News
You can share your WiFi password safely by using a strong password, creating a guest network, enabling your router’s encryption and regularly updating your router. Sharing your WiFi password safely is important because someone with bad intentions could use it to hack into your network, steal your personal information or infect your devices with malware.
Keep reading to learn about the consequences of insecurely sharing your WiFi password, ways to securely share it and best practices for sharing it with others.
The risks of insecurely sharing your WiFi password
When guests visit your house for the first time, one of the first things they might ask for is your WiFi password. Here are several insecure ways you could share your WiFi password with friends, family or other guests:
- Leaving your WiFi password on a sticky note
- Sending it via unencrypted methods, such as emails or text messages
- Sharing it in a group chat on a messaging app
- Saying it during a phone call
- Showing guests the default password on your router
Imagine inviting a few friends over to watch a movie, and they ask for your WiFi password. You may have never changed your WiFi network’s default password, or you might be using a very weak WiFi password because it’s easier for people to type. Regardless of how secure your WiFi password is, sharing it with your friends through a group chat, individual text messages or email can leave your router vulnerable to hacking. Since emails and text messages are unencrypted, a cybercriminal could intercept your messages, revealing your WiFi password.
With your password, a cybercriminal could access your WiFi network, launch a malware infection and potentially infect other Internet of Things (IoT) devices connected to your network. By sharing your WiFi password via text with one of your friends, you risk a cybercriminal gaining unauthorized access to your WiFi network and potentially spying on you through any devices with cameras that are also connected to it.
How to securely share your WiFi password
Now that you know several insecure ways of sharing your WiFi password, let’s dive into how you can securely share it between Apple devices, Android devices and other devices.
Sharing your WiFi password between Apple devices
Before sharing your WiFi password with someone using an Apple device, make sure that both of your devices’ software is updated with the latest iOS version, WiFi and Bluetooth are turned on and you are signed in to your iCloud account with your Apple ID. Once you’re ready to share your WiFi password, unlock your device and connect to your WiFi network. A pop-up will appear at the bottom of your screen asking if you want to share your WiFi password with the other person. Tap Share Password, and the screen will indicate that the sharing was successful.
Sharing your WiFi password between Android devices
One way to share your WiFi password from one Android device to another is by turning your password into a scannable QR code. On Pixel and other Android phones, visit Settings, tap Network & Internet, then select Wi-Fi. Tap the settings icon next to your network, then tap Share. A screen will appear with a QR code displaying the name of your WiFi network and your WiFi password.
Not all Android devices follow the same steps, but the process is relatively similar. For example, if you use a Samsung phone, you will need to visit Settings, tap Connections, then select Wi-Fi. Tap the settings icon, then select QR Code in the bottom-left corner of your screen. On Samsung devices, you will not see your WiFi password written out.
How to safely share your WiFi password between any device
For a safe way to share your WiFi password between devices, consider using a password manager like Keeper®. Although you may think password managers only store passwords, you can use Keeper Password Manager to send passwords safely through its One-Time Share feature without jeopardizing your privacy. If your WiFi password is saved as a record in your digital vault, you can share that record for a limited time using the One-Time Share feature, even if the recipient doesn’t have a Keeper account. One-Time Share encrypts your WiFi password and other login credentials with zero-knowledge security, reducing the risk of someone intercepting your WiFi password while it’s being shared.
Best practices to follow when sharing your WiFi password
Whenever you share your WiFi password with someone, follow best practices to do so safely and minimize your chances of allowing a hacker access to your network or connected devices.
Use a strong, unique WiFi password
Change your default WiFi router’s password, if you haven’t already, to a strong, unique password that you don’t use for any other account. Even if you have changed the default password but it is weak or reused, update it with a randomly generated, secure password. A strong password for your WiFi should consist of at least 16 characters, with a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols. An easy way to create a strong, unique password for your WiFi network is by using a password generator, which produces random passwords based on customizable criteria.
Create a guest network
Instead of having guests use your primary WiFi network, create a guest WiFi network with a limited connection that won’t affect your devices. Your guest WiFi network should have a different password than your primary network, but it should be just as strong to keep your guests’ devices secure. Creating a guest network is a smart practice because you never know if any of your guests’ devices might be infected with malware. If an infected device connects to your primary WiFi network, malware could spread to other devices connected to your network.
Enable your router’s encryption
Make sure your WiFi router is encrypted to prevent cybercriminals from stealing transferable information by hacking into your network. Enable your router’s encryption with WPA3, which is the newest and best type of encryption protocol for WiFi. To enable encryption on your router, update it through your Internet Service Provider (ISP) settings.
Keep your router up to date
It’s important to keep your WiFi router up to date with the latest software because software updates equip your router with the most recent security patches, bug fixes and improved features. Keeping your WiFi router updated ensures it remains secure and stable, protecting your network and devices from cyber threats.
Securely share your WiFi password using Keeper
Instead of jeopardizing your network’s privacy by sending your WiFi password via email or SMS, securely share it using Keeper’s One-Time Share feature. With Keeper Password Manager, you can create a strong WiFi password, update it to be more unique, store it in a secure vault and share it with anyone you choose for a limited time to protect its safety.
Start your free 30-day trial of Keeper Password Manager today to protect your WiFi password and securely share your other login credentials.
Source: Keeper Security
For over two decades, Autotask has been a trusted go-to solution for IT professionals worldwide. As technology has evolved, so has Autotask — from client-server beginnings to a cloud-based powerhouse. Now, with the release of the 2025.1 update, we’re excited to usher in the next chapter: a reimagined user interface (UI) designed to modernize, simplify and empower.
Whether you’re a long-time Autotask power user or new to the platform, this update delivers a refreshed experience that adapts to your workflow, reduces friction and introduces a consistent design philosophy across the Kaseya IT Complete platform. Let’s take a closer look at the journey and what you can expect.
The philosophy behind the UI refresh
“Revamping the Autotask UI has been one of our biggest initiatives yet,” says Kevin Sequeira, General Manager of Kaseya’s PSA Suite. “We’ve invested heavily to make it not just visually appealing, but truly intuitive and efficient, so our customers can work smarter and get more done with less hassle.”
At the heart of the new UI refresh, our commitment is to create a more intuitive, streamlined and empowering user experience. You will see it kickstart starting in the 2025.1 release. This UI update is a thoughtful reimagining of how Autotask serves you in your day-to-day tasks. By focusing on user feedback and real-world workflows, we’ve developed a philosophy that prioritizes consistency, accessibility and ease of use.
Unified consistency across IT complete
The new Autotask UI is built on the Kaseya Design System (KDS), which ensures consistency across the IT Complete suite. Whether you’re switching between Autotask, IT Glue or other Kaseya tools, the familiar layout and functionality make the transition seamless. Think of it as learning one tool and being able to navigate them all effortlessly.
User-centric modernization
Our mission with this refresh is to make Autotask align seamlessly with your workflow. By minimizing clicks and maintaining context, features like collapsible navigation and inline editing simplify tasks, boost efficiency and improve usability. This update ensures you can stay focused on what truly matters, without unnecessary distractions.
Accessibility for all
We’ve enhanced keyboard navigation, improved mobile usability and made strides in screen reader support to ensure that Autotask is accessible to everyone, regardless of environment or ability. From the desk to on-the-go scenarios, we’re making it easier to stay productive.
Empowerment through simplicity
Autotask’s new UI strikes the perfect balance between simplicity and capability. Designed to help you get started quickly, it eliminates the overwhelm often associated with advanced tools. As you grow more comfortable, the intuitive interface allows you to self-discover Autotask’s powerful features, unlocking its full potential at your own pace.
A look back: Autotask’s evolution
Autotask has undergone three major UI overhauls in its history, each building upon the last to meet the needs of modern IT professionals.
From its client-server roots to its web-based iteration and cloud-based transition, every evolution has brought new features and opportunities.

The 2025.1 release marks the beginning of Autotask’s new UI, laying the foundation for even more transformative updates in the coming months and years.
What’s new in the 2025.1 release?
The phased rollout of the 2025.1 release begins January 22, 2025, and will be complete by February 6, 2025.
Here’s what’s included:
Enhanced navigation
Navigating Autotask has never been smoother. With thoughtful updates to both the top and left navigation menus, users can expect a cleaner, more intuitive experience that minimizes clicks and maximizes productivity.
- Left navigation: A collapsible left navigation menu replaces the previous top hover-navigation, offering more screen space and flexibility.
- Top navigation reordering: Icons have been introduced for a cleaner and more intuitive interface.
- Search bar improvements: Now located on the right-hand side, with plans for a global search feature later this year.
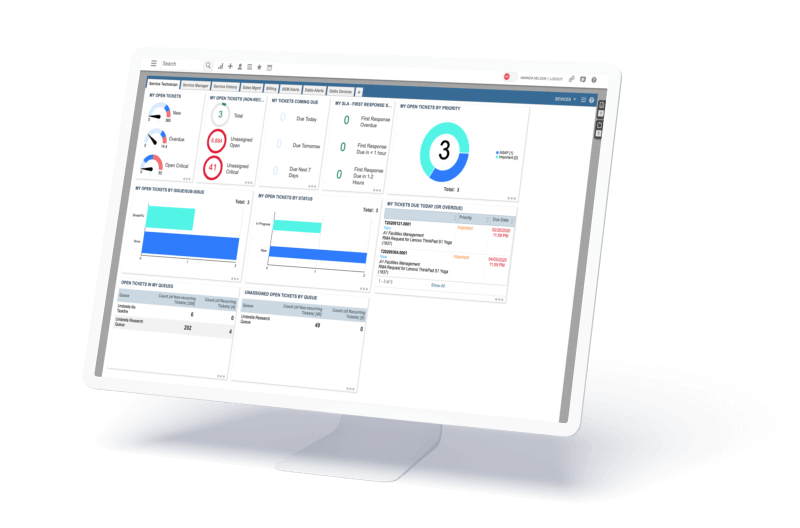
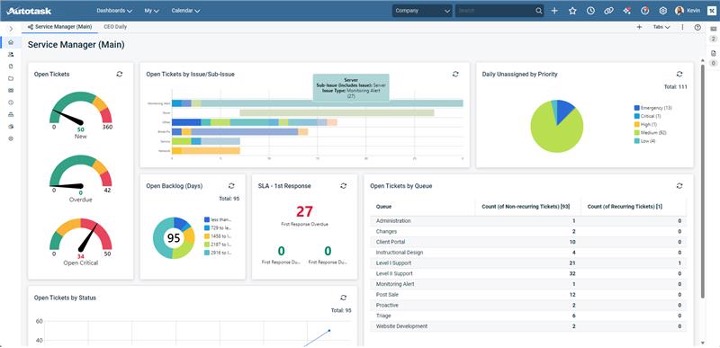
Refreshed dashboards
Dashboards now feature a modern look and improved layout capabilities. You can resize and rearrange widgets directly on the screen for a personalized experience.
Streamlined Worklist panel
The updated Worklist panel makes it easier than ever to access pinned tickets and tasks, keeping your priorities front and center.
What’s next?
The 2025.1 release is just the beginning. Future updates will focus on key areas in Autotask such as contracts (including umbrella contracts), devices, tickets, projects and scheduling with core changes to the user experience:
- Refreshed grids and filters
- In-line editing
- At-a-glance preview panels for related items
- Bulk updates
We’re taking a progressive approach to the rollout, actively gathering feedback from users to refine and improve. If something feels new or unfamiliar, know that we’re here to listen and evolve.
Why change is worth it
Change can be uncomfortable, especially when it’s with a tool as central to your workflow as Autotask. However, history shows that every Autotask refresh has ultimately delivered greater value and usability. This update is no different. It’s about resetting how Autotask serves you in your day-to-day work, removing unnecessary steps and creating a platform that grows with your needs.
Share your feedback
We’re committed to making Autotask the best it can be. Help shape the future by sharing your thoughts through our UX Research Interest Form.
Together, we’re building the next generation of Autotask, one click at a time.
Source: Datto
In 2024, we introduced Generative AI features in the Sophos Extended Detection and Response (XDR) platform, empowering security analysts to operate confidently and make smart decisions fast.
Today, we are excited to extend these capabilities with the launch of the Sophos AI Assistant.
Crafted by experts, created for everyone
Designed and developed by Sophos experts for your in-house team, the Sophos AI Assistant guides security professionals of all skill levels through each stage of a case investigation, maximizing efficiency to identify and neutralize threats fast.
Feature video: Introducing the Sophos AI Assistant
The Sophos AI Assistant makes it easy for all users — from IT generalists to Tier 3 SOC analysts — to get the information they need to progress threat investigations and rapidly neutralize threats.
- Conduct an extensive range of SecOps tasks: Identify impacted entities, check URL reputation, analyze suspicious and complex commands, enrich data with the latest threat intelligence, and more.
- Accelerate investigations with accessible insights: The AI Assistant provides clear explanations and summarized information to help you understand context — and recommends next steps.
- Get the data you need quickly, without complex SQL: Ask your own questions using everyday language or use pre-defined prompts provided by Sophos’ threat detection and response experts.
- Create detailed case reports: Communicate with stakeholders with clear, focused reports that summarize investigations, highlight issues, and outline protective measures.
SecOps expertise — from our team to yours
Our people are at the heart of our AI-powered cybersecurity solutions. The Sophos AI Assistant isn’t just another AI tool — it’s expertise from the team behind the world’s leading Managed Detection and Response service, distilled into an intelligent agent.
- Designed in partnership with Sophos’ frontline security analysts, enabling your in-house team to benefit from real-world workflows and the experience of Sophos MDR experts.
- Developed by the Sophos AI team who apply their extensive AI expertise to design, build, and maintain over 50 AI models specific to cybersecurity. Our robust development processes — following secure-by-design principles — allow you to use Sophos AI with confidence.
- Continually updated based on the evolving threat landscape, ensuring you have access to the latest investigation techniques and current threat intelligence from Sophos X-Ops, our cross-functional cybersecurity task force.
Demo: See the new Sophos AI Assistant in action in this end-to-end real-world scenario
Outcome-focused AI
We’ve been elevating cybersecurity with AI since 2017, with deep learning and GenAI capabilities embedded across Sophos products and services and delivered through the largest AI-native platform in the industry. We know how to deliver real-world impact. While other vendors focus on the AI technology itself, we focus on the benefits and security outcomes it can deliver.
