News
After a year of big data breaches like Home Depot and Sony, and widespread security vulnerabilities in our shared software, which spawned the likes of Heartbleed and Shellshock, it’s easy to predict that cyber security will be a hot topic in 2015. Our new Security Threat Trends 2015 report investigates the biggest security risks on the horizon and explains the real-world impact of evolving threats on businesses and consumers. Here are the 10 things we believe will have the biggest impact on security in 2015 and beyond.
1. Exploit mitigations reduce the number of useful vulnerabilities.
Cybercriminals have for years feasted on Microsoft Windows. Fortunately, Microsoft has invested in exploit mitigations, which makes writing attack code more difficult. As the difficulty of exploitation increases, some attackers are moving back to social engineering and we also see attackers focusing on non-Microsoft platforms.
2. Internet of Things attacks move from proof-of-concept to mainstream risks.
In 2014 we’ve seen more evidence that manufacturers of Internet of Things (IoT) devices have failed to implement basic security standards, so attacks on these devices are likely to have nasty real world impact. The security industry needs to evolve to deal with these devices.
3. Encryption becomes standard, but not everyone is happy about it.
With growing awareness of security and privacy concerns due to revelations of intelligence agency spying and newsworthy data breaches, encryption is finally becoming more of a default. Certain organizations like law enforcement and intelligence agencies are unhappy about it, under the belief that it will adversely impact safety.
4. More major flaws in widely-used software that had escaped notice by the security industry over the past 15 years.
From Heartbleed to Shellshock, it became evident that there are significant pieces of insecure code used in a large number of our computer systems today. The events of 2014 have boosted the cybercriminals’ interest in typically less-considered software and systems for the years to come – so you should be preparing your response strategy.
5. Regulatory landscape forces greater disclosure and liability, particularly in Europe.
The law moves slowly compared to the technology and security fields, but massive regulatory changes that have been a long time coming are nearly here. It is likely these changes will trigger consideration of more progressive data protection regulation in other jurisdictions.
6. Attackers increase focus on mobile payment systems, but stick more to traditional payment fraud for a while.
Mobile payment systems were the talk of 2014 after Apple stormed ahead with Apple Pay. Cybercriminals will be looking for flaws in these systems, but the present designs have several positive security features. Expect cybercriminals to continue abusing traditional credit and debit cards for a significant period of time as they are the easier target for now.
7. Global skills gap continues to increase, with incident response and education a key focus.
As technology becomes more integrated in our daily lives and a supporting pillar of the global economy, the cybersecurity skills shortage is becoming more critical and broadly recognized by governments and industry. This gap is growing larger with some governments forecasting that they will need until 2030 to meet the present demand for security professionals.
8. Attack services and exploit kits arise for mobile (and other) platforms.
The last few years of cybercrime have been hallmarked by the rise of products and services to make hacking and exploitation point-and-click easy. With mobile platforms being so popular (and increasingly holding juicy data too) it won’t be long until we see more crime packs and tools focusing on these devices explicitly. We may also see this trend come to fruition for other platforms in the IoT space as these devices proliferate around us.
9. The gap between ICS/SCADA and real world security only grows bigger.
Industrial Control Systems (ICS) are typically 10 years or more behind the mainstream in terms of security. Over the next couple of years I anticipate we will see a number of far more serious flaws exposed and used by attackers as motives vacillate between state-sponsored attacks and financially motivated ones. In short, it is an area where many are at significant risk.
10. Interesting rootkit and bot capabilities may turn up new attack vectors.
We are in the process of changing major platforms and protocols from those that we have relied on for some time and these lower level changes will bring interesting lower level flaws that cybercriminals may be able to capitalize on. We are on the edge of a mass of major changes to the old guard technology standards. Watch this space for old wounds re-opened and major new security flaw categories.
That’s just a taste … read the full report here (it’s a free download, no registration necessary): Security Threat Trends 2015.
Read the original article, here.
Sophos announced the release of Sophos Cloud Server Protection, a high performance malware protection solution designed specifically for servers. The solution expands Sophos Cloud to a comprehensive security platform designed to protect desktops, laptops, mobile phones, tablets and now servers with the most effective and simplest to manage business security offering available. Servers store large amounts of sensitive information and have become popular targets for cybercriminals. To secure servers, administrators have traditionally had to choose between desktop-oriented security software and complex, expensive server-specific security tools. Perhaps this is why two thirds of the IT professionals surveyed on Spiceworks identified the complexity of learning, configuring and maintaining server security software as an “important” or “very important” concern.
The new Sophos Cloud Server Protection solution delivers malware protection, host intrusion prevention and web security, as well as clear visibility into the current security status of all managed servers via a simple web-based interface. The new offering from Sophos is also the only server security product that can continually monitor the server environment, detect new applications on an ongoing basis and intelligently adjust policies to maintain operational efficiency.
“If compromising desktops is like stealing a wallet, then hacking a server is like robbing a bank,” said Bill Lucchini, SVP & GM for Sophos Cloud. “Today’s businesses need the most up-to-date protection, and Sophos Cloud Server Protection gives overtaxed IT personnel an innovative, high performance and simple to manage solution for securing server environments.”

“As part of the recent Sophos Cloud beta program, I was able to preview the Server Protection functionality added into the product,” said Scott Hartung, IT Director, The Rivett Group . “We currently use Sophos Cloud to protect our Windows, Mac, and mobile devices. I like the fact that Sophos truly understands server security, and I can see that this new version of Sophos Cloud will help me reduce the time spent on maintaining server security.”
