News
Keeper Password Manager was rated as a leading enterprise, mid-market and small business password manager for Spring 2025 by users on G2, the world’s largest and most trusted software marketplace. Within the Spring 2025 report cycle, Keeper earned a G2 Milestone Badge, surpassing 1,000 reviews from a variety of customers, including Small Business, Mid-Market and Enterprise end users and admins alike. Keeper Security was also named a leader in password management globally, with distinctions in the Americas, Canada, Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA) regions, and named grid leader, high performer and momentum leader across nine cybersecurity categories, earning a total of 59 badges.
Keeper has been recognized as a leader in multiple cybersecurity categories on G2, including Password Managers, Passwordless Authentication, Single Sign-On (SSO), Dark Web Monitoring, Secrets Management Tools, Encryption, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Data Security software. These distinctions are based on positive reviews from verified users, highlighting Keeper’s excellence compared to similar solutions.
The recognition is based on the responses of real users for each of the related questions featured in the G2 review form. Within the Password Managers category, 96% of users rated Keeper 4 or 5 stars, achieving an average rating of 4.6 out of 5. 91% of users believe it is headed in the right direction, and users said they would be likely to recommend Keeper Password Manager at a rate of 92%. Keeper’s intuitive user interface also received increased ratings, with 95% of users stating the solution meets requirements, along with a 92% satisfaction rating in regards to ease of use.
Password manager capabilities
To qualify as a solution in the Password Managers Software category, Keeper met the following capabilities with industry-leading features:
- Store and save passwords for websites — The Keeper Vault provides users with a secure repository to store passwords, passkeys, logins and other personal information with full end-to-end encryption.
- Automate the filling of password forms and logins — KeeperFill® autofills your login credentials so you don’t have to toggle back and forth between tabs or apps to retrieve passwords.
- Provide tools for securely sharing credentials — Keeper enables secure, vault-to-vault sharing, as well as one-time sharing with anybody (including non-Keeper users), allowing teams and organizations to securely collaborate on shared accounts. Keeper also offers enhanced password security features such as Time-Limited Access and Self-Destructing Records.
- Integrate with browsers or function atop applications — Keeper can be accessed via a browser extension on every major browser, a desktop app that enables autofilling credentials into native apps and on iOS and Android devices.
- Allow users to create, change or randomize passwords — Keeper makes it simple for users to identify and change weak passwords, create new strong passwords and generate unique passwords for accounts. Keeper also supports passkey and passphrase across all devices.
Strengthening cybersecurity beyond password management
In addition to earning leadership distinctions in the Password Managers and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) categories, Keeper was also named a Momentum Leader in the Encryption category, a Leader in Data Security, a High-Performer and Leader in Single Sign-On, as well as a Leader in Secrets Management Tools.
Keeper received the highest User Satisfaction score among products in Secrets Management Tools. 97% of users believe it is headed in the right direction, and users said they would be likely to recommend Keeper Secrets Manager at a rate of 93%. Keeper is also included in the Data Security, Web Security, Passwordless Authentication, Dark Web Monitoring, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Biometric Authentication categories on G2.
Secrets manager capabilities
To qualify as a solution in the Secrets Management Tools category, Keeper met the following capabilities with industry-leading features:
- Centrally manage keys and other secrets — Keeper Secrets Manager is a fully managed cloud-based, zero-knowledge platform for securing infrastructure secrets such as API keys, database passwords, access keys, certificates and any type of confidential data.
- Securely store secrets with encryption and tokenization — With Keeper’s zero-knowledge encryption, secrets can only be decrypted on the designated devices that you manage.
- Automate pushing secrets to applications and infrastructure — Keeper Secrets Manager seamlessly integrates with all popular CI/CD systems and SDKs for all major programming languages and supports any type of machine to protect your infrastructure.
- Create audit trail of secrets use and lifecycle — Keeper provides granular event reporting and alert capabilities with SIEM integration.
Why users prefer Keeper
Reviewers on G2 noted that Keeper meets their security requirements and indicated they are extremely satisfied with Keeper’s intuitive user interface. Product deployment, training, administration and end-user experience also stood out as compelling features.
Keeper leverages best-in-class security with a zero-trust and zero-knowledge security architecture to safeguard your information and mitigate the risk of a data breach. Keeper has the longest-standing SOC 2 attestation in the industry; is ISO 27001, 27017 and 27018 certified; GDPR compliant; CCPA compliant; HIPAA compliant; and FedRAMP and StateRAMP Authorized. Furthermore, Keeper recently achieved FIPS 140-3 validation for its cryptographic module, reinforcing its dedication to exceeding federal security standards for protecting sensitive government data. Keeper makes the adoption of cybersecurity best practices easy for administrators and end users alike.
Keeper’s support team is available globally 24×7. On-demand resources, including the Keeper101 tutorial videos, the Documentation Portal and regular Training Webinars, guide new administrators and end users through product onboarding and utilization.
Reviewers favored the ease of doing business with Keeper and the strong return on investment. Keeper earned the “Best Relationship” for Mid-Market badge in the Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) category. In use by millions of end users and thousands of organizations around the globe, Keeper Password Manager supports all major platforms, devices and applications, seamlessly protecting any type of organization and in any industry, regardless of company size or technical expertise.
What customers are saying about Keeper
When asked, ‘What do you like best about Keeper Password Manager?’ an enterprise user stated:
«The user interface is very simple and user friendly which has helped drive user adoption. New features rolled out to the platform with no need for additional licensing. The recent addition of supporting MFA codes within the vault has been a huge benefit to us».
When asked, ‘What problems is Keeper Password Manager solving and how is that benefiting you?’ the enterprise user stated:
“Eliminating unsanctioned storage of company secrets, providing an audit trail on password utilization. Features such as Security Audit reports, helping the security team easily identify weak passwords, password reuse and password hygiene reports to better educate users. Secure file storage allowing the storage of certificates and keys within the vault.”
Learn more about what actual users have to say about Keeper, or leