
This year’s report provides readers with a comprehensive evaluation of the industry’s most prevalent endpoint prevention, endpoint detection and response (EDR), extended detection and response (XDR), and managed detection and response (MDR) offerings.
Sophos has been recognized in the Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP) since its inaugural publication in 2007, and we believe our continued focus on a protection-first approach is a key factor contributing to our continued position as a Leader in this evaluation. While the threat landscape has evolved, Sophos has continued to keep organizations of all sizes ahead of even the most advanced attacks, with customers benefiting from recent industry-first innovations such as Adaptive Attack Protection, which dynamically enables heightened protection in response to the detection of an active adversary on endpoint devices.
Accelerating detection and response with extended third-party compatibility
We have significantly enhanced our XDR and MDR offerings in 2023, including additional integrations with an extensive range of third-party security tools, including identity, network, firewall, email, cloud, productivity, and endpoint security solutions.
Third-party integrations for Sophos XDR and MDR provide greater visibility of threats across all key attack surfaces and enable organizations to get a higher ROI from their existing technology investments. Security detections from Sophos and non-Sophos products are created, ingested, filtered, correlated, and prioritized – providing more value from third-party tools than solutions that only use telemetry to enrich existing endpoint detections.
Sophos has also extended MDR service coverage across the full suite of Microsoft security solutions. Over 500 Sophos security experts deliver 24/7 monitoring, investigation, and human-led response for organizations that have invested in the Microsoft security suite.
Gartner® Peer Insights™ Customers’ Choice
Our Gartner Magic Quadrant for EPP recognition follows Sophos being named a Gartner® Peer Insights™ Customers’ Choice for Endpoint Protection Platforms for the second consecutive year and Customers’ Choice for MDR in the first-ever report in this segment. Sophos was also one of only ten vendors recognized in the 2023 Gartner Market Guide for XDR. We believe these Gartner recognitions are a testament to the quality of the protection and service we provide to Sophos customers.
To find out why Sophos was named a Leader in the Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Endpoint Protection Platforms for the fourteenth consecutive time, read the full report at https://www.sophos.com/en-us/report/magic-quadrant-endpoint-protection-platforms.
Source: Sophos
Around 60% of human-operated ransomware attacks now involve malicious remote encryption. Read on to learn about this prevalent ransomware attack vector and Sophos’ industry-leading protection capabilities.
What is remote ransomware?
Remote ransomware, also known as malicious remote encryption, is when a compromised endpoint is used to encrypt data on other devices on the same network.
In human-led attacks, adversaries typically try to deploy ransomware directly to the machines they want to encrypt. If their initial attempt is blocked (for example, by security technologies on the target devices) they rarely give up, choosing instead to pivot to an alternative approach and try again, and again.
Once attackers succeed in compromising a machine they can leverage the organization’s domain architecture to encrypt data on managed domain-joined machines. All the malicious activity – ingress, payload execution, and encryption – occurs on the already-compromised machine, therefore bypassing modern security stacks. The only indication of compromise is the transmission of documents to and from other machines.
Eighty percent of remote encryption compromises originate from unmanaged devices on the network, although some start on under protected machines that lack the defenses needed to stop attackers getting onto the device.
Why is remote ransomware so prevalent?
A key factor driving the widespread use of this approach is its scalability: A single unmanaged or under-protected endpoint can expose an organization’s entire estate to malicious remote encryption, even if all the other devices are running a next-gen endpoint security solution.
To make matters worse, adversaries are not limited in their choice of ransomware variant for these attacks. A wide range of well-known ransomware families support remote malicious encryption, including Akira, BitPaymer, BlackCat, BlackMatter, Conti, Crytox, DarkSide, Dharma, LockBit, MedusaLocker, Phobos, Royal, Ryuk, and WannaCry.
Furthermore, most endpoint security products are ineffective in this scenario because they focus on detecting malicious ransomware files and processes on the protected endpoint. However, with remote encryption attacks, the processes run on the compromised machine, leaving the endpoint protection blind to the malicious activity.
Fortunately, Sophos Endpoint includes robust protection against malicious remote encryption, powered by our industry-leading CryptoGuard protection.
Sophos CryptoGuard: Industry-leading, universal ransomware protection
Sophos Endpoint contains multiple layers of protection that defend organizations from ransomware, including CryptoGuard, our unique anti-ransomware technology that is included in all Sophos Endpoint subscriptions.
Unlike other endpoint security solutions that solely look for malicious files and processes, CryptoGuard analyzes data files for signs of malicious encryption irrespective of where the processes are running. This approach makes it highly effective at stopping all forms of ransomware, including malicious remote encryption. If it detects malicious encryption, CryptoGuard automatically blocks the activity and rolls back files to their unencrypted states.
CryptoGuard actively examines the content of all documents as files are read and written, using mathematical analysis to determine whether they have become encrypted. This universal approach is unique in the industry and enables Sophos Endpoint to stop ransomware attacks that other solutions miss, including remote attacks and never-before-seen ransomware variants.
Detects malicious encryption by analyzing file content
Unlike other solutions that look at ransomware from an anti-malware perspective by focusing on detecting malicious code, CryptoGuard looks for mass rapid encryption of files by analyzing content using mathematical algorithms.
Blocks both local and remote ransomware attacks
Because CryptoGuard focuses on the content of files, it can detect ransomware encryption attempts even when the malicious process is not running on the victim’s device.
Automatically rolls back malicious encryption
CryptoGuard creates temporary backups of modified files and automatically rolls back changes when it detects mass encryption. Sophos uses a proprietary approach, unlike other solutions that use Windows Volume Shadow Copy, which adversaries are known to circumvent. There are no limits to the size and type of file that can be recovered, minimizing the impact on business productivity.
Automatically blocks remote devices
In a remote ransomware attack, CryptoGuard automatically blocks the IP address of the remote device attempting to encrypt files on the victim’s machine.
Protects the master boot record (MBR)
CryptoGuard also protects the device from ransomware that encrypts the master boot record (preventing startup) and from attacks that wipe the hard disk.
CryptoGuard is one of the unique capabilities in Sophos Endpoint and is included with all Sophos Intercept X Advanced, Sophos XDR, and Sophos MDR subscriptions. What’s more, the capability is enabled automatically by default, ensuring organizations enjoy full protection from both local and remote ransomware attacks straight away – no fine tuning or configuration required.
Discover unprotected devices
A single unprotected endpoint can leave your organization vulnerable to a remote encryption attack. Deploying Sophos Endpoint provides robust universal ransomware protection from malicious encryption. But how can you identify if you have unprotected devices on your network in the first place?
This is where Sophos Network Detection and Response (NDR) can help. Sophos NDR monitors network traffic for suspicious flows and, in doing so, identifies unprotected devices and rogue assets in the environment.
For the strongest protection against remote ransomware attacks, install Sophos Endpoint on all machines in the environment and deploy Sophos NDR to discover unprotected devices on your network.
Elevate your protection against remote ransomware today
Malicious remote encryption is a popular ransomware technique that most leading endpoint security solutions struggle to stop. If you’re not using Sophos Endpoint, there’s a high chance you’re exposed.
To learn more about Sophos Endpoint and how it can help your organization better defend against today’s advanced attacks, including remote ransomware, speak with a Sophos adviser or your Sophos partner today. You can also take it for a test drive in your own environment with a no-obligation 30-day free trial.
Source: Sophos