“We are finding that more of our customers are trying to support a geographically diverse workforce,” said Pete Greco, VP of Sales and Technology, Productive Corporation. “Sophos Cloud with Server Protection provides comprehensive visibility and manageability, regardless of where employees and their devices are located. With Sophos, we are certain our clients’ workforce is both secure and available.” Watch a video about Sophos Cloud Server Protection and sign up for your 30-day trial right now.
We’re pleased to commence the roll-out of our latest major UTM software update: UTM Advantage (9.3). More and more organizations are switching to Sophos UTM for their next firewall to take advantage of our all-in-one protection with on-box reporting, simplicity and performance. This release continues to add even more value and protection while making things easier for everyone. If you’re not already a Sophos UTM customer, UTM Advantage (9.3) adds to the 5 great reasons why you should switch to a better Firewall. Watch our brief demo video of what’s new in UTM Advantage (9.3). The complete release notes are provided below.
UTM Advantage (9.3) brings dozens of new features including:
Stronger protection for web, email and WAF
Smarter Wi-Fi performance and hotspot management
Better everywhere-deployment flexibility
Release Availability and Roll-out Timing
We are rolling out UTM Advantage (9.3) in three main phases over the coming weeks to provide a great upgrade experience for everyone:
- Phase 1: We are starting with an initial Up2Date to select customer systems today.
- Phase 2: Around mid-November, we plan to make the installation package generally availability for download via our FTP site as we continue the release roll-out to additional systems. Any customers wishing to update their UTM as soon as possible can take advantage of the manual download at this time. We’ll post a notification here on the Sophos Blog when the download is available.
- Phase 3: By mid-December we will have rolled-out the Up2Date package for all customer installations including HA/Cluster environments.
Release Notes for UTM 9.300
Major New Features:
- Live AV Look-ups in Email Protection
Introduced previously in UTM 9.2 for Web Protection, Live AV look-ups now come to UTM Email Protection. This option will improve the malware detection rates by consulting the cloud infrastructure from SophosLabs in real-time for possible threat matches. Look-ups that fail will still be scanned by the AV engine, and as part of our global feedback network unknown files will be sampled for execution and deep analysis by SophosLabs to benefit the global community while allowing you to tap the knowledge gained by these events worldwide.
- SPX Email Encryption – Self-Registration
With the self-registration feature, recipients of our unique SPX encrypted email now have the option to register themselves through an online portal where they will be able to create, reset and recover passwords to access their encrypted emails. This eliminates the need to manually communicate passwords to recipients of encrypted emails, and allows them to use the same password (which they will remember) for all encrypted emails. It makes SPX Email Encryption simpler for everyone.
SPX Email Encryption – Support for Attachments on Reply Portal
SPX encrypted email recipients are now able to add attachments when securely replying to the sender using the SPX online portal. This allows for full encryption of all communications both ways.
- URL Tagging
With UTM 9.2 we introduced the Website List feature where customers can add URLs and override the site category. URL tagging extends this feature by allowing customers to apply custom tags, or labels to URLs, in effect creating their own custom site categories. They can then use these tags in Web Policy just like regular system categories. For example, if a customer has a restrictive policy but needs to access customer websites that would otherwise be blocked, they can add their customer sites to the Website List, tag them as ‘Customer Sites’ and then modify the policy to enable access to the ‘Customer Sites’ tag.
- Browsing Time Quotas
Many organizations want to allow users a limited amount of personal browsing time during the day. In many situations, limiting this to specific times of day does is too restrictive. With this new feature in Web Protection, administrators can allocate time quotas to specific sets of sites or categories for specific users or groups. Users can choose when to consume their time quota throughout the day. When they browse to a quota site, they will be warned that they’re about to use their quota. When a quota expires, they’ll be informed accordingly. Administrators can reset quota if necessary through the Web Protection Helpdesk area of the UTM.
- Selective HTTPS Scanning
To allow more flexibility and provide better performance we have implemented an option to allow selective HTTPS filtering. This allows organizations to balance the need for security or visibility into some encrypted traffic, with the privacy and performance concerns that come with decrypting all HTTPS content. For example, customers can focus on performing important scans in HTTPS like (a) the ability to detect malicious content in uncategorized sites, (b) the ability to identify search terms and enforce safe search for Google and other search engines, and (c) the scanning webmail traffic for DLP only for specific sites. Previously, HTTPS decryption had to be enabled for all traffic, with exclusions being set up for individual sites where necessary.
- Support for SG1xx Wireless Hardware
This release will add support for new SG 1xx wireless models we are going to introduce later this year.
- Hotspot Improvements
This release improves our hotspot capabilities with a few new features: First, we built an interface to communicate with Micros Fidelio hotel management software via its FIAS protocol. Second, we have implemented HTTPS support for hotspot login pages. And finally, hotspots can now be configured in a more multi-tenant-like fashion by restricting the “Allowed Users” option on a per-hotspot basis.
- Multiple Bridge Support
Many more advanced firewall configurations can be solved by allowing more then one network bridge. With this release we added support for multiple bridges. With introduction of this feature we at the same time cleaned up the configuration options in the UTM WebAdmin by moving the bridge configuration directly into the interfaces pane to allow you user-friendly and simple control over all aspects of your interface configuration.
Other New Features:
- VLAN DHCP & Tagging
We removed some restrictions around VLANs to make them easier to administer: you can now allow DHCP on VLAN interfaces and you can now tag and untag interfaces on the same hardware.
- True-File-Type Detection
In our web and mail proxy we now traverse archive files (zip, rar, etc.) to detect the types of files inside. This allows granular policy enforcement based on file types included in an archive rather than blocking archive files in general.
One-Click Secure Sophos Customer Support Access to UTM
With an ever increasing number of Sophos global support sites with different IP ranges, it can often be challenging to enable Sophos Support access to the UTM via WebAdmin and SSH . As a result, we’ve implemented a feature that enables administrators to easily enable access to the UTM by Sophos Support upon request with just a single-click.
- WAF Allow/Block Lists
For the Web Application Firewall we’ve now added support of lists to allow and block IP ranges. This is configured in the site paths settings.
- WAF Wildcard Extension
Exceptions for internal servers now allow wildcards also in the middle of the server path. This allows administrators to easily add exceptions for multiple servers effectively eliminating the need to maintain long lists in WebAdmin.
- WAF Prefix/Suffix Option
Some environments, most notably Microsoft servers like Exchange and Sharepoint, require UPN/domain-style user names for log in. By adding an option to append a prefix or suffix to user-names customers now are able to add a default domain (for example) to facilitate this in order to streamline the user experience.
- HyperV 3.5 Support
The UTM 9.3 now fully supports Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2012 R2. We’ve also incorporated MS Integration Tools v3.5 for Hyper-V which include the latest drivers and additional capabilities like high availability and load balancing.
- Improved performance for URL categorization
In version 9.2 we introduced Live URL Filtering, a new way of doing URL categorization lookups to our cloud data services that offers better performance than the existing CFFS system. On the UTM it provides better local caching of commonly-visited site data. In the cloud, it provides greater responsiveness and automated scaling. With version 9.3 we are enabling this feature by default. Although the URL data used has not changed, this new system will only return one category for each site. This may impact the operation of policy for a small number of sites that previously had more than one category.
Read the original article, here.
Recently recognized as an enterprise mobility management (EMM) market leader by Forrester, Sophos today announced the immediate availability of additional security and device management capabilities for the Android mobile platform. These simple-to-deploy, yet powerful solutions deliver mobile security for businesses of any size. IT professionals can now allow employees to take advantage of all that the Android platform has to offer without putting sensitive data at risk.
According to Nielsen, mobile users are now spending 30 more hours per month on mobile devices than on their laptops, and cybercriminals are taking notice. SophosLabs has identified over 1 million new and unique pieces of Android malware and potentially unwanted applications (PUAs) just since the beginning of 2014. Android malware has grown 1,800 percent over the last two years, by far the fastest growing of any attack surface.
Approximately two billion mobile phones and tablets will be shipped this year, 85 percent of those will be Android devices, and 75 percent of apps on those devices will fail basic security tests. With a mix of corporate-owned and employee-owned devices being used for business anywhere and anytime, organizations clearly require a more comprehensive approach to mobile security. And that’s where Sophos comes in.
Sophos delivers comprehensive Android protection
Sophos Cloud now features Android support, delivering one central and hosted console for managing both desktops and mobile devices. With a simpler user-centric approach, it helps keep corporate information safe with mobility management features like remote lock, remote wipe, password reset, theft protection, Wi-Fi configuration and Microsoft Exchange setup help.
Sophos Mobile Security brings a powerful new antivirus engine and web protection technology to the Android platform. Without reducing device performance or diminishing battery life, this powerful engine provides comprehensive malware protection. In fact, Sophos received a perfect 100 percent Android malware detection rate in the latest AV-Test.
Sophos is the only enterprise mobility management vendor that offers built-in antivirus capabilities and web filtering without relying on third-party software. Additionally, only Sophos delivers a centrally managed, cloud-based mobile security solution that is compatible with Windows, Mac, iOS and now Android platforms – providing simple and complete security for businesses of all sizes.
In addition, Sophos today announced the new Sophos Anti-Malware SDK for Android, which features the core Sophos antivirus engine. Now Telco providers, mobile carriers and other IT vendors can integrate Android anti-malware technology into their own mobile offerings.
With an increasing number of viruses and other malware samples entering the corporate network via mobile devices, it’s more important than ever to deploy Android management and security technology to ensure that sensitive corporate data stays out of the wrong hands.
“Sophos mobile security technology helps us remain secure and shielded from data loss and unexpected costs without reducing staff performance,” commented Josh Moore, network engineer at FF Thompson Hospital. “We get both protection and functionality with Sophos.”
“Sophos has increased our control over various mobile devices, including the Android devices we have deployed,” said David Bridgman, IT security manager at Northcentral University. “With the newest release, the most notable benefit—in addition to the added security—is that there is no difference in our users’ experience.”
“Well over half of all mobile apps fail basic security measures, and these sobering figures are on the rise,” said Dan Schiappa, senior vice president and general manager, end user protection group, Sophos. “Every day the risk is growing, and we’re proud to offer the most comprehensive mobile protection for businesses to keep confidential information out of the wrong hands.”
Watch the Sophos Android Security video now
Read the original article, here.
Every quarter Sophos announces the SPAMPIONSHIP league highlighting the worst offending countries for spam. As we approach Halloween, the Q3 (July-August-September) results for 2014 are in. The Spampionship is a clear reminder that while spam is a global problem, prevention begins at home. That’s because most spam comes from so-called “zombies” – computers infected by malware that puts them under the remote control of cybercrooks who could be on the other side of the world, and probably are.
For example, SophosLabs has clocked a single infected computer sending more than 5,000,000 spams in a single week, illegally promoting an ever-changing cocktail of shady products and services, and pumping out malware in attachments.
And as SophosLabs monitor where spam comes from, they are also simultaneously mapping out where in the world the zombies are. As Cybersecurity Awareness Month draws to a close, it’s time to be part of the solution, and go zombie bashing with Sophos!
Just download and run Sophos’ free Virus Removal Tool to check your computer isn’t infected, and do your bit today!
In this Sophos Naked Security article, Sophos expert Paul Ducklin provides his analysis of the latest Spampionship results.
Highlights of the Q3 2014 Spampionship
Being high on the spam-sending charts, means you’re also high on the scale of people who put their personal information, finances, and even identity at risk.
The Spampionship is the league that everyone wants to lose, and below are the results for Q3 (July, August, September) of 2014.
The “Dirty Dozen” countries

Measuring spam entirely by volume-per-country is a little unfair, because populous countries like China, or very well-connected, like the USA, inevitably bubble up to the top of the list.
Things get fairer – and more interesting – when each country’s spam volume is divided by its approximate population:

Read the original article, here.
Back in the summer we ran a little survey on SpiceWorks and almost 400 Small and Medium Business IT managers gave us their view on the main challenges they have with their current firewall. But some of the results weren’t exactly what we were expecting.
The #1 rated issue was the lack of reporting options
 35% of respondents said their firewall provides insufficient reporting and 22% also cited lack of visibility into infected machines which speaks to a lack of useful insight too. Users are hungry for bandwidth and regulatory compliance is Insufficient reporting becoming increasingly important so it’s not really surprising that IT managers crave a better view into what’s happening on their network.
35% of respondents said their firewall provides insufficient reporting and 22% also cited lack of visibility into infected machines which speaks to a lack of useful insight too. Users are hungry for bandwidth and regulatory compliance is Insufficient reporting becoming increasingly important so it’s not really surprising that IT managers crave a better view into what’s happening on their network.
What is surprising is that so few firewall vendors offer their users what they need. Compare the leading UTM/Firewall vendors and you’ll find just one who has over 1000 reports available built-into the appliance. I’ m sure you can guess who check here if you can’t!
At Sophos we prioritize reporting and in addition to the on-box reports we also offer Sophos iView our dedicated virtual reporting appliance for those that simply need more reports or want to correlate reporting across multiple appliances.
Complexity is still the enemy of security
 We all know IT threats are coNot easy to managemplex and the survey confirms that all too often the products designed to solve security problems are far too complex too.
We all know IT threats are coNot easy to managemplex and the survey confirms that all too often the products designed to solve security problems are far too complex too.
Ease of use only narrowly misses out on top spot with 34% saying its a frustration.
Adminstrators need a strong link between seeing what is happening and doing something about it. This is essential in security products where a weakness at one point on the network can quickly become a problem for the entire organization.
Advanced threats? We’re covered, at least we think we are!
 Other surprising results were hreportingow few people cited lack of protection against advanced threats and poor performance as weaknesses. We hear a lot about how traditional firewall and antivirus technologies can no longer protect against sophisticated Advanced Persistent Threats. This is seemingly a non-issue for 90% of those surveyed.
Other surprising results were hreportingow few people cited lack of protection against advanced threats and poor performance as weaknesses. We hear a lot about how traditional firewall and antivirus technologies can no longer protect against sophisticated Advanced Persistent Threats. This is seemingly a non-issue for 90% of those surveyed.
IT managers are either confident their firewalls have the necessary protection place, like command and control detection and sandboxing, or simply have more pressing needs and don’t see advanced threats as their concern but for governments and larger enterprises to worry about.
Performance matters or does it?
![]() That performance rates so lowpoor perf is possibly the biggest surprise. Performance is often a key concern for buyers when selecting a firewall with technical data, sizing guides and comparative reports providing useful guidance for buyers to select the right firewall for their needs. This result suggests the guidance and advice of channel resellers is proving effective and buyers are right-sizing their firewalls.
That performance rates so lowpoor perf is possibly the biggest surprise. Performance is often a key concern for buyers when selecting a firewall with technical data, sizing guides and comparative reports providing useful guidance for buyers to select the right firewall for their needs. This result suggests the guidance and advice of channel resellers is proving effective and buyers are right-sizing their firewalls.
All in all some interesting results that suggest reporting and ease of management should be carefully looked at when selecting a replacement firewall. But maybe this is not really that surprising after all as these areas do reflect the core focus of network security managers. Without visibility into what’s happening, or the ability to quickly put protection in place an IT Manager’s life becomes very difficult.
Sophos UTM – ease of use and on-box reporting as standard
Sophos UTM is designed to be easy to use and includes extensive on-box reporting as standard – no need for additional hardware or subscriptions. Our new SG Series appliance all include a hard drive or a solid-state disk, giving you comprehensive reporting that you can access in seconds. So you can see what’s happening on your network in real-time and quickly access historical data.
Watch this short video to see it in action. On-box reporting as standard is just one of the reasons to make your next firewall a Sophos firewall.
Read the original article, here.
Dropbox usernames and passwords were leaked online this week. It’s the latest in a string of recent data breaches involving compromises of third-party websites that take advantage of password re-use to get at users’ accounts on multiple services. In 2014 alone, millions have had their private information and passwords compromised, leading to what some are calling data breach “fatigue.” Dropbox was quick to respond, denying a breach on their end while urging their users to enable tighter password security measures. Dropbox’s response was refreshing when compared to that of other major brands, such as Home Depot, which chose to communicate very little with the public, distributing only a few carefully crafted press releases.
As businesses learn to navigate their way through crisis management in the digital age, there are solutions that can mitigate risk, greatly saving these companies both dollar value and reputation value. Sophos offers a complete suite of solutions to ensure your customers’ data is safe and secure. A major component of this is our SafeGuard Encryption solution. Simply put, encryption adds the crucial layer of security in situations where a customer’s data is breached. Even if a bad guy gets hold of a user’s data, it’s utterly useless when encrypted, whether that data is at rest or in motion (e.g, being uploaded/downloaded from the cloud).
Although this breach was not due to a compromise of Dropbox itself, are you confident that your important files are safe when stored in the public cloud? In the case of cloud storage services, of which Dropbox is one of many, encryption prevents any breach, regardless of who caused it, from resulting in the loss or exposure of data. Using an encryption solution where the keys and control mechanisms are stored far from the potential points of compromise means you can control how data is stored, and manage who has access.