Our robust, battle-proven AI-powered solutions make a material difference by neutralizing threats faster and empowering analysts to make smart decisions. In addition to the new Sophos AI Assistant, GenAI capabilities in Sophos XDR enable your security team to neutralize adversaries faster, increasing both analyst and business confidence:
- AI Case Summary provides an easy-to-understand overview of detections, helping analysts make smart decisions fast.
- AI Command Analysis delivers insights into attacker behavior by examining commands that create detections.
- AI Search uses natural language search to accelerate day-to-day tasks and lower the technology barrier to security operations.
Sophos’ GenAI features are included with Sophos XDR subscriptions and are available on an opt-in basis, giving you full control over their use.
Elevate your cybersecurity with GenAI today
To explore how GenAI capabilities in Sophos XDR can help your organization better defend against active adversaries, speak with a Sophos adviser or your Sophos partner.
Already using Sophos XDR? Learn more about the GenAI features available to you, and how to activate them, on the Sophos Community.
Source: Sophos
Making sure your password is strong yet memorable can be challenging and stressful. However, following best practices – like using passphrases, incorporating acronyms and relying on a password manager – will ensure your passwords are strong and safe. A strong password should contain at least 16 characters, with a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols. Never use common phrases or personal information in your passwords, as these can be easily guessed by cybercriminals. Also, do not reuse the same passwords across multiple accounts because they can become compromised due to poor password practices.
Continue reading to learn the best practices for creating strong and memorable passwords.
1. Use passphrases
Passphrases are made up of multiple unrelated words, making them longer than typical passwords. The longer your password is, the harder it is for a cybercriminal to crack. Since passphrases are random words rather than random letters, numbers and symbols, they are easier to remember and provide more security benefits than a normal password due to their length and complexity.
You can create a strong passphrase by including a combination of words that have uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols, but make sure the words you use are completely random. For example, if you enjoy going to the beach and create a passphrase using words related to the beach (ocean, dolphin, sunshine, etc.), those words are not completely random, making the passphrase unsafe. A strong passphrase could look like this: Mixture-Pie-Met-State-Planning6. None of these words have anything in common, and this passphrase also includes a variety of characters and symbols separating the words.
2. Incorporate acronyms
Remember when you needed to learn a complex subject or study for an exam? You probably used an acronym to help you remember a concept. Acronyms are still useful when it comes to creating strong and memorable passwords. To incorporate acronyms into your password creation process, think of a sentence or phrase that holds meaning for you. Take the first letter of each word and turn it into a password, but don’t forget to still include numbers and symbols.
Let’s create a strong password using acronyms together. Imagine the sentence “I like going to the diner to eat strawberry chocolate cheesecake with my best friend Amy” is very meaningful to you. As an acronym, that sentence would be “IlgttdtesccwmbfA,” but you still need to incorporate a mixture of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols to make it stronger; more on that below.
3. Replace letters for numbers and symbols
Following our example above, we still need to swap out letters for numbers or symbols to make our password strong. After making these changes, your password has gone from the acronym “IlgttdtesccwmbfA” to something like “I1g2tD2eSccWmbfA!.” To anyone who didn’t know your original sentence or phrase, this password would be challenging to guess since it contains random letters, numbers and symbols.
You can also replace letters with numbers and symbols in a passphrase. For example, if you have the words “cheese,” “sofa,” “motorcycle” and “sapling,” you can incorporate numbers and symbols to turn these random words into a strong passphrase. The outcome of replacing some letters with numbers and symbols could look like this: Ch3e5e_s0fA!Mot0rcYc1E-5ap1iNg. Because this password is long, contains a variety of characters and is completely random, it is a very strong passphrase.
4. Avoid common dictionary words and related phrases
Make sure to avoid using common dictionary words and phrases in your passwords. You may be thinking, “Doesn’t the dictionary have the kinds of words I’d use in a password? How am I supposed to avoid using common words?” Your password can still incorporate commonly used words; however, they should include a variety of characters or have letters replaced by numbers and symbols to make them more secure. Make sure your password does not contain the word “password” or the phrase “qwerty,” since cybercriminals expect people with poor password practices to use these for convenience. Common dictionary phrases might also include “iloveyou,” “goodmorning” or other popular sayings that could be cracked in a dictionary attack.
Dictionary attacks occur when a cybercriminal cracks your login credentials by guessing familiar phrases or words found in dictionaries. Even if you think adding “123456” to the end of your password makes it unique and more secure, it does not, because cybercriminals know this is a popular pattern. A good way to avoid using common dictionary words or phrases is to use a password or passphrase generator, which provides random combinations of characters and words, making it much harder for cybercriminals to crack your credentials.
5. Start using a password manager
In addition to using a password or passphrase generator, you should start using a password manager, which not only creates strong passwords but also stores them in a safe place. Keeper Password Manager offers a built-in passphrase generator, allowing you to replace any weak or reused passwords with strong, random passphrases at the click of a button. Keeper Password Manager can also automatically fill in your login credentials using KeeperFill®, which enters the username and password from your digital vault into websites by recognizing which website or account you need the login credentials for. To access your password manager, all you need to remember is your master password, which is a single password or passphrase that unlocks your digital vault.
How Keeper® helps you create strong passwords
By following these best practices for creating strong and memorable passwords, you will protect your online accounts and private information from potential cyber threats. Using Keeper Password Manager helps you create and store strong passwords and passphrases in a secure digital vault, making it a helpful tool for maintaining password security.
Start your free 30-day trial today to explore the convenient and safe features that Keeper Password Manager has to offer.
Source: Keeper Security
We’re excited to announce that Sophos has officially acquired Secureworks.
Please watch the video from Sophos CEO Joe Levy to hear why we’ve brought these two industry pioneers together and how we intend to transform cybersecurity for small, midmarket and enterprise organizations.
While today is our first day as a combined company, we already have a full and clear roadmap for the way ahead together. By integrating the combined expertise and technologies of Sophos and Secureworks, we will accelerate our mission to deliver cybersecurity products and services that solve the most critical problems for organizations of all sizes amid persistent and constantly changing cyberattacks.
To share just one example, we will combine the MDR/XDR and other key capabilities of both organizations into a single, unified security operations platform that enables us to deliver unparalleled cyber defenses for today’s diverse IT environments, including hundreds of built-in integrations. This advanced platform will further enhance visibility, detection and response for mitigating cyberattacks, setting a new standard for security operations.
Extending the threat intelligence that powers our defenses
Cyber threats never sleep. With the acquisition, the Secureworks’ Counter Threat Unit (CTU), renowned for intelligence about advanced persistent threats (APT) and state sponsored attackers, will join the Sophos X-Ops advanced threat response joint task force. This expanded unit will deliver unrivalled and diverse threat intelligence, further extending our customers’ defenses through expert insights into today’s complex threat landscape.
Customers remain fully protected at all times
We deeply value the trust that customers have placed in Sophos and Secureworks and we are unwavering in our commitment to continue to defend them against today’s advanced threats while maintaining the high levels of service they already value. In addition to continuing to deliver our current set of services and technologies to Sophos and Secureworks customers, our customer experience teams will ensure seamless, continued support during the integration period. Please reach out to your Sophos representative with any questions.
Source: Sophos
While AI brings many advantages, like all technological capabilities, it also introduces a number of risks. The survey revealed varying levels of awareness of these potential pitfalls.
AI risk awareness
Defense risk: Poor quality and poorly implemented AI
With improved protection from cyber threats jointly at the top of the list of desired benefits from GenAI, it’s clear that reducing cybersecurity risk is a strong factor behind the adoption of AI-powered defense solutions.
However, poor quality and poorly implemented AI models can inadvertently introduce considerable cybersecurity risk of their own, and the adage “garbage in, garbage out” is particularly relevant to AI. Building effective AI models for cybersecurity requires extensive understanding of both threats and AI.
Organizations are largely alert to the risk of poorly developed and deployed AI in cybersecurity solutions. The vast majority (89%) of IT/cybersecurity professionals surveyed say they are concerned about the potential for flaws in cybersecurity tools’ generative AI capabilities to harm their organization, with 43% saying they are extremely concerned and 46% somewhat concerned.

It is therefore unsurprising that 99% (with rounding) of organizations say that when evaluating the GenAI capabilities in cybersecurity solutions, they assess the caliber of the cybersecurity processes and controls used in the development of the GenAI: 73% say they fully assess the caliber of the cybersecurity processes and controls and 27% say they partially assess the caliber of the cybersecurity processes and controls.
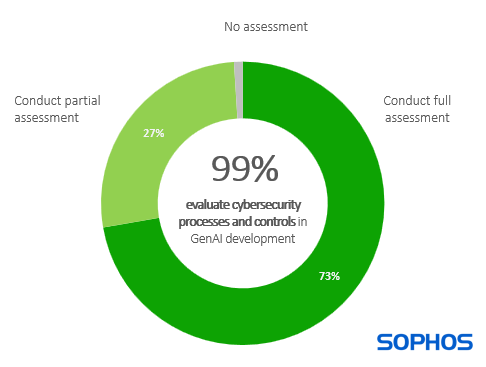
While the high percentage that report conducting a full assessment may initially appear encouraging, in reality it suggests that many organizations have a major blind spot in this area.
Assessing the processes and controls used to develop GenAI capabilities requires transparency from the vendor and a reasonable degree of AI knowledge by the assessor. Unfortunately, both are in short supply. Solution providers rarely make their full GenAI development roll-out processes easily available, and IT teams often have limited insights into AI development best practices. For many organizations, this finding suggests that they “don’t know what they don’t know”.
Financial risk: Poor return on investment
As previously seen, improved return on cybersecurity spend (ROI) also tops the list of benefits organizations are looking to achieve through GenAI.
High caliber GenAI capabilities in cybersecurity solutions are expensive to develop and maintain. IT and cybersecurity leaders across businesses of all sizes are alert to the consequences of this development expenditure, with 80% saying that they think GenAI will significantly increase the cost of their cybersecurity products.
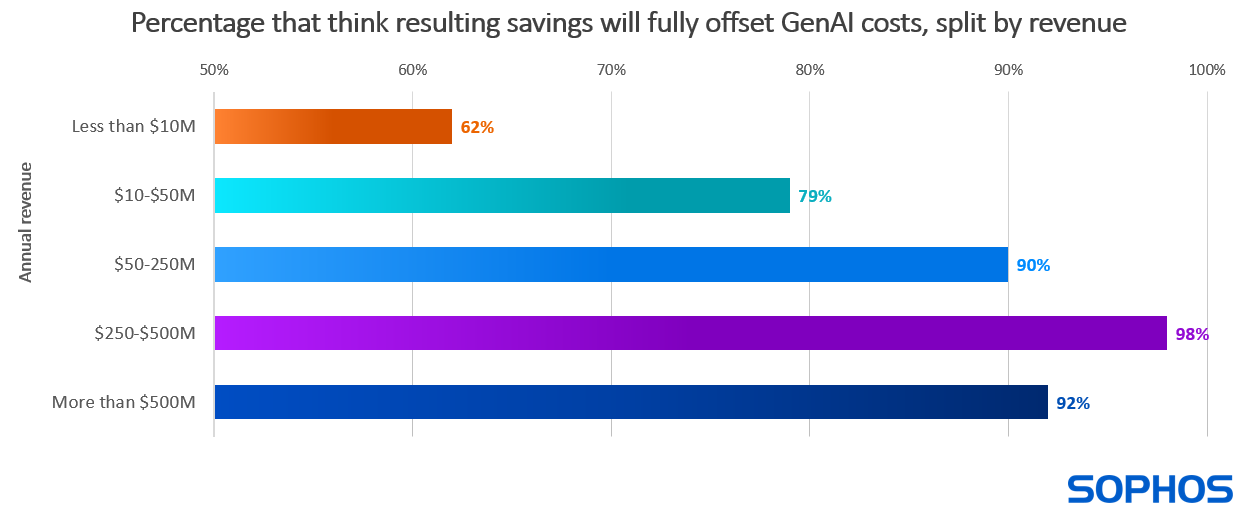
Despite these expectations of price increases, most organizations see GenAI as a path to lowering their overall cybersecurity expenditure, with 87% of respondents saying they are confident that the costs of GenAI in cybersecurity tools will be fully offset by the savings it delivers.
Diving deeper, we see that confidence in gaining positive return on investment increases with annual revenue, with the largest organizations ($500M+) 48% more likely to agree or strongly agree that the costs of generative AI in cybersecurity tools will be fully offset by the savings it delivers than the smallest (less than $10M).
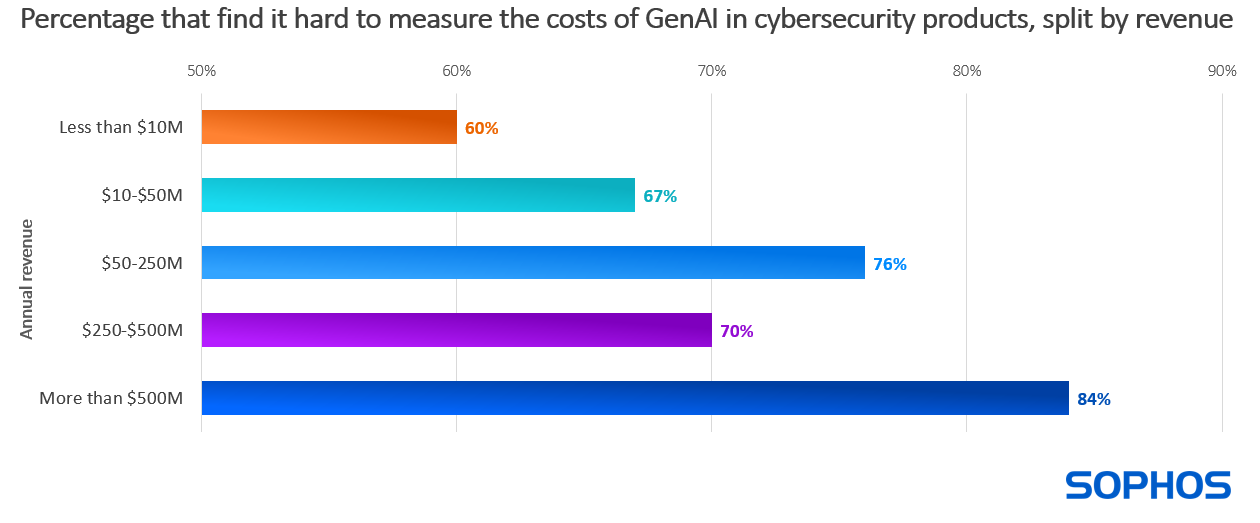
At the same time, organizations recognize that quantifying these costs is a challenge. GenAI expenses are typically built into the overall price of cybersecurity products and services, making it hard to identify how much organizations are spending on GenAI for cybersecurity. Reflecting this lack of visibility, 75% agree that these costs are hard to measure (39% strongly agree, 36% somewhat agree).
Broadly speaking, challenges in quantifying the costs also increase with revenue: organizations with $500M+ annual revenue are 40% more likely to find the costs difficult to quantify than those with less than $10M in revenue. This variation is likely due in part to the propensity for larger organizations to have more complex and extensive IT and cybersecurity infrastructures.
Without effective reporting, organizations risk not seeing the desired return on their investments in AI for cybersecurity or, worse, directing investments into AI that could have been more effectively spent elsewhere.
Operational risk: Over-reliance on AI
The pervasive nature of AI makes it easy to default too readily to AI, assume it is always correct, and take for granted that AI can do certain tasks better than people. Fortunately, most organizations are aware of and concerned about the cybersecurity consequences of over-reliance on AI:
- 84% are concerned about resulting pressure to reduce cybersecurity professional headcount (42% extremely concerned, 41% somewhat concerned)
- 87% are concerned about a resulting lack of cybersecurity accountability (37% extremely concerned, 50% somewhat concerned)
These concerns are broadly felt, with consistently high percentages reported by respondents across all size segments and industry sectors.
Recommendations
While AI brings risks, with a thoughtful approach, organizations can navigate them and safely, securely take advantage of AI to enhance their cyber defenses and overall business outcomes.
The recommendations provide a starting point to help organizations mitigate the risks explored in this report.
Ask vendors how they develop their AI capabilities
- Training data. What is the quality, quantity, and source of data on which the models are trained? Better inputs lead to better outputs.
- Development team. Find out about the people behind the models. What level of AI expertise do they have? How well do they know threats, adversary behaviors, and security operations?
- Product engineering and rollout process. What steps does the vendor go through when developing and deploying AI capabilities in their solutions? What checks and controls are in place?
Apply business rigor to AI investment decisions
- Set goals. Be clear, specific, and granular about the outcomes you want AI to deliver.
- Quantify benefits. Understand how much of a difference AI investments will make.
- Prioritize investments. AI can help in many ways; some will have a greater impact than others. Identify the important metrics for your organization – financial savings, staff attrition impact, exposure reduction, etc. – and compare how the different options rank.
- Measure impact. Be sure to see how actual performance relates to initial expectations. Use the insights to make any adjustments that are needed.
View AI through a human-first lens
- Maintain perspective. AI is just one item in the cyber defense toolkit. Use it, but make clear that cybersecurity accountability is ultimately a human responsibility.
- Don’t replace, accelerate. Focus on how AI can support your staff by taking care of many low-level, repetitive security operations tasks and providing guided insights.
About the survey
Sophos commissioned independent research specialist Vanson Bourne to survey 400 IT security decision makers in organizations with between 50 and 3,000 employees during November 2024. All respondents worked in the private or charity/not-for-profit sector and currently use endpoint security solutions from 19 separate vendors and 14 MDR providers.
Sophos’ AI-powered cyber defenses
Sophos has been pushing the boundaries of AI-driven cybersecurity for nearly a decade. AI technologies and human cybersecurity expertise work together to stop the broadest range of threats, wherever they run. AI capabilities are embedded across Sophos products and services and delivered through the largest AI-native platform in the industry. To learn more about Sophos’ AI-powered cyber defenses visit www.sophos.com/ai.
Source: Sophos
AI is firmly embedded in cybersecurity. Attend any cybersecurity conference, event, or trade show and AI is invariably the single biggest capability focus. Cybersecurity providers from across the spectrum make a point of highlighting that their products and services include AI. Ultimately, the cybersecurity industry is sending a clear message that AI is an integral part of any effective cyber defense.
With this level of AI universality, it’s easy to assume that AI is always the answer, and that it always delivers better cybersecurity outcomes. The reality, of course, is not so clear cut.
This report explores the use of AI in cybersecurity, with particular focus on generative AI. It provides insights into AI adoption, desired benefits, and levels of risk awareness based on findings from a vendor-agnostic survey of 400 IT and cybersecurity leaders working in small and mid-sized organizations (50-3,000 employees). It also reveals a major blind spot when it comes to the use of AI in cyber defenses.
The survey findings offer a real-world benchmark for organizations reviewing their own cyber defense strategies. They also provide a timely reminder of the risks associated with AI to help organizations take advantage of AI safely and securely to enhance their cybersecurity posture.
AI terminology
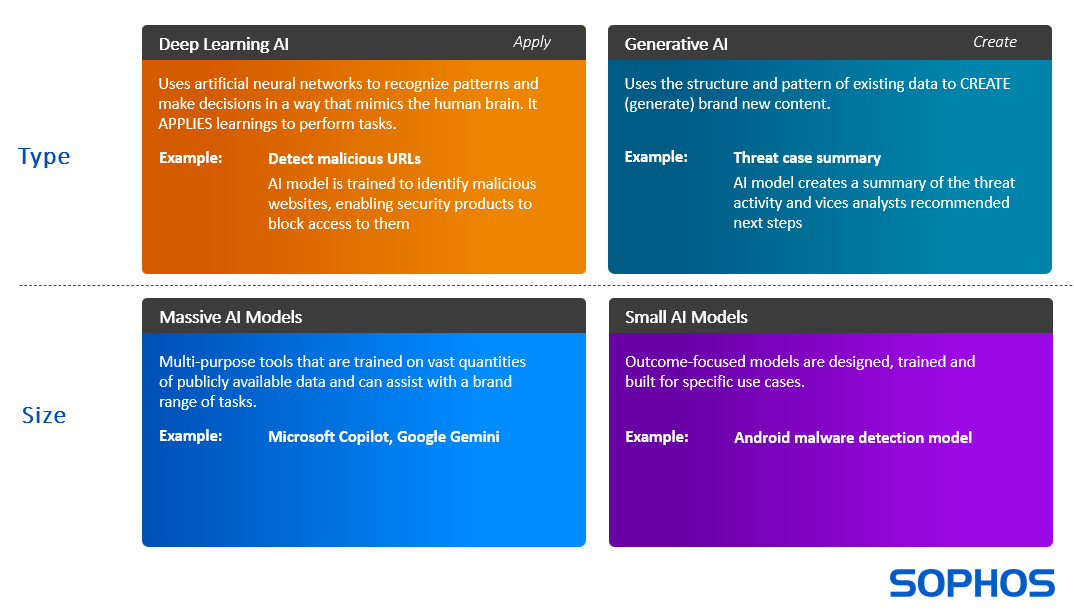
AI is a short acronym that covers a range of capabilities that can support and accelerate cybersecurity in many ways. Two common AI approaches used in cybersecurity are deep learning models and generative AI.
- Deep learning (DL) models APPLY learnings to perform tasks. For example, appropriately trained DL models can identify if a file is malicious or benign in a fraction of a second without ever having seen that file before.
- Generative AI (GenAI) models assimilate inputs and use them to CREATE (generate) new content. For example, to accelerate security operations, GenAI can create a natural language summary of threat activity to date and recommend next steps for the analyst to take.
AI is not “one size fits all” and models vary greatly in size.
- Massive Models, such as Microsoft Copilot and Google Gemini, are large language models (LLMs) trained on a very extensive set of data that can perform a wide range of tasks.
- Small models are typically designed and trained on a very specific data set to perform a single task, such as to detect malicious URLs or executables.
AI adoption for cybersecurity
The survey reveals that AI is already widely embedded in the cybersecurity infrastructure of most organizations, with 98% saying they use it in some capacity:
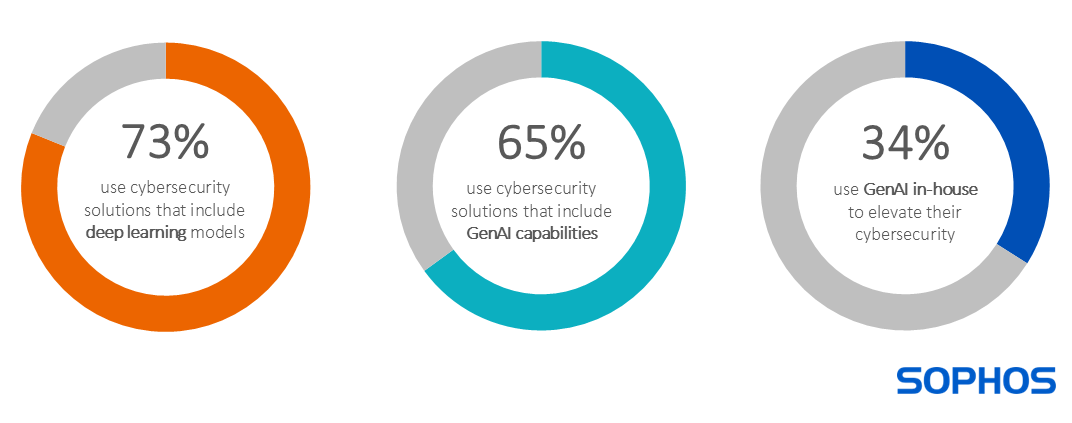
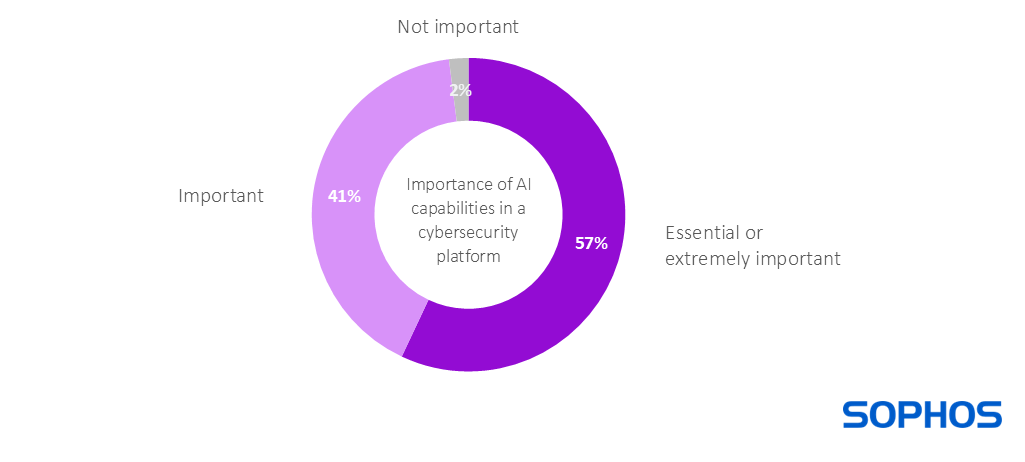
AI adoption is likely to become near universal within a short time frame, with AI capabilities now on the requirements list of 99% (with rounding) of organizations when selecting a cybersecurity platform:
With this level of adoption and future usage, understanding the risks and associated mitigations for AI in cybersecurity is a priority for organizations of all sizes and business focus.
GenAI expectations
The saturation of GenAI messaging across both cybersecurity and people’s broader business and personal lives has resulted in high expectations for how this technology can enhance cybersecurity outcomes. The survey revealed the top benefit that organizations want genAI capabilities in cybersecurity tools to deliver, as shown below.
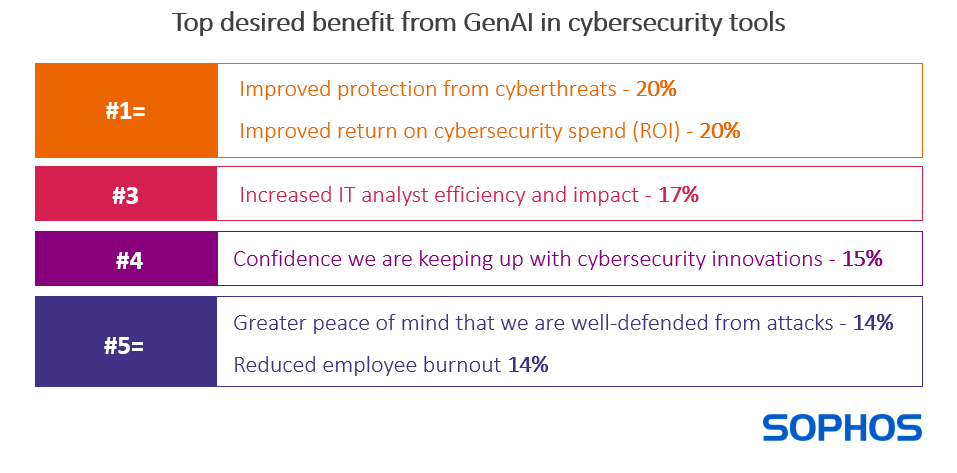
The broad spread of responses reveals that there is no single, standout desired benefit from GenAI in cybersecurity. At the same time, the most common desired gains relate to improved cyber protection or business performance (both financial and operational). The data also suggests that the inclusion of GenAI capabilities in cybersecurity solutions delivers peace of mind and confidence that an organization is keeping up with the latest protection capabilities.
The positioning of reduced employee burnout at the bottom of the ranking suggests that organizations are less aware of or less concerned about the potential for GenAI to support users. With cybersecurity staff in short supply, reducing attrition is an important area for focus and one where AI can help.
Desired GenAI benefits change with organization size
The #1 desired benefit from GenAI in cybersecurity tools varies as organizations increase in size, likely reflecting their differing challenges.
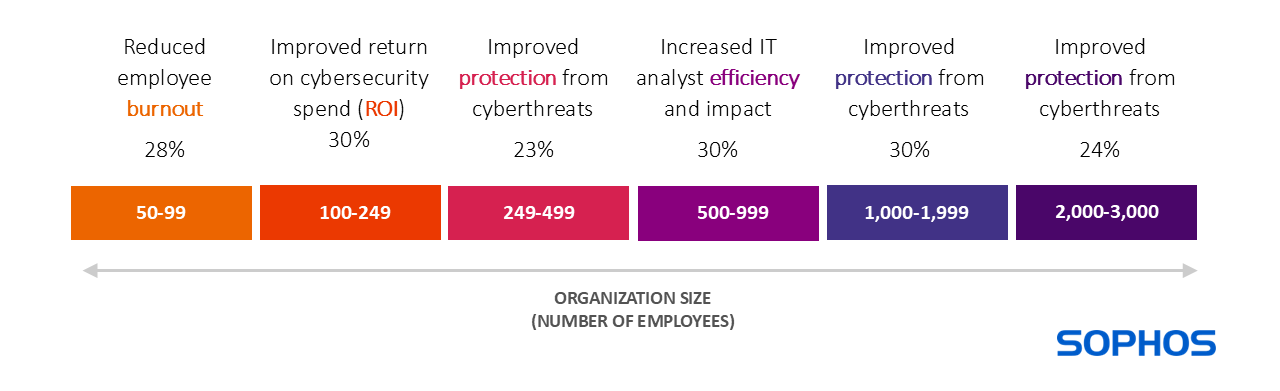
Although reducing employee burnout ranked lowest overall, it was the top desired gain for small businesses with 50-99 employees. This may be because the impact of employee absence disproportionately impacts smaller organizations who are less likely to have other staff who can step in and cover.
Conversely, highlighting their need for tight financial rigor, organizations with 100-249 employees prioritize improved return on cybersecurity spend. Larger organizations with 1,000-3,000 employees most value improved protection from cyberthreats.
About the survey
Sophos commissioned independent research specialist Vanson Bourne to survey 400 IT security decision makers in organizations with between 50 and 3,000 employees during November 2024. All respondents worked in the private or charity/not-for-profit sector and currently use endpoint security solutions from 19 separate vendors and 14 MDR providers.
Sophos’ AI-powered cyber defenses
Sophos has been pushing the boundaries of AI-driven cybersecurity for nearly a decade. AI technologies and human cybersecurity expertise work together to stop the broadest range of threats, wherever they run. AI capabilities are embedded across Sophos products and services and delivered through the largest AI-native platform in the industry. To learn more about Sophos’ AI-powered cyber defenses visit www.sophos.com/ai
Source: Sophos
Sophos, a global leader of innovative security solutions for defeating cyberattacks, today announced that its Sophos Managed Detection and Response (MDR) service has reached a major milestone, now protecting more than 26,000 organizations globally, growing its customer base by 37% in 2024. This achievement highlights the increasing demand for Sophos’ proactive, expert-led security solutions, which help organizations of all sizes stay protected 24/7 against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, including the most advanced ransomware, business email compromise (BEC) and phishing attacks.
Sophos MDR offers a comprehensive suite of capabilities that go beyond standard threat containment to include full-scale incident response, such as root cause analysis, the removal of malicious tools or artifacts used by attackers, and investigations across customers’ environments to ensure adversaries are fully ejected to prevent another attack. What further differentiates Sophos is that these incident response services are included with Sophos MDR on an unlimited basis, meaning customers are not additionally charged and there is no limit on the number of incident response hours. Sophos MDR Complete also includes a breach protection warranty covering up to $1 million USD in incident response expenses. Sophos provides flexibility for how customers can work with the MDR analysts, including the ability to pre-authorize them to contain an active threat.
Sophos Investment in MDR and New Features
Sophos has made significant investments into its MDR offering with increased analyst capacity, AI assisted workflows, new features and expanded integrations to help deliver the best possible outcomes through improved protection, detection and investigation of threats. Sophos has added the following new features:
- Proof of Value: New Sophos MDR service insights to explain the MDR team’s actions including highlighting the human hours spent threat hunting and creating and tuning detections. High-value dashboard enhancements include details of MITRE ATT&CK tactics uncovered in proactive threat hunts conducted by Sophos’ MDR team, MDR analyst coverage, case investigation summaries and an account health check status.
- Enhanced Security for Microsoft Customers: New Sophos-proprietary detections for Microsoft Office 365 identify threats including business email compromise and adversary in the middle account takeover attacks, independent of the customer’s Microsoft license level.
- Expanded Compatibility with Third Parties:This expanded ecosystem of turnkey integrations with third-party cybersecurity and IT tools includes a new Backup and Recovery integration category.
- Proactive Vulnerability Mitigation:Sophos Managed Risk powered by Tenable provides attack surface vulnerability management as a new managed service option for Sophos MDR customers.
- Efficiencyand Automation:Sophos MDR has added AI-powered workflows to streamline the operational processes and drive better security outcomes for our customers. This innovation delivers a reduced mean time to respond (MTTR) through more efficient triage, while also ensuring that all legitimate threats are rapidly investigated. This enables analysts to concentrate on other tasks such as threat hunting, account health monitoring and detection engineering.
“Attackers are continuously advancing their tactics to out manoeuvre traditional security defenses,” said Rob Harrison, senior vice president of product management at Sophos. “Our customers rely on Sophos MDR to help their organizations tackle today’s threats 24/7 with full-scale incident response to remove active adversaries and conduct root cause analysis to identify the underlying issues that led to an incident. We’re consistently evolving our solutions with new offerings and integrations, just like attackers are constantly evolving their tactics, so customers can disrupt threats before they escalate into destructive attacks.”
Better Together: Sophos MDR Integrations
Sophos has invested significantly in third party integrations for its MDR customers to ingest and analyze events and alerts from an even broader range of tools and products, while also expanding propriety detections based on suspicious behaviour identified in Microsoft environments. This includes:
- A new Backup and Recovery integration pack with Acronis, Rubrik and Veeam integrations to strengthen defenses against ransomware.
- Microsoft Office 365 Management Activity integrations, enabling the ingestion of audit logs and security alerts across the Microsoft ecosystem. More than 9,000 customers have this integration in the Sophos MDR solution.
Sophos MDR Accolades
Sophos MDR has received multiple recognitions and accolades from customers, analysts and media in 2024:
- Sophos named a Leader in the IDC MarketScape: Worldwide Managed Detection and Response (MDR) 2024 Vendor Assessment *
- Sophos named a Leader in the IDC MarketScape: European Managed Detection and Response (MDR) Services in 2024 Vendor Assessment **.
- Sophos named a Leader in Frost & Sullivan’s 2024 Frost Radar™ forGlobal Managed Detection and Response (MDR)
- Sophos MDR declared the Winner of the “Best Managed Detection and Response Service” award in the 2024 SC Awards, and“Best Managed Security Service” award in the 2024 SC Awards Europe
- Sophos named a Gartner® Peer Insights™ Customers’ Choice for MDR Services for the 2nd year in a row
- Sophos MDR named CRN 2024 Products of The Year for Revenue and Profit
Threat Landscape from Sophos MDR
In the last 12 months, Sophos shared findings from the following MDR cases it analyzed for customers:
- In December 2024, Sophos released The Bite from Inside: The Sophos Active Adversary Report that provides an in-depth look at the changing behaviors and attack techniques that adversaries used in the first half of 2024. The data is derived from nearly 200 IR and MDR cases and found that attackers are looking for ways to hide in plain sight by abusing trusted applications or “Living off the Land” binaries or LOLbins. Sophos saw a 51% increase in abusing these applications.
- Sophos X-Ops released information that it is seeing an uptick of Akira ransomware cases across its MDR and Incident Response customers with eight cases since November 2024 across Akira’s 127 victims disclosed in the past six months.
- In June 2024, Sophos MDR published details on a nearly two-year long cyber espionage campaign they uncovered against a high-level government entity in Southeast Asia. The operation, which Sophos named Crimson Palace, involved three separate clusters of threat activity that overlapped with several well-known Chinese nation-state groups.
What Sophos MDR Customers Are Saying
Sophos was named a Customers’ Choice vendor in the second Gartner® Peer Insights™ Voice of the Customer Report for MDR. Sophos scored the highest overall customer rating of 4.9/5, based on 344 reviews, as of Sept. 30, 2024, with verified customer reviews celebrating Sophos MDR’s innovation.
Here’s what customers are saying about Sophos MDR:
- “Earlier it was very difficult for us to manage the alerts and incidents generated by the tools and technology but after MDR deployment we have complete peace of mind. We also have other products from Sophos so our overall experience from a manageability point of view is also good,” from assistant director of IT in the healthcare and biotech industry (Review link)
- “Sophos MDR is a wonderful product and services by Sophos, you don’t need a SOC after getting MDR,” from an IT manager in the IT services industry (Review link)
- “Sophos MDR is one of the best in the market. It’s a good service to have good sleep at night, as the burden of threat hunting is offloaded,” from an IT infrastructure specialist in the retail industry (Review link)
- “We have had an incredibly positive experience using Sophos MDR. We rest more easily knowing that their team is acting as an extension of our own team in doing threat hunting/detection/remediation in our environment on a 24/7 basis,” from an operations associate (Review link)
For more information about Sophos MDR, visit https://www.sophos.com/products/managed-detection-and-response
Source: Sophos
Kaseya, the leading global provider of AI-powered cybersecurity and IT management software, released today its 2025 State of the MSP Industry Look Ahead: Trends, Growth and Strategies for Success. MSPs reported profitability as a top focus in 2025 and are optimistic about their future growth. The report observes trends among top-earning MSPs that can be emulated by those looking for competitive advantages in the new year. The results of the survey are featured in the State of the MSP Industry 2025 Look Ahead: Trends, Growth and Strategies for Success.
“Small and medium-sized businesses are becoming more and more tech savvy – and MSPs are reaping the rewards,” said Gary Pica, Founder, TruMethods, a Kaseya Company. “They’re seeing revenue growth and want to continue that momentum long into the future. MSPs are an essential service and they’re making the right moves to build sustainable, high-margin businesses. By streamlining their operations and utilizing automation, MSPs are preparing to capitalize on big opportunities in 2025.”
Profitability
Looking ahead to 2025, 91% of MSPs cited profitability as a priority. When asked their concerns, new customer acquisition (43%), revenue growth (37%) and profitability (36%) topped the list. These results show that MSPs are shifting their focus toward growing their businesses to help them excel financially this year. This is a good time for them to take a look at their pricing structures, as well as their spending, to ensure they’re not undercharging, which hinders their ability to deliver exceptional results to their clients.
Growth and Competition
Despite their concerns about profitability, 64% of MSPs reported revenue increases last year and 67% of them expect further growth over the next three years. While the landscape remains competitive, MSPs are finding ways to stand out in the crowd. Smaller MSPs are often able to find success over larger ones by leveraging their niche expertise. Further, 83% of MSPs offer co-managed services, helping internal IT teams with business continuity and disaster recovery (38%), cloud-based infrastructure design and management (37%) and data backup & protection (36%). Client apathy toward cyber-risks as a barrier to offering cybersecurity solutions rose from 7th last year to 1st this year – with nearly half of respondents citing it as a concern.
“It can be difficult to get small businesses to understand the importance of investing in security when they often don’t see themselves as a target,” said Pica. “While educating clients is important, it’s pivotal for MSPs to invest in platforms and tools that allow their customers to be better protected without breaking the bank.”
The Opportunity and Threat of AI
In the drive for increased growth and profitability, MSPs can utilize AI-driven tools that increase efficiency by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks. Unfortunately, AI is a double-edged sword that both enables and threatens businesses. More than two-thirds of MSPs saw an increase in AI-driven attacks in the last 12 months. In 2024, more MSPs were affected by AI-supported attacks (32%) than supply chain attacks (29%) or endpoint threats (29%). This shouldn’t scare technicians away from AI – ironically, the best soldier in the battle against AI is AI itself. Top-earning MSPs are leveraging AI-driven security tools to stay ahead of emerging threats.
Lessons from Top Earners
The survey analyzes what sets MSPs making $10 million or more a year apart and offers guidance to smaller MSPs who want to grow. First and foremost, they are proactive in adopting new technologies and delivering remarkable service. More than half of the top earners have migrated their client workloads to the cloud and a whopping 97% offer managed security services. These high earners are focused on smart growth and always expand their services in alignment with their clients’ needs and leverage automation to improve their efficiency.
To download the State of the MSP Industry 2025 Look Ahead: Trends, Growth and Strategies for Success, click here.
Source: Kaseya
Sophos ZTNA has received a couple of important updates to improve deployment ease and flexibility. These changes are part of updates to Sophos Central and don’t require any updates to your gateways or clients.
Let’s Encrypt certificates
 Sophos ZTNA now adds Let’s Encrypt certificate support for your gateways.
Sophos ZTNA now adds Let’s Encrypt certificate support for your gateways.
As you probably know, Let’s Encrypt is a non-profit open certificate authority run by the Internet Research Group (ISRG) that provides X.509 certificates for TLS encryption at no charge.
Let’s Encrypt makes certificates free and easy but comes with the inconvenience of only being valid for 90 days. This means they require more frequent maintenance than other certificates, which often have a duration of 12, 24, or 36 months.
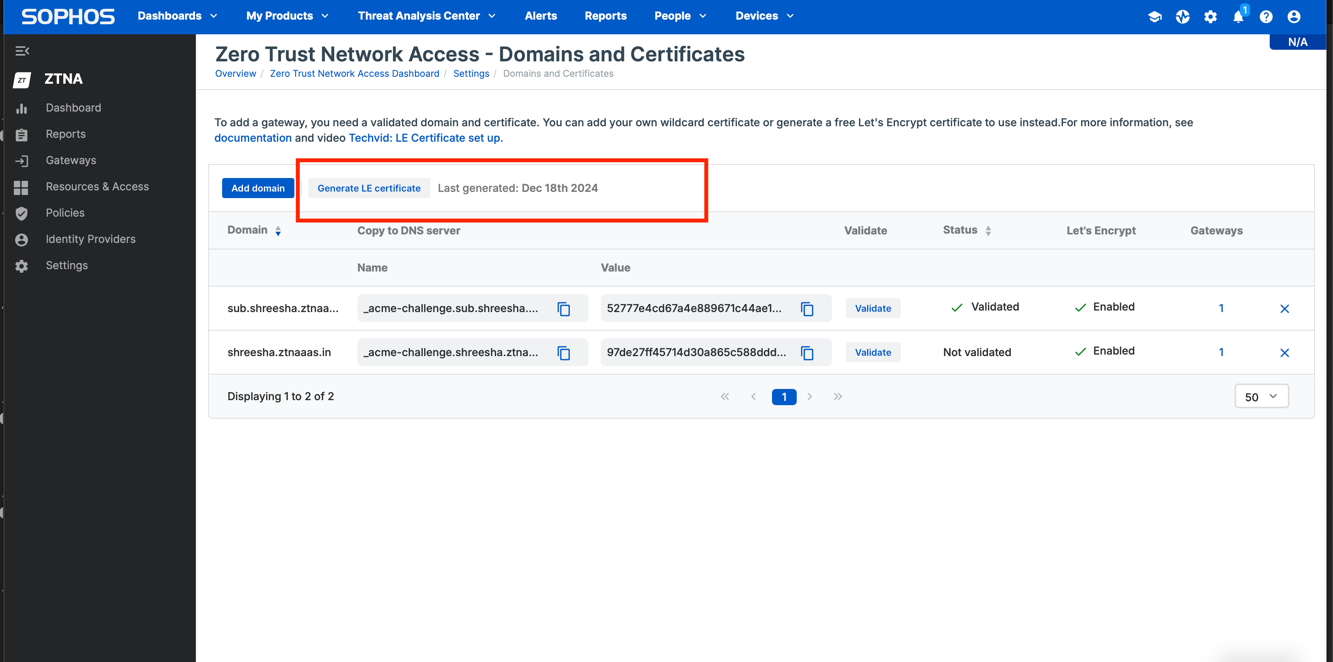
Fortunately, Sophos ZTNA helps overcome this issue with support for auto-renewal 30 days prior to expiry.
You can take advantage of this with your existing gateways anytime, regardless of your deployment mode (cloud or on-premises).
Added Sophos Central regions
Sophos ZTNA central management is now supported beyond the standard US and EU regions, adding five new regions: Australia, Brazil, India, Japan, and Canada.
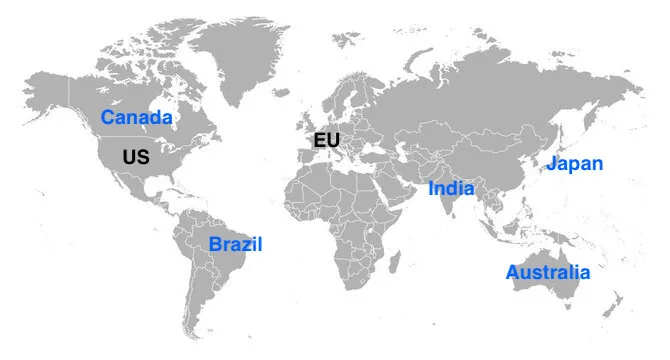
If you currently manage your Sophos Firewall and/or Endpoints in one of these regions you can now easily add Sophos ZTNA to your account.
Get started with ZTNA for free
If you’re not already using Sophos ZTNA, you can get started for free. There’s a free trial available via Sophos Central, and if you’re already a Sophos Firewall customer, you can get three free one-year licenses and take advantage of the ZTNA gateway integrated into your firewall.
Check out the Deployment Checklist for other considerations when deploying ZTNA and the latest online documentation.
Πηγή: Sophos
You can protect your IP address by hiding it and masking your location to prevent cybercriminals from impersonating or tracking you. An IP address, also called an Internet Protocol address, is a series of unique numbers that identifies your device on the internet or the network it’s connected to. Your IP address allows information to be sent across a network and distinguishes your device from others on the internet. Since your IP address reveals identifying information about you, it is important to protect it because cybercriminals can use it to track you or target you with scams.
Continue reading to learn what may happen if you don’t protect your IP address and how to hide it from people with bad intentions.
What happens if you don’t protect your IP address?
If you don’t protect your IP address, cybercriminals can do the following:
- Track your location: Someone with your IP address can determine your geographical location, narrowing it down to your state, city or even ZIP code. Even though your IP address will not reveal your exact location, cybercriminals can use the information it provides to conduct further research. They may publish the information they find about you online in a process called doxxing.
- Exploit your IP address: Using your IP address, a cybercriminal can download illegal content, including pirated games or inappropriate videos. If that illegal activity is traced to your IP address, it could be difficult to prove that you were not responsible for those actions.
- Target your network: Failing to protect your IP address can also lead to your home WiFi network being hacked. For example, if the IP address of your computer is compromised, a cybercriminal may be able to find other devices connected to your same home WiFi network and attempt to hack them.
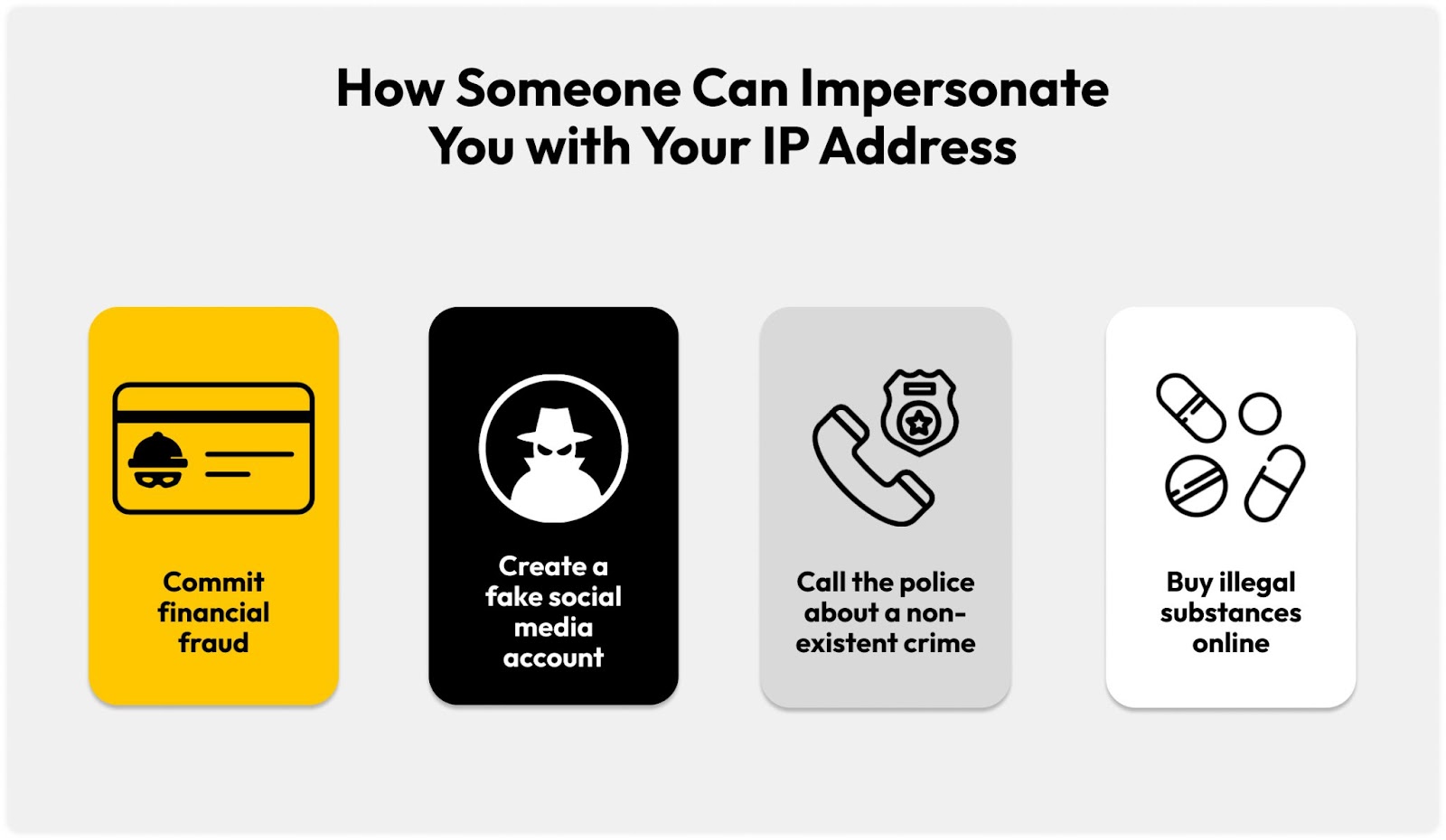
How to hide your IP address from cybercriminals
The best way to protect your IP address from falling into cybercriminals’ hands is to hide your device’s private IP address and mask your location. You can hide your device’s IP address by using a Virtual Private Network (VPN), a proxy server, the Tor web browser or your phone’s mobile data.
Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) protects your internet connection, online privacy and IP address by encrypting your connection. VPNs mask your IP address and allow you to use public WiFi without jeopardizing your privacy. Although there are many benefits to using a VPN, most charge a subscription fee, and some websites may block access when you use a VPN.
Use a proxy server
A proxy server is an in-between server so you can access online resources with enhanced privacy and security. Using a proxy server is an effective way to hide your IP address from cybercriminals because it retrieves data from the internet without exposing your identity to any websites you visit. Unlike most VPNs, proxy servers are generally free to use. If you need to access a website and want your IP address concealed, a proxy server is often a more convenient option.
Use the Tor browser
Even if your default web browser is Chrome or Safari, you can use the Tor browser specifically when you want to hide your IP address. Tor is a unique web browser that lets you browse the internet anonymously by scrambling data about your online activity, making it very challenging for anyone to track your browsing. The browser hides your IP address by routing your internet traffic through different nodes. However, because this process requires significant resources, using Tor may slow your internet connection, and some websites you attempt to visit may be blocked.
Connect to your phone’s mobile data
By turning off WiFi on your phone and relying on mobile data, you make your IP address much more challenging for cybercriminals to track because your IP address will change as you move. Even though connecting to your phone’s mobile data does not completely hide your IP address, it will change frequently, making your location harder to detect since you are not connected to a set WiFi network.
Should I be worried if someone has my IP address?
You don’t need to panic if someone has your IP address, but you should take the necessary steps to change it to maintain your privacy. Changing your IP address is as simple as unplugging your WiFi router for several minutes and then plugging it back in. When you reconnect your device to the router, it will have a refreshed IP address, making it easier to protect your identity from anyone with malicious intent.
Keep your IP address protected
Because your IP address can reveal private information about you, you should stay safe by hiding your device’s IP address and masking your location. Using a VPN, proxy server or Tor browser helps prevent your online activity from being tracked and keeps your IP address out of the wrong hands.
Source: Keeper Security
G2, a major technology user review platform, has just released its Winter 2025 Reports, and Sophos ranks as the #1 overall Firewall, MDR, and EDR solution.
Sophos is – once again – the only vendor named a Leader across the G2 Overall Grid® Reports for Endpoint Protection Suites, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), Extended Detection and Response (XDR), Firewall Software, and Managed Detection and Response (MDR). Based on user feedback, Sophos was ranked the #1 solution in 36 individual reports spanning the Antivirus, EDR, Endpoint Protection Suites, XDR, Firewall, and MDR markets.
It’s written in the stars
Customer review platforms like G2 are crucial in empowering buyers, holding businesses accountable, and driving market innovation and competition. These platforms allow customers to leave honest, unfiltered feedback about products and services, providing potential buyers access to actual user experiences rather than just marketing and messaging. The transparency and visibility of reviews encourage companies to improve their products and customer experiences continuously.
Managed Detection and Response
Sophos MDR enables more than 26,000 customers to maximize the value of their cybersecurity investments. In addition to the #1 overall ranking among MDR solutions, Sophos MDR is also rated the top solution in seven additional report segments for the category, including the Overall, Enterprise, and Mid-Market Grids, as well as earning the Best Results and Best Usability distinctions for the Enterprise and Mid-Market segments.
Endpoint Detection and Response/Extended Detection and Response
Sophos EDR/XDR was named a Leader across five different segments in the Winter 2025 Reports, including the Overall, Enterprise, Mid-Market, and Small Business Grids, as well as an Overall Momentum Leader.
Firewall
In addition to being named the #1 Overall Firewall solution, Sophos Firewall was also rated as the #1 firewall solution by Mid-Market and Enterprise users. All 4 user segments (Overall, Small Business, Mid-Market, and Enterprise) named Sophos Firewall a Leader in their respective G2 Grid Reports.
Independent Third-party Validation
The accolades from the G2 Winter 2025 Reports come off the heels of another major user review-based report in Gartner’s 2024 Voice of the Customer for Managed Detection and Response, where Sophos was the highest rated Customers’ Choice vendor to go along with the most user reviews featured in the report.
With this latest distinction, Sophos was the only cybersecurity vendor named a Customers’ Choice across the Endpoint Protection Platforms, Network Firewalls, and MDR markets in 2024 on Gartner Peer Insights – a testament to Sophos’ capabilities of providing end-to-end security for organizations of all sizes.
Furthermore, it’s not just our customers raving about Sophos protection. MITRE ATT&CK Evaluations, one of the world’s most respected independent security tests, just released their 2024 MITRE ATT&CK® Evaluations: Enterprise. Sophos XDR detected 100% of the adversary behaviors in attack scenarios targeting Windows and Linux platforms, mimicking malware strains from ruthless ransomware-as-a-service gangs LockBit and CL0P. All of Sophos’ responses to these ransomware attack scenarios were marked “technique” – the highest possible rating that denotes who, what, when, where, why and how attacks were carried out.
What Sophos customers are saying
“Sophos MDR: 360 degree MDR solution for endpoint security” said a user in the Enterprise segment
“Sophos MDR helps us sleep at night knowing our environment is monitored 24/7” said a user in the Mid-Market segment
“Sophos Firewall is a robust and user-friendly security solution that provides comprehensive protection through advanced threat detection, deep packet inspection, and synchronized security with other Sophos products” said a Head of IT in the Mid-Market segment
“Sophos Firewall automatically identifies and blocks active threats, prevents the lateral movement of attacks, and delivers immediate insights into compromised devices, users and application” said a user in the Small Business segment
“What stands out the most is how effortlessly Sophos Firewall streamlines security tasks, allowing users to focus on protecting their networks without getting bogged down in complex configurations” said a user in the Mid-Market segment
“We can rest easy knowing that Sophos Intercept X is continuously guarding our endpoints from ransomware assaults, which are the kind of thing that keep IT administrators up at night” said a SOC Analyst in the Mid-Market segment
Elevate your cyber defenses with Sophos
As the G2 ratings illustrate, Sophos provides unparalleled breadth and depth of protection. Our world-leading endpoint, network, email, cloud, and security operations solutions defend over 600,000 organizations from advanced cyberthreats, including ransomware.