Learn more about SafeGuard Encryption
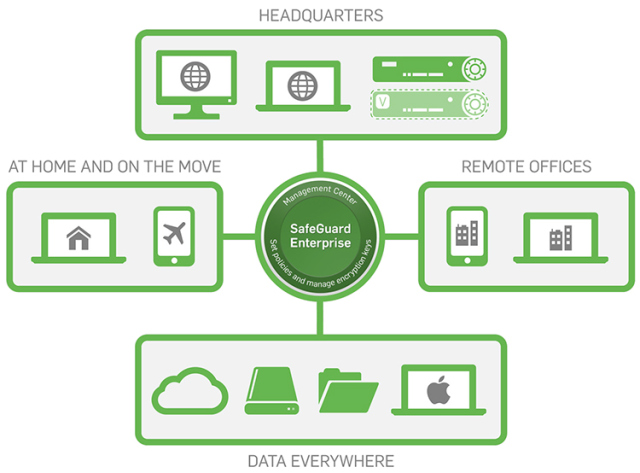
Sophos SafeGuard Encryption solves the major challenge of managing encryption across multiple platforms, devices, and cloud environments. Users and IT staff can share data safely between Windows, Mac and mobile devices – securing data wherever it lives and wherever it is sent. For more information about SafeGuard Encryption, get our free whitepaper Managing BitLocker With SafeGuard Enterprise (registration required).
Or download our Encryption Buyers Guide to learn more about how to choose the best encryption solution for your needs. You can also read interesting articles about SafeGuard Encryption, here and here.
Read the original article, here.
Sophos announced additions to its range of SG Series firewall/UTM appliances, WiFi access points, and the availability of Sophos iView, a new dedicated virtual reporting appliance. By extending its Network Security portfolio with new entry-level and enterprise class appliances, Sophos now provides businesses of any size and the channel partners that serve them with the flexibility to consolidate their security with a complete proven solution set.
Sophos SG Series Appliances
In April 2014 Sophos released the first of its new generation of network security appliances, the Sophos SG Series. Today, Sophos announced six additional firewall appliances, meaning that Sophos customers and partners can now choose from 12 SG Series models. As with the existing models, each uses the latest Intel multi-core technology to provide optimal performance. The new appliances include four desktop models ideal for small office deployments and two new 2U models that utilize the fastest Intel Chips and deliver extensive redundancy and customization features. Further desktop models will be available later in the year with integrated wireless connectivity, including two which support the 802.11ac standard.

Sophos iView
The release of the Sophos iView virtual appliance addresses what a recent Sophos survey on Spiceworks of SMB IT managers identified as their most significant frustration with existing firewalls from any vendor – insufficient reporting. This was the number one complaint with 35 percent of respondents saying they’d like greater reporting options. With over 1,000 built-in reports, including regulatory compliance reports, Sophos iView will give IT managers the extra depth they need. Users can also build their own custom reports and dashboards, focusing on problem areas or users on their network. Available as a virtual appliance only, Sophos iView supports VMware, Hyper-V, Citrix, and KVM virtual environments.
As a dedicated reporting appliance, Sophos iView can offload reporting duties and provide a range of added capabilities such as:
- Compliance reporting for industry standard regulations such as HIPAA, PCI, SOX, and GLBA
- Consolidated reporting across multiple UTM firewalls for a complete view of all network traffic from a single console
- Long-term persistent log management and storage for security and backup with convenient access for audits or forensics
- Licensing that is based on storage requirements, with the entry level vSI-Light including 100GB of storage and the vSI-Unlimited

Wireless Access Points
In addition to the SG Series and iView appliances, Sophos also announced the AP 100, the first in a new generation of wireless access points that support the latest 802.11ac protocols, and an entry level access point, the AP 15. As with previous Sophos wireless access points, the new AP15 and AP100 models can be managed directly from the Sophos SG Series appliances, meaning the wireless network is tightly integrated with the firewall protection.

You can read the original article here.
Sophos announced that it has acquired cloud-based security firm Mojave Networks of San Mateo, Calif. This acquisition will strengthen Sophos cloud-managed and appliance-based security solutions. To Sophos Cloud, an integrated cloud-managed security offering, Mojave will add a rich cloud-based web security solution. And to Sophos’ line of network security hardware it will enable hybrid deployment options (SaaS and non-SaaS) to meet diverse web security needs. An increasingly mobile workforce and an explosion of mobile devices have created a serious challenge for IT. To safeguard valuable corporate data and to secure roaming devices, Mojave’s innovative security platform provides an effective cloud-based network security solution that is easy to deploy and manage. It will allow Sophos customers to benefit by providing:
- A cloud-based web filtering engine enabling full protection for web interactions without requiring additional on-site technology
- Near instantaneous protection from emerging threats by supplying real-time threat intelligence from the cloud
- A simple and intuitive management experience designed for small and mid-market enterprises or pragmatic enterprises of any size
- A zero-compromise approach to security across Windows, Mac, iOS, and Android devices, delivering context-awareness, visibility and seamless protection whether they are on or off the corporate network
“Mojave Networks is a young innovative company that has built a leading platform right at the intersection of three cutting-edge areas of security: cloud, web security, and mobile,” said Kris Hagerman, CEO, Sophos. “We’re dedicated to delivering security that is both powerful and comprehensive, but also simple. By integrating Mojave Networks’ technology into Sophos Cloud, we’re extending our leadership position and enhancing an offering that is already one of the fastest growing products in Sophos’ history.”