For more information on our services and products, speak to your Sophos partner or representative and visit our website.
Source: Sophos
The best way to adjust your Privileged Access Management (PAM) strategy for growth is to choose a cloud-based PAM solution that scales with your organization. You may face many challenges when adjusting your PAM strategy as your organization grows, including more complex infrastructure, a higher number of login credentials to manage and increased security risks, so you need to have a flexible PAM solution.
Continue reading to learn more about the challenges your organization may face when adjusting its PAM strategy and why you should choose a cloud-based PAM solution that grows with you.
Challenges in adjusting your PAM strategy as you grow
As your organization grows, your PAM strategy must scale and evolve to address increased complexity, manage access, balance security with usability, meet compliance requirements and overcome scalability issues with your current PAM solution, if you have one. However, for organizations that aren’t prepared, these challenges can become significant obstacles to maintaining a secure and efficient infrastructure.
Infrastructure becomes more complex
As your organization grows, your infrastructure becomes more complex because you may have an increased number of users, devices and resources across different regions. You may need to shift to cloud services or combine on-premises with cloud solutions, which can bring its own set of challenges.
The more employees your organization hires, the more endpoint devices your IT team will need to manage and secure. Having diverse endpoints, such as laptops, tablets, phones and other Internet of Things (IoT) devices, makes it difficult for your IT team to manage and track access across all platforms and devices. In addition to an influx of new employees, your organization will likely need to grant new users privileged access to sensitive data. With each new privileged account, there is a greater need to ensure these accounts are secure across all systems.
Credential management
When you hire more employees, managing credentials becomes more challenging, especially for users who require privileged access, such as those in key roles like IT or HR. As your organization expands, it’s not just about adding accounts but about managing who needs access to what and when. It’s important to have a PAM strategy in place that allows you to track who has privileged access, both permanently and temporarily. With a strong system in place that follows the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP), you can more easily audit privileged accounts and determine whether they still require the same access as they once did.
Balancing security with usability
Your organization must keep its systems secure and usable to ensure employees can do their jobs productively. However, this can be challenging with more employees, since they have varied access needs. Overly strict security can hinder productivity, while lenient controls can increase the risk of breaches. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) ensures that each employee can access only the sensitive data they need to perform their job within your organization. By assigning access based on roles, RBAC helps control who can access specific data and limits which employees can access certain sensitive systems without preventing them from accessing the systems and data they need to do their jobs. Single Sign-On (SSO), on the other hand, enables employees to log in once and gain access to all authorized systems without needing to log in separately each time. This not only improves security by reducing the need to manage multiple sets of credentials but also improves productivity by saving employees time and streamlining their access to necessary resources. As you adjust your PAM strategy, ensure that your PAM solution supports both RBAC and SSO.
Overcoming scalability issues with your current PAM solution
The PAM solution you currently use may work well for a smaller team or fewer systems, but as your organization continues to grow, it may fail to scale with you. Your organization should adopt a cloud-based PAM solution that can grow with you and won’t sacrifice security or performance while adapting to more privileged users, systems, platforms and data.
Keeping up with compliance requirements
As your organization expands into new regions or countries, it will face new challenges regarding regulatory and compliance requirements. Since each jurisdiction has its own requirements for securing privileged data, you must ensure your organization complies with a variety of regulations based on location.
Some common compliance requirements that vary based on industry and location include:
-
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Applies to organizations that sell to customers located in the European Union.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): Applies to the healthcare industry in the United States.
- Service Organization Control Type 2 (SOC 2): A voluntary compliance framework primarily relevant to companies that sell cloud-based products and services, emphasizing data security, availability, processing integrity, privacy and confidentiality.
These frameworks require your organization to enforce strict controls over who can access sensitive data. Ensuring that your PAM solution scales with your organization’s growth and provides a centralized dashboard for managing and auditing privileged access is needed for meeting compliance requirements and minimizing risks.
Choose a cloud-based PAM solution that grows with you
To address the growing pains that your organization may face, you need to choose a cloud-based PAM solution that grows with you, like KeeperPAM®: a cloud-based, zero-trust and zero-knowledge security solution.
KeeperPAM is highly scalable, making it the best solution for growing organizations. As your organization adds new users or departments, IT administrators can quickly provision new accounts with RBAC, ensuring that employees only have access to the data and systems they need. Additionally, features like Just-In-Time (JIT) access make it seamless to grant temporary access only when needed and automatically revoke that access once a task is complete. As you continue to add to your infrastructure and tech stack, Keeper has hundreds of integrations that allow teams such as security and DevOps to continue using their preferred solutions securely.
For a growing organization, KeeperPAM’s scalability helps you maintain high security standards while supporting increased access demands. Users can access their Keeper Vaults from anywhere, providing a better experience across locations and devices, ensuring your PAM solution grows with your business needs.
Future-proof your PAM strategy with KeeperPAM
Prepare for the future of your growing organization by switching to a scalable PAM solution like KeeperPAM. By future-proofing your PAM strategy with KeeperPAM, you can overcome the challenges most organizations face when adjusting their PAM strategies, including complex infrastructure, managing more privileged accounts, balancing security with usability and overcoming scalability issues.
Request a demo of KeeperPAM today and enhance your PAM strategy.
Source: Keeper
Most password managers on the market require only the user’s master password to access their password vault. If the master password is compromised, a cybercriminal could use it to log in to the user’s account from any device. This would mean that the cybercriminal would have access to all of that user’s saved passwords.
In contrast, Keeper requires device-level approval. Even if a cybercriminal has your master password, they would first need to have physical access to one of your approved devices to log in. This adds an extra layer of security against cyber threats like password spraying or data breaches on the dark web.
Continue reading to learn how Keeper’s device-level approval feature makes it much harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access to your Keeper account.
What is device-level approval in Keeper?
In Keeper Password Manager, device-level approval means that each new device attempting to access a Keeper Vault must be explicitly approved before gaining access. This device approval process occurs before an attempt to use a master password. In Keeper’s security architecture, the backend system does not allow an attempt to log in without first approving a device. This means that the existence of an account is never confirmed or denied by the application until a user proves their identity. This also means that the attacker would not know if a master password is correct.
When a user attempts to access their Keeper Vault from a new device, that device needs to be approved by one of the following:
- The account owner
- An administrator (in enterprise environments)
- Through an existing trusted device
Each new device receives a unique device ID, preventing unauthorized devices from accessing a user’s vault even if the login credentials have been compromised. This provides an additional layer of security that goes beyond Two-Factor Authentication (2FA).
How device-level approval protects against password stuffing attacks
Device-level approval requires both the user’s password and an authorized device to access their vault. Even if a cybercriminal manages to steal a user’s master password, they still wouldn’t be able to access the vault, as the cybercriminal’s device is not approved. This prevents common password attacks, such as password stuffing and brute force attempts, from succeeding.
When data is in transit, Keeper’s encryption model also stops other types of cyber attacks, like Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks, because each approved device is double-encrypting traffic on top of Transport Layer Security (TLS). Cybercriminals cannot simply intercept and decode traffic between your device and Keeper’s servers. Even if they capture the data, it’s useless without the device-specific keys.
The device approval system further helps protect against social engineering attacks. Even if someone convinces you to reveal your password through phishing, they won’t be able to use it because none of their devices are approved.
How Keeper differs from other password managers
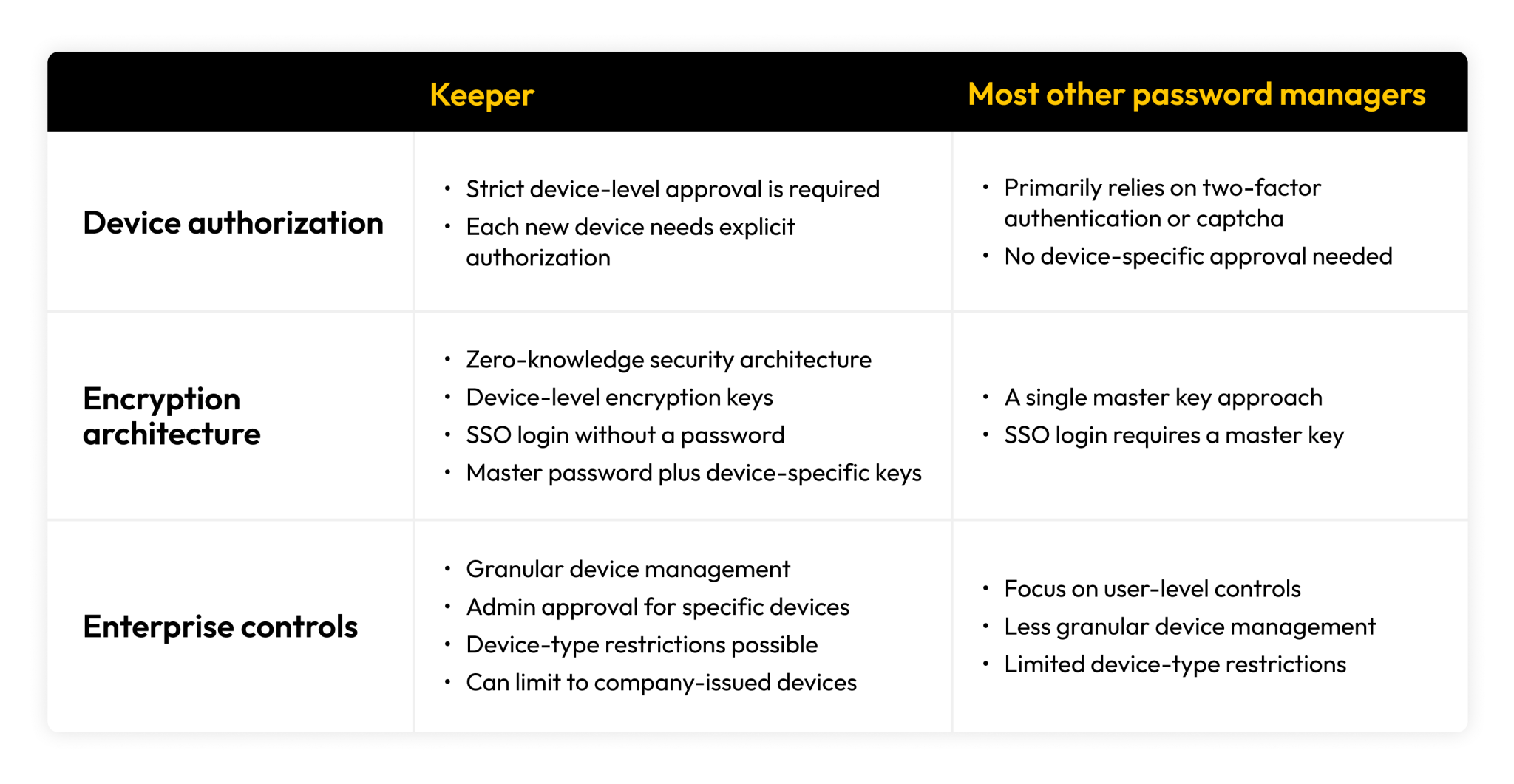
Device authorization model
Unlike most other password managers that typically rely on 2FA without device-specific approval, Keeper uses strict device-level approval. This requires that each new device be explicitly authorized, making Keeper more secure against unauthorized device access.
Encryption architecture
Keeper uses a zero-knowledge security architecture with device-level keys. Each device has its own encryption key in addition to the master password. This differentiates Keeper from most competitors, which use only a single master password.
Enterprise controls
Keeper offers more granular device management for organizations with multiple users and multiple devices. Administrators can approve or reject specific devices and enforce device-type restrictions (e.g., only company-issued devices). Most password management competitors focus more on user-level rather than device-level controls.
Get peace of mind over your passwords with Keeper
Keeper’s unique security architecture, which uses device-level approval and zero-knowledge encryption, is superior to other password managers. By requiring both the correct password and explicit authorization for each new device, Keeper makes unauthorized access significantly more difficult. This helps protect against common cyber threats, such as password spraying, brute force attacks and social engineering.
Source: Keeper
When businesses operate 24/7, downtime is simply not an option. Downtime — whether due to cyberattacks, natural disasters or system outages — cripples operations, causes revenue loss and impacts long-term brand reputation. That’s why disaster recovery (DR) is a critical component of operational resilience for businesses today, ensuring they bounce back swiftly and effectively from any setback.
On that front, Datto has been a reliable partner for businesses in facilitating seamless disaster recovery and operational continuity. Trusted by thousands of businesses worldwide, Datto manages over 200 petabytes of data and facilitates 230,000+ cloud restores annually across file restores, image exports and virtualizations. These staggering figures highlight Datto’s capability to handle complex recovery needs with unmatched efficiency.
At the heart of Datto’s popularity is its 1-Click disaster recovery feature — a revolutionary approach that combines speed with simplicity. By significantly reducing the steps required to spin up a disaster recovery environment, Datto ensures minimal disruption to business operations. In moments of crisis, where every second counts, this seamless recovery process enables businesses to restore operations faster than ever before.
Let’s take a look at how Datto’s innovation in disaster recovery underscores a new paradigm: one where simplicity drives impact and resilience.
Rising data threats and traditional DR woes: The need for change
Today, businesses face a deluge of threats, ranging from sophisticated cyberattacks, like ransomware, to unforeseen natural disasters and hardware malfunctions. These incidents not only disrupt daily operations but also pose existential risks for businesses of all sizes. The frequency and complexity of such threats demand a disaster recovery approach that’s fast, reliable and efficient, yet traditional methods often fall short.
Traditional DR strategies are riddled with pain points that make them less effective when seconds count.
- Lengthy recovery times mean businesses remain vulnerable, often losing revenue and customer trust.
- Configuring recovery environments is notoriously complex, requiring intricate setups that leave room for error.
- Furthermore, downtime comes with a hefty price tag, especially for SMBs where every minute of disruption has a ripple effect.