“We are proud of the work we’ve done at Mojave to pioneer a cloud-based approach to mobile and web security that offers unrivaled protection from malicious threats, security for mobile workers, and uniform policies across platforms,” said Garrett Larsson, CEO of Mojave Networks. “As part of Sophos we can continue to pursue our vision of comprehensive security for a mobile workforce at an accelerated pace, as we take full advantage of the rapid growth of Sophos Cloud, Sophos’ world-class community of more than 15,000 partners, and Sophos’ global presence. We’re excited to join such an innovative and disruptive leader in the IT security space.”

Sophos plans to integrate Mojave Networks’ technology into its fast-growing Sophos Cloud product line in early 2015 and then later in 2015 into appliance-based network security solutions. This will allow Sophos partners to offer their customers an integrated security platform that brings together best-of-breed PC, Mac, mobile, and network protection abilities through a single cloud-based console. This represents another leap forward in delivering comprehensive protection to organizations seeking enterprise-class security without enterprise-class complexity.
You can read theoriginal article here.
InfoCom World Congress is the largest event on digital technologies in SE Europe, attracting more than 3,500 delegates per year. It successfully records and captures for many years to run the course taken and convergence happening in Technology, Informatics, Telecommunications & Media sectors. The 16th InfoCom World titled «Techonomy: Time for Synergies!» will take place on October 21, 2014 at Divani Caravel Hotel. This year’s conference takes place in a period when special emphasis is given to technology, business strategies and synergies that are now unanimously recognized as a driver for growth.
NSS could not be absent so is one of the Sponsors of the conference. Come to chat with us !!
A lot has changed since 1995, the last time a major European law was passed on the subject of data protection (the Data Protection Directive 95/46/EC). For example, mobile devices are ubiquitous, and it’s not unusual to carry two or even three at a time. Meanwhile, sensitive company data is moving outside the safety of the traditional corporate security perimeter. Employees email documents to themselves, access data from personal smartphones and tablets, and store data in the cloud. Major data breaches are commonplace today, putting customers at risk of identity theft and financial loss, and businesses at risk of losing customer and investor loyalty. European businesses are not prepared to meet regulatory requirements outlined in the EU Data Protection Regulation, due to be enacted by the EU parliament in 2015. That’s the story told by a survey of 1,500 office workers in the UK, France and Germany, conducted by Sophos. Although a large majority of poll respondents (84%) agree that stricter data protection requirements are needed, most lack confidence that their employers are compliant (77%), and many do not know what type of data protection their companies currently have in place.
During a roundtable discussion about the survey, our security experts talked about the current state of data protection and how the new requirements might impact businesses. Anthony Merry, director of product management in the data protection group at Sophos, said companies have to get a better understanding of not just what regulations require, but what data protection actually is. “Many of the companies I talk to still do not understand what data protection is, why businesses need to do it and why it is important, and that needs to change,” he said, according to ComputerWeekly.
Some of the proposed changes to the EU Data Protection Directive include huge fines for non-compliant companies in the event of a data breach — as much as 5% of global turnover, or €100m, whichever is higher. Compared to relatively lax data protection laws in the United States, such punitive laws could be seen as harmful to businesses.
However, if companies are encrypting their data — on disks, mobile devices, storage drives, and in the cloud — they don’t have to worry as much. “If data is encrypted, even if IT systems are breached, companies will not be liable under the law,” Anthony said. Unfortunately, businesses in the countries we surveyed have a long way to go to complete data protection. According to our survey, only 62% of UK companies are encrypting laptops, along with 36% in France and 56% in Germany. Encryption of mobile devices is even farther behind: 41% in the UK, compared to 21% in France and 32% in Germany.

Learn more about data protection
Sophos SafeGuard Encryption solves the major challenge of managing encryption across multiple platforms, devices, and cloud environments. Users and IT staff can share data safely between Windows, Mac and mobile devices – securing data wherever it lives and wherever it is sent. For more information about SafeGuard Encryption, get our free whitepaper Managing BitLocker With SafeGuard Enterprise (registration required). Or download our Encryption Buyers Guide to learn more about how to choose the best encryption solution for your needs.
Jan
a conference featuring prominent Chief Executives representing mobile operators, device manufacturers, technology providers, vendors and content owners from across the world.
Ipoque participates at industry tradeshows and conferences around the world. If you are interested in viewing a full demonstration of Ipoque’s products and solutions join at GSMA Mobile World Congress 2013.
25 – 28 February 2013
Fira Gran Via, Barcelona
Booth #6E126 – Hall 6
For more information click here
Jan
coverage of your Jacarta solution by using Vibration Sensors with Adjustable sensitivity and Airflow Sensors to ensure you know of AC problems.
Generally, interSeptor systems have been designed for ease of installation and use. Multiple temperature/humidity sensors are provided out-of-the-box to ensure individual rack and room monitoring can begin immediately as well as many others, essential for your environmental monitoring needs. Alternative cable lengths are available with all Jacarta Go-Probe sensors if required.
For more information about Jacarta sensors, click here
The email reads:
Hello,
A Secure Document was sent to you by your financial institute using Google Docs.
Follow the link below to visit Google Docs webpage to view your Document
Follow Here. The Document is said to be important.
Regards.
Happy Emailing,
The Gmail Team
Phishing emails aren’t exactly rare, but this one caught my eye. In addition to being a somewhat plausible lure, it is an equal opportunity exploit. If you click the link you are presented with a phishing page hosted in Thailand. The page not only asks for your Google credentials, it also suggests it will accept Yahoo!, Outlook.com, Hotmail, AOL, Comcast, Verizon, 163.com or any other email account.