Let’s not forget the high-stress environment of disaster recovery — IT teams, already under pressure, are prone to manual errors that can further delay restoration efforts. These challenges underscore the need for a simplified, modernized approach to DR.
Datto’s recipe for DR: As effortless as reordering your go-to meal
Datto is redefining disaster recovery with a focus on speed and simplicity. Previously, spinning up a DR environment in the Datto Cloud involved multiple steps: creating cloud compute resources (virtual machines), configuring cloud networking and establishing user connectivity via cloud VLANs, site-to-site IPsec tunnels and VPNs. While effective, this process can be tedious, time-consuming and susceptible to user mistakes, especially during a crisis.
To solve this, Datto has introduced a seamless process that allows users to quickly clone test configurations and apply them to live disaster recovery environments. By streamlining these tasks, Datto makes disaster recovery as effortless as a few clicks, ensuring businesses can restore operations without delay or complexity.
Scalable, simple and reliable: Why Datto Cloud is a DR game changer
Datto Cloud stands apart as a purpose-built platform designed specifically to meet the needs of MSPs and SMBs. Unlike generic cloud solutions, it is finely tuned to handle the unique challenges these businesses face, offering unparalleled scalability and reliability. Datto Cloud’s infrastructure is built to grow with your business, whether you’re managing a few clients or scaling across multiple locations. Its resilience guarantees that data is secure and accessible when it matters the most, giving MSPs the confidence to protect their customers and SMBs the assurance of business continuity.
At the core of Datto’s innovation is the 1-Click DR process, which dramatically reduces the complexity of restoring operations after a disruption. This streamlined approach minimizes downtime by enabling real-time failover to the Datto Cloud, ensuring business-critical applications are back online within moments. Its user-friendly interface eliminates the technical barriers often associated with disaster recovery, allowing IT teams to execute recovery plans seamlessly — even under pressure.
By simplifying workflows and cutting recovery times, Datto empowers businesses to focus on what they do best, knowing their operations are secure and quickly restorable.
1-Click capabilities: The Datto Cloud advantage
Datto Cloud delivers best-in-class recovery time objectives (RTOs) for customers and partners, setting the gold standard in disaster recovery. On average, Datto achieves RTOs of less than six minutes, with 42% of recoveries completed in under two minutes. These remarkable figures underscore Datto’s commitment to speed and efficiency when it matters most.
Let’s look at some of the 1-Click DR capabilities of Datto:
1-Click Cloud Virtualization
Datto simplifies the virtualization process by enabling seamless 1-click cloud recovery. This feature clones a virtual machine (VM) using the most recent cloud restore point by default, or users can select from the last five restore points. The virtualized environment automatically reconnects to its previous network configuration, if available, or defaults to a straightforward networking setup. This ensures that businesses can restore critical workloads with minimal effort and zero guesswork.
1-Click Cloud VLAN
Managing VM connectivity has never been easier with Datto’s 1-Click Cloud VLAN feature. By cloning previous VLAN configurations, users save significant time and reduce manual data entry. This includes defining network addresses, subnet masks, gateway IPs, enabling DHCP, and configuring optional settings like outbound internet connectivity. With built-in search and sort capabilities, this feature ensures that network settings from past configurations can be quickly located, reused and applied, streamlining recovery workflows.
1-Click DR Plan
With the 1-Click DR Plan, Datto allows partners to create and save a default disaster recovery plan for all SIRIS devices. Users can select which systems to enroll in the plan, clone all VMs for testing or live recovery, and easily configure options through a user-friendly wizard. This includes selecting different restore points or cloud VLANs as needed, ensuring that every disaster recovery scenario is handled with precision and efficiency.
1-Click IPsec Tunnels
Thanks to Datto’s 1-Click IPsec Tunnels, building secure site-to-site VPN connections during disaster recovery is no longer a complex task. This feature enables users to apply previously saved IPsec configurations with a single click, eliminating the need for manual setup of passkeys, local IKE IDs, on-prem IPs, subnets and encryption settings. Users can also select and clone configurations from history, ensuring quick and secure connectivity without unnecessary complications.
Ensure business continuity with Datto Cloud
Datto Cloud’s 1-Click capabilities are revolutionizing how businesses approach disaster recovery, making it faster, simpler and more reliable than ever. By combining speed with ease of use, Datto ensures businesses can minimize downtime, reduce complexity and stay resilient in the face of disruptions. Are you ready to take the first step toward securing your business’s future? Explore how Datto Cloud can protect your operations with its game-changing features. Get a personalized demo today and discover why businesses worldwide trust Datto to deliver unparalleled business continuity and disaster recovery solutions.
Source: Datto
Sophos has once again achieved exceptional results in the latest 2024 MITRE ATT&CK Evaluations for Enterprise. In this round, Sophos XDR achieved:
- The highest possible (‘Technique’) ratings for 100% of adversary activities in the Windows and Linux ransomware attack scenarios
- The highest possible (‘Technique’) ratings for 78 out of 80 total adversary activities across all three comprehensive scenarios
- ‘Analytic coverage’ ratings for 79 out of 80 total adversary activities activities
The eagerly anticipated results of the sixth round of MITRE ATT&CK® Evaluations for Enterprise have been released, assessing the ability of nineteen endpoint detection and response (EDR/XDR) solutions to accurately identify and report the malicious activities of sophisticated threat groups.
Watch this short video for an overview of the evaluation:
What are MITRE ATT&CK® Evaluations?
MITRE ATT&CK® Evaluations are among the world’s most respected independent security tests. They emulate the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) leveraged by real-world adversarial groups and evaluate each participating vendor’s ability to detect, analyze, and describe threats, with output aligned to the language and structure of the MITRE ATT&CK® Framework.
There is no singular way to interpret the results of ATT&CK Evaluations, and they are not intended to be competitive analyses. The results show what the evaluation observed and do not result in a “winner” or “leader” – despite what some vendors might like you to think!
There is nuance in the ways each vendor’s tool works and how it presents information to the analyst using it, and your individual needs and preferences play a vital role in determining which solution is best for you and your team. Learn about Sophos Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
Evaluation overview
This was the sixth round of ATT&CK Evaluations for Enterprise — MITRE’s product-focused evaluation — designed to help organizations better understand how endpoint detection and response (EDR) offerings like Sophos XDR can help them defend against sophisticated, multi-stage attacks.
This round focused on behaviors inspired by three known threat groups:
- Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK). The evaluation emulated DPRK’s adversary behaviors targeting macOS via multi-stage operations, including elevating privileges and credential theft.
- CL0P and LockBit Ransomware. The evaluation emulated behaviors prevalent across campaigns using CL0P and LockBit ransomware targeting Windows and Linux platforms, including the abuse of legitimate tools and disabling critical services.
Evaluation participants
Nineteen EDR/XDR solution vendors participated in this evaluation round (in alphabetical order):
Understanding the results
Each adversary activity (called a ‘sub-step’) emulated during the evaluation received one of the following ratings, indicating the solution’s ability to detect, analyze, and describe the adversary activity, with output aligned to the language and structure of the MITRE ATT&CK® Framework.
- Not applicable — a “miss”: The adversary activity was not detected or the evaluation for the sub-step was not completed.
- None: Execution of the sub step was successful; however, evidence provided did not meet the documented Detection Criteria, or there was no evidence of Red Team activity provided.
- General: The solution autonomously identified that the malicious/suspicious event(s) occurred and reported the What, Where, When, and Who.
- Tactic: In addition to meeting the criteria for a ‘General’ rating, the solution also provided information on the attacker’s potential intent; the Why, aligned to MITRE ATT&CK Tactics.
- Technique — the highest possible rating: In addition to meeting the criteria for a ‘Tactic’ rating, the solution also provided details on the attacker’s method for achieving a goal; How the action was performed.
Detections classified as General, Tactic, or Technique are grouped under the definition of Analytic Coverage, which measures the solution’s ability to convert telemetry into actionable threat detections.
How did Sophos perform in this evaluation?
Throughout the evaluation, MITRE executed three discrete attack scenarios (DPRK, CL0P, and LockBit), comprising a total of 16 steps and 80 sub-steps.
Sophos XDR delivered impressive results, achieving:
- The highest possible (‘Technique’) ratings for 100% of adversary activities in the Windows and Linux ransomware attack scenarios
- The highest possible (‘Technique’) ratings for 78 out of 80 total adversary activities across all three comprehensive scenarios
- ‘Analytic coverage’ ratings for 79 out of 80 total adversary activities activities
Attack scenario 1: DPRK (macOS only)
North Korea has emerged as a formidable cyber threat, and by expanding its focus to macOS, they have gained the ability to target and infiltrate additional high-value systems. In this attack scenario, the MITRE team used a backdoor from a supply chain attack, followed by persistence, discovery, and credential access, resulting in the collection and exfiltration of system information and macOS keychain files.
This scenario comprised 4 steps with 21 sub-steps on macOS only.
- Sophos XDR detected and provided rich ‘analytic’ coverage for 20 out of 21 sub-steps (95%) in this scenario.
- 19 sub-steps were assigned ‘Technique’ level categorization — the highest possible rating.
Attack scenario 2: CL0P ransomware (Windows)
Active since at least 2019, CL0P is a ransomware family affiliated with the TA505 cyber-criminal threat actor (also known as Snakefly) and is widely believed to be operated by Russian-speaking groups. The MITRE team used evasion techniques, persistence, and an in-memory payload to perform discovery and exfiltration before executing ransomware.
This scenario comprised 4 steps with 19 sub-steps on Windows only.
- Sophos XDR detected and provided full ‘technique’ level coverage — the highest possible rating — for 100% of sub-steps in this scenario.
Attack scenario 3: LockBit ransomware (Windows and Linux)
Operating on a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) basis, LockBit is a notorious ransomware variant that has gained infamy for its sophisticated tools, extortion methods, and high-severity attacks. The MITRE team gained access using compromised credentials, ultimately deploying an exfiltration tool and ransomware to stop virtual machines and exfiltrate and encrypt files.
This scenario comprised 8 steps with 40 sub-steps on Windows and Linux.
- Sophos XDR detected and provided full ‘technique’ level coverage — the highest possible rating — for 100% of sub-steps in this scenario.
Learn more at sophos.com/mitre and explore the full results on the MITRE website.
How do Sophos’ results compare to other participants?
As a reminder, there’s no singular way to interpret the results of ATT&CK Evaluations, and you will see different charts, graphs, and other visualizations created by participating vendors that frame the results in different ways.
Detection quality is critical for providing details on the adversary’s behavior so analysts can investigate and respond quickly and efficiently. Therefore, one of the most valuable ways to view the results of ATT&CK® Evaluations is by comparing the number of sub-steps that generated a detection that provided rich detail on the adversarial behaviors (analytic coverage) and the number of sub-steps that achieved full ‘technique’ level coverage.
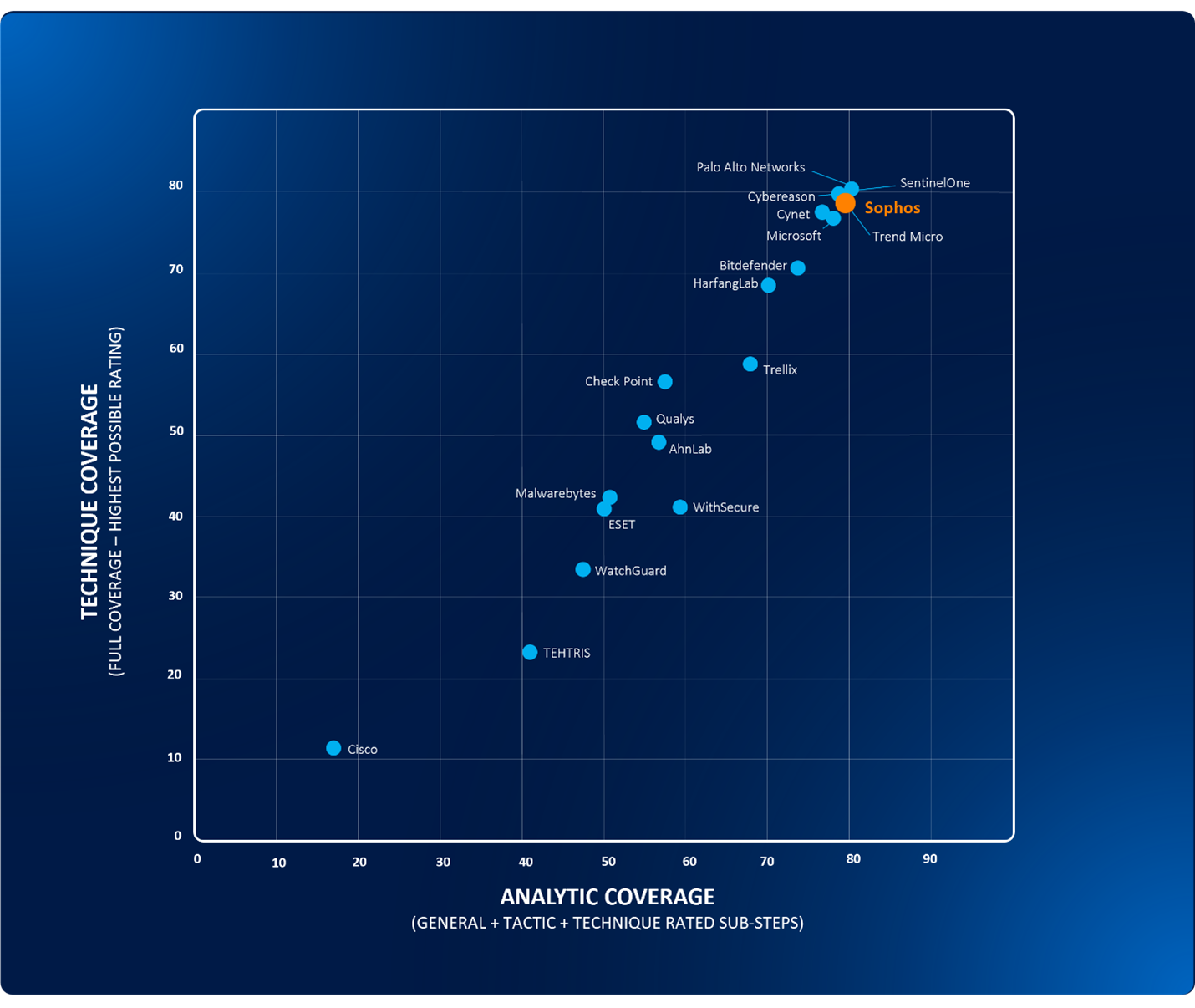
How to use the results of MITRE ATT&CK Evaluations
When considering an EDR or extended detection and response (XDR) solution, review the results from ATT&CK Evaluations alongside other reputable third-party proof points, including verified customer reviews and analyst evaluations. Recent third-party recognitions for Sophos XDR include:
- Sophos named a Leader in the 2024 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Endpoint Protection Platforms for the 15th consecutive time
- Sophos is the only vendor named a Leader for Endpoint, Firewall, MDR, XDR and EDR in the G2 Fall 2024 Grid Reports
- Sophos named a 2024 Gartner® Peer Insights™ Customers’ Choice for Endpoint Protection Platforms
As you review the data available in the MITRE portal for each participating vendor, consider the following questions as they pertain to you, your team, and your organization:
- Does the evaluated tool help you identify threats?