Of course, filling out this form can only end in tears. Your details are sent off to the compromised servers for whatever purposes these thieves desire. You might think, “So what? My Gmail isn’t full of secrets that will destroy my nation/life/career.” You would likely be wrong, because your email is the key to unlocking much of your online identity. Forget your banking password? No worries, they will email you a password reset link. Does your company utilize cloud services? Your email account is likely key to accessing these systems. Phishing is an amazingly successful technique. Just ask the Syrian Electronic Army, who with little technical talent have been able to compromise some of the most powerful media organizations in the world. As an IT administrator, these are opportunities to educate your staff on the risks.

This might not be the most convincing of the phishes that are out there, but it is a useful tool to educate your staff. Many organizations are using Google and other cloud service providers to provide critical IT services. At first glance this could be very believable. What do I do to avoid being a victim? I create shortcuts in my browser for all sensitive services. If I need to access my email, bank or other online service, I don’t click the link; I click the favourite.
You can read the original article, here.
Jan
Keenan brings more than 20 years of sales and sales management experience to Sophos, including 13 years with SonicWALL, where he most recently built a new sales organization for mid-market accounts and developed the division’s channel strategy. As vice president of North America Sales, Keenan grew the business by fostering key relationships with the company’s channel partners.
“John Keenan is widely respected by the security channel, and I am thrilled to welcome him to Sophos. He brings a proven track record of success in the security space and has winning experience in leading channel and sales teams,” said Michael Valentine, senior vice president of sales for Sophos. “Every day, the Sophos team is working hard to be the preferred vendor in security for the channel and customers. Our products, our people and our partner programs continue to gain industry accolades. In bringing John aboard, we have an ideal leader for continued growth in our North American business.”
“I am excited to join Sophos; the company’s value proposition of ‘security made simple’ clearly resonates with customers and the channel,” said Keenan. “The company’s relentless focus on empowering the channel, a best-in-class portfolio of endpoint, mobile, server and network solutions, and the opportunity to contribute to Mike Valentine’s winning team made my decision to join Sophos an easy one.”
Jan
This joint solution provides a highly efficient, scalable and effective network-based platform for service providers and enterprise networks. In turn, they can deliver increased levels of security to their consumer, business and internal customers without any need for end-device software or new network elements. Utilizing DNS, a lightweight, multi-network, multi-end device protocol, this solution is available for both fixed (xDSL, Cable, NBN) and wireless networks offering protection for PCs, tablets, smartphones, wireless dongles, games consoles, and any IP- enabled device.
“Sophos provides threat intelligence feeds to our network, gateway and endpoint security products. Our partnership with Nominum extends this intelligence to the DNS level, offering security in the core operations of the network,” said Stuart Fisher, Managing Director, Sophos APAC. “SophosLabs identifies more than 30,000 new malicious URLs daily. By adding intelligence from the DNS into the equation, the joint Nominum–Sophos solution offers maximum protection for all network users.”
“Both our companies are highly committed to making the Internet a safer, more secure place for users. Considering the value this partnership will bring into our core markets such as Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, ASEAN, China and India, we anticipate we will see a high-level of adoption.”
“By joining our partner ecosystem, Sophos and Nominum can provide increased protection to Internet users across multiple platforms,” said Brian McElroy, Vice President of Business Development, Nominum. “A joint Nominum-Sophos security solution offers near real-time (zero day) in-network protection, like the Interpol-fed Nominum Content Blocking solution deployed in Australian carrier networks, which protects Internet users from child sexual exploitation content. Adding this new policy and protection in-network from malicious threats makes great sense.”
Jan
Bolstered Channel Team
Sophos has recently strengthened its channel team with the appointments of Kendra Krause, Americas channel chief and Karen Delaney, Australia & New Zealand channel chief.
Prior to Sophos, Krause served most recently as Fortinet’s Channel Sales and Operations vice president. She previously served in channel sales and marketing roles at SonicWall, WatchGuard and CDW. Delaney spearheaded channel strategies at IBM, Acer and Dell/SonicWALL. Since joining the company, she has played an integral part in bringing Distribution Central and Connector Systems onboard as Sophos’ first distribution partners in Australia and New Zealand.
Channel Honors
Sophos has received considerable recognition for both its channel team and channel program. Included among this year’s honors:
- CRN UK’s Channel Sales & Marketing Award—The Sophos Partner Program was declared “best in the UK”. This award recognizes and rewards the achievements of those individuals and teams responsible for making the UK IT channel so successful.
- CRN’s 2013 Top Women of the Channel—Several Sophos’ channel leaders were among the honorees: Kendra Krause, vice president of Americas channel sales, Amy Gelpey, senior channel marketing manager, and Regina Vignone, director of sales.
- CRN’s Power 100 Most Powerful Women of the Channel—Kendra Krause was among the elite list of executives recognized for their channel achievements.
- CRN’s 2013 5-Star Partner Rating—The 5-Star Partner Program rating recognizes an elite subset of Partner Program Guide vendors that give solution providers the best partnering elements in their channel programs.
- CDW—Sophos was named Sapphire Partner of the Year for 2012; Sophos was one of CDW’s fastest-growing partners of the year.
Key Channel Recognition for Sophos UTM
The company was also highlighted in the 2013 CRN Annual Report Card (ARC). This prestigious study is considered the definitive benchmark for measuring excellence in the IT Channel community and recognizes the top-rated vendor partners in the industry. Sophos was given the highest honors for product innovation in the Network Security Appliances category for its unified threat management (UTM) solution, Sophos UTM. Winners were announced live at an awards reception on Tuesday, August 20, 2013, at the XChange 2013 event in Washington, D.C.