- Does it present information to you the way you want it?
- Who will be using the tool? Tier 3 analysts? IT specialists or Sysadmins?
- How does the tool enable you to conduct threat hunts?
- Are disparate events correlated? Is that done automatically, or do you need to do that on your own?
- Can the EDR/XDR tool integrate with other technology in your environment (e.g., firewall, email, cloud, identity, network, etc.) including solutions from other vendors?
- Are you planning to use the tool by yourself, or will you have the support of a Managed Detection and Response (MDR) partner?
Why we participate in MITRE ATT&CK Evaluations
MITRE ATT&CK Evaluations are among the world’s most respected independent security tests due to the emulation of real-world attack scenarios and transparency of results. Sophos is committed to participating in these evaluations alongside some of the best security vendors in the industry. As a community, we are united against a common enemy. These evaluations help make us better, individually and collectively, for the benefit of the organizations we defend.
Get started with Sophos XDR
Our results in this latest evaluation further validate Sophos’ position as an industry-leading provider of endpoint detection and response (EDR) and extended detection and response (XDR) capabilities to over 43,000 organizations worldwide.
Visit our website or speak with an expert to see how Sophos can streamline your detection and response and drive superior outcomes for your organization today.
Source: Sophos
When you invest in a password manager, you should follow some best practices when setting it up to ensure your information stays secure. Some of the best practices when using a password manager include creating a strong master password, enabling MFA, changing weak passwords, auditing your passwords and setting a short inactivity logout timer.
Continue reading to learn more about the best practices when you use a password manager like Keeper®.
1. Create a strong master password
A password manager is convenient because all of your login credentials are kept in one place, and the only password you need to remember to access your private information is your master password. Since your master password is the key to accessing all your sensitive information, it is important to make it a strong one.
There is a fine line between making this master password easy for you to remember yet also unique enough to be secure. You can create a strong master password by making sure it is at least 16 characters long, uses a combination of letters, numbers and symbols, and does not include any personal information.
2. Enable MFA on your password manager
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is important to enable on your password manager and all of your accounts. MFA refers to an additional security measure that requires you to give an app or website an extra form of authentication to verify your identity. With MFA enabled on your password manager, a cybercriminal could not access your digital vault without an additional form of authentication, such as a code from an authenticator app, your fingerprint, a PIN or even your location.
3. Immediately change weak, reused and compromised passwords
Changing your weak, reused and compromised passwords is very important because the longer you keep your weak passwords, the higher the chance cybercriminals will crack them and access your information. Keeper Password Manager helps users avoid using weak or reused passwords by scanning existing passwords and identifying which ones should be replaced with new stronger passwords.
Depending on the functionality offered by your password manager, it may also be able to tell you which of your passwords have been compromised, which means they have been exposed on the dark web. After notifying you when one of your passwords has been compromised, a password manager is very useful and can help you make quick changes to your login credentials before your private information gets accessed by cybercriminals.
4. Frequently audit your passwords
For users who have many online accounts, a password manager will help you keep track of your login credentials as well as keep them safe. Since some password managers can tell you which of your passwords are weak, reused or compromised, it is helpful to do password audits often to ensure your passwords are all strong. Keeper Password Manager has an auditing feature called Security Audit, where you can see if your passwords fall under strong, medium or weak categories, as well as if they’re reused. For the passwords that are classified as weak, you can update them easily by using Keeper Password Manager.
5. Set a short inactivity log-out timer
Imagine you are at a coffee shop getting work done. Unbeknownst to you, someone in the coffee shop watched you type in your PIN on your laptop. When you step away from your laptop for a quick moment, a cybercriminal unlocks your laptop and steals your passwords and other private information before you come back because you don’t have a log-out timer set.
Luckily, if you enable a log-out timer with KeeperFill, your device will sign you out of your password manager after a certain length of inactivity. Since most password managers built into your browser keep you logged in, your passwords would be easily accessible to anyone who goes onto your device. When you use KeeperFill and its inactivity log-out timer, your passwords will stay protected, even after you step away from your device.
Secure your password manager for optimal security
Using a password manager to store your private information and login credentials keeps you much safer than not using one at all. However, if you use a password manager and implement these helpful practices, you’ll ensure your online accounts and sensitive information will remain secure.
If you don’t currently keep your login credentials in a password manager, try Keeper Password Manager today when you start a free 30-day trial. If you do use another password manager, Keeper offers direct importing from other password managers to make switching a breeze.
Source: Keeper
It’s that time of year when people in many parts of the world are looking forward to spending time with family and friends and taking a bit of a break.
Unfortunately, this time of year also sees a surge in cyber threats, as bad actors like to exploit the reduction in network monitoring over the holidays. Ransomware attacks, as an example, often spike significantly during this time.
To help you navigate this period safely, here are a few quick and easy best practices to better protect your network while you take some well-deserved time off.
For a full list of best practices to secure your network from ransomware and other attacks be sure to download our white paper on this topic.
1. Update your network infrastructure
Make sure that before you depart for the holidays, all your network infrastructure has been updated with the latest firmware. These updates often contain important security patches for known vulnerabilities or hardening enhancements.
If you’re a Sophos Firewall customer, make sure all your firewalls are updated to v21.
If you’re one of our customers still using soon to be end of life XG Series appliances, get an order in for your new XGS Series before you depart. Upgrading is easy and there are tremendous savings to be had – and if you upgrade early, you can overlap your licenses.
There’s also a new backup/restore assistant that makes upgrading to your new XGS Series appliance easy with full port-mapping options. And we just released a new line of desktop XGS Series models with new levels of performance and efficiency.
If you have other internet facing infrastructure like a VPN concentrator or WAF, make sure it’s also up to date.
2. Shut down any non-essential systems over the holidays
Any system that’s exposed to the internet is an attractive target for attackers looking to get a foothold on your network. If you have systems exposed to the internet, particularly via RDP or VNC, disable these systems over the holidays.
As you plan for the new year, explore implementing Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) to provide robust, next-generation protection for these systems and fortify your security posture. ZTNA will enable secure access only for specific authenticated users and will otherwise make your networked applications and systems invisible to attack.
If you don’t have ZTNA and you still need to access any systems remotely over the holidays, be sure to only allow access from the LAN and use remote access VPN – disable any port forwarding or NAT rules on your firewall. This also applies to any user portals that you may have provisioned – at least temporarily disable them over the holidays.
3. Ensure authentication is secured with MFA
Attackers often use brute force login attempts to exploit weak credentials, especially during the holidays. Make sure all systems on your network are properly protected with strong passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA). These measures significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and keep your network secure.
Sophos has products and services that can help
As you would expect, Sophos Firewall and our full line of network security solutions are secure by design as we take your organization’s network security extremely seriously.
Our network security products seamlessly integrate with our full suite of cybersecurity products and services – including our 24/7 Managed Detection and Response service designed to provide you with unmatched protection and peace of mind—especially during the holiday season.
Under attack? Contact us in an emergency
If you experience an emergency incident over the holidays (or any time), you can engage our fixed-fee Sophos Rapid Response service. Our team of expert incident responders will help you triage, contain, and eliminate active threats, and remove all traces of the attackers from your network.
Whether it is an infection, compromise, or unauthorized access attempting to circumvent your security controls, we’ve seen and stopped it all. Sophos Rapid Response is available 24/7/365, including over the holiday period.
Get the full set of network security best practices to secure your network
For a full list of best practices to secure your network from ransomware and other attacks be sure to download our white paper on this topic.
Source: Sophos
When searching for the best password manager for your small business, there are several features you should consider based on your preferences and needs.
Zero-knowledge and end-to-end encryption
Your password manager should use zero-knowledge encryption, meaning all data stored in your vault can only be encrypted and decrypted by you. No one besides you can access your passwords if your password manager uses zero-knowledge encryption. For a password to be encrypted, it must be converted from a readable format into ciphertext, which neither people nor machines can read until it’s decrypted using an encryption key. The combination of a zero-knowledge model and end-to-end encryption is important for a business password manager because it ensures your employees’ passwords will only be known to them and protected from cybercriminals.
Passkey support
The password manager you choose for your small business should support passkeys for added security. A passkey allows you to log in to your accounts and apps without entering a password. Instead, you log in the same way you unlock your device. Keeper Password Manager supports passkeys, simplifying your employees’ login process by enabling them to manage their passkeys within their vault.
Secure sharing capabilities
Sharing login credentials and private files is important for your small business, so your password manager should enable you to share encrypted passwords and files with ease. Everything stored in your digital vault is encrypted, and when all your employees use a business password manager, you can easily give them access to any passwords or files they need. By using vault-to-vault record sharing, Keeper users can share records with team members while keeping information encrypted the entire time. Keeper also offers a feature known as One-Time Share, enabling users to share passwords and files with anyone, including non-Keeper users, for a limited time.
Cross compatibility
Your password manager should allow you and your employees to access your passwords and other important information from any device, web browser or operating system. A password manager like Keeper is ideal for small businesses that allow their employees to use different types of devices or web browsers because Keeper can be used on any device, no matter what web browser or operating system your employees use.
2FA code storage
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a form of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), where you are required to enter another form of verification beyond your username and password to access an account. If you require your employees to enable 2FA, you should make sure whichever password manager you use for your small business can store 2FA codes. Some types of MFA that can be saved in a secure password manager like Keeper include answers to security questions and Time-based One-Time Password (TOTP) codes. A password manager that can store these 2FA codes reduces the amount of time your employees spend trying to log in to their accounts and increases their productivity and safety.
Dark web monitoring
An essential feature of your password manager should be its ability to monitor the dark web. Dark web monitoring is a tool that searches for specific information, like your email address or passwords, on the dark web, to ensure they have not been compromised. When you use Keeper Password Manager for your small business, you can use BreachWatch, an add-on feature that constantly scans the dark web and notifies you immediately if your stored login credentials are found. By receiving notifications about your credentials being found on the dark web, you and your small business can stay protected and take action quickly to secure your passwords.
The best password manager for small businesses
If you’re looking for a password manager that covers all your security needs, look no further than Keeper Password Manager. Using Keeper is the best way to protect your employees, customers and small business from potential cyber attacks due to its zero-knowledge encryption, passkey support, secure sharing abilities, cross compatibility, MFA storage and dark web monitoring features.
Start your free 14-day trial of Keeper Business to discover the vast benefits of using a password manager to protect your small business from cyber threats.
Source: Keeper
Your small business should rely on a password manager to ensure your employees use strong passwords, to simplify onboarding and offboarding processes, securely share files, avoid potentially losing money from a cyber attack and improve employee productivity. A business password manager allows you and your employees to store and protect all passwords, with each employee having their own digital vault.
Continue reading to learn the five benefits of using a password manager for your small business and what to look for in an effective password manager.
1. Ensures each employee is using strong passwords
If your small business uses a password manager, you can easily enforce strong password security policies for all your employees. You can set a minimum password length and require that all employees use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) on their accounts related to your business for extra security. A password manager can also identify passwords that are weak or being reused, which can help employees determine which passwords need to be changed. With complete visibility into employee password practices, a password manager makes it easy to enforce the use of strong passwords.
2. Simplifies employee onboarding and offboarding
Your small business deserves a convenient way to onboard and offboard employees, and having a password manager can simplify these tedious tasks. A password manager aids the onboarding and offboarding processes by enabling you to securely share passwords when an employee first arrives and quickly change them if an employee leaves. For onboarding, a password manager conveniently stores and organizes an employee’s login credentials based on their role, taking less time for you to set up the new employee’s accounts. When offboarding, a password manager lets you remove a former employee’s access to all systems and quickly change their passwords so they cannot compromise any business data. Most password managers also support automated provisioning and de-provisioning when integrated with your identity provider.
3. Enables secure password and file sharing
You and your employees need to be able to securely share passwords and files within your small business to reduce the risk of compromised data. Passwords and files shared over email are unencrypted, which means they could be intercepted by a cybercriminal. Worse than sharing important information over email is writing passwords down on a sticky note or piece of paper that could easily be picked up by anyone and used to compromise business data. Using a password manager to share important passwords and files keeps your business’ confidential data secure and ensures it goes to the correct recipient.
4. Saves money in the long run
Password managers can help your small business save money in the long run in the event of a cyber attack. For example, if your small business did not have a password manager in place and used weak passwords, it could suffer a data breach and be forced to shut down completely if its data or finances were compromised, not to mention the tarnished reputation. According to Verizon’s 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report, 68% of data breaches occur due to an employee making an error or falling victim to phishing scams. It would cost much less to invest in a password manager to protect your financial information, customer data and other online accounts than to risk being unable to recover following a cyber attack.
5. Improves employee productivity
With a password manager, your employees can be more productive since they won’t have to remember passwords on their own or spend time resetting them. The only password employees need to remember is their master password, which acts as the key to enter their vault. Additionally, since password managers also help employees generate strong passwords with its built-in password generator, employees save time by not having to create them on their own.
With Keeper®, there is even a feature called KeeperFill, which automatically logs you in on any device, web browser or operating system, as long as you’ve downloaded the app or browser extension. Having this feature for your small business’ password management will help any employee log in to their accounts without needing to adjust to a different device, web browser or operating system for work.
Source: Keeper