“At Sophos, every year is the year of the partner, but this year in particular has truly demonstrated our ‘channel-first’ commitment—from hosting the largest partner conferences in our history to a game-changing new MSP program, our focus is our channel,” said Mike Valentine, senior vice president, worldwide sales, Sophos. “We offer partners the most complete IT security value proposition—proven and award-winning security solutions that are simple to use, combined with the industry’s most powerful channel program. And with an aggressive roadmap that features an impressive array of offerings, we’re very excited about delivering partners even more value in the coming months to help them grow.”
To learn more about the Sophos Partner Program, please click here or visit http://www.sophos.com/en-us/partners.aspx.
Jan
Increased migration to virtual servers and the ever-growing threat of attack on critical data are presenting new challenges to IT professionals, as they look to maintain high performance and density of servers, without compromising on security. Sophos Server Protection addresses these challenges by integrating agentless antivirus for vShield and full antivirus clients for Windows, Linux, Mac and UNIX into one centrally managed product.
“Servers need the best protection against malware, but managing that protection while maintaining server performance across a diverse environment has inevitably increased complexity and demands on time,” said John Shaw, vice president of product management, Sophos. “We’ve delivered on what matters – server performance and security. Sophos Server Protection provides a single, easy to use management console to assign policies, view alerts and generate reports across platforms. Even licensing, often the bane of IT professionals, is straightforward: one server, one license, any platform.”
Standalone and virtual systems use fewer resources with Sophos Server Protection than with conventional antivirus products. Agentless scanning via vShield Endpoint prevents scan and update storms, automatically protecting every Windows virtual machine on the host through a centralized virtual security appliance. Systems without vShield benefit from a full featured client optimized for performance. Advanced features, including HIPS, application control, and device control, are also included for select platforms.
Sophos Server Protection supports a broad range of server and virtualization platforms, including Windows, Linux, UNIX, Mac, Hyper-V, vSphere/ESX/ESXi and XenServer. It provides proven protection against known and unknown threats, supported by real-time communication with SophosLabs. The Windows client offers additional layers of security, including HIPS, application control and patch assessment.
“Sophos Server Protection is server security made simple, because at Sophos we believe good security shouldn’t have to require the undivided attention of the IT team to make it work. Sophos Server Protection secures your business’s critical assets, without sacrificing performance or adding unnecessary complexity,” concluded Shaw.
Sophos Server Protection will be showcased at VMworld, which takes place in San Francisco between August 25 and 29. Sophos is a VMware Elite Technology Alliance Partner.
Υou can read the original article here.
Jan
One risk is that attackers will have the advantage over defenders who choose to run Windows XP because attackers will likely have more information about vulnerabilities in Windows XP than defenders. The problem is, of course, that once patches stop being provided for newly-discovered vulnerabilities, any problems that are found for more recent versions may well be backwards-compatible with XP. As details of these issues will be widely publicised, for very good reasons, there’s bound to be plenty of research going on into which ones can be used to penetrate the systems of anyone still clinging on to XP. Indeed, some people have already speculated that the bad guys will soon be stockpiling newly-found bugs until after the patch deadline, building up an arsenal of woes to unleash on those too lazy, poor, or stuck in their ways to upgrade.
Once the April 2014 deadline has passed, the world of Windows XP will be a perpetual zero-day, with no hope of relief from danger. It’s clearly in Microsoft’s interest to spread maximum fear, to squeeze as much revenue as they can out of Windows users who will have to pay to step up to Windows 7 or 8. But their warnings do carry considerable weight. In operating system terms, XP is pretty ancient, having been released in 2001 and reaching the end of its standard back in 2009. When the five-year extended support phase ends the platform will have very nearly reached its teens. It remains remarkably popular though, with the best available stats putting it on anywhere from 13 to 30% of systems browsing the web – well overtaken by Windows 7 nowadays, but still streets ahead of Windows 8. Its stability, simplicity and familiarity will make it hard to dislodge from a huge residual user base.
This has led to some speculation that Microsoft might relent and extend the support period further, but this seems unlikely. As Rains also points out in his blog piece, even with regular patching, the security provisions in XP just don’t cut it any more, leaving its users open to all sorts of dangers they would be immune from out-of-the-box with less creaky platforms.
You can read the original article here.
Jan
An equally alarming industry statistic, users not running the most recent version of Android (comprising more than 90 percent of active users) are vulnerable to known exploits, resulting in a more than 600 percent increase in Android malware infections.
In order to keep up with and prevent these risks, Sophos has introduced the latest version of its free Android security app, Sophos Mobile Security 3.0, its full-featured mobile securityand anti-virus application.
What’s New in Sophos Mobile Security 3.0
- Application protection: Protects the start of selected applications with a password, meaning you can let others use your phone without risking your corporate data security. You can protect your settings or Google Play app and any other mobile application.
- Faster Scanning: Significantly improves scan speed by leveraging the power of multi- core phones
- Web Protection (now included in free version): Blocks access to malicious or phishing websites, so you can access the Internet worry-free
“If Android malware risks weren’t enough, Android device loss and theft are an enormous issue, especially considering that more than 100 cell phones are lost or stolen every minute just in the US alone,” said Thomas Lippert, senior product manager, mobile, Sophos. “Mobile malware leads to data loss and unexpected cost issues, while actual device loss and theft leads to potentially much worse. Either way, it’s imperative for users to ensure their devices are protected. And we’re providing this protection—for free.”
Sophos Mobile Security is offered for free in Google Play: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.sophos.smsec. Optionally, Sophos Mobile Security can integrate into the company’s flagship mobile device management and security solution, Sophos Mobile Control, providing full central management and integration into the compliance enforcement engine. For more information about Sophos’ mobile offerings, please visit:http://www.sophos.com/en-us/products/mobile.aspx.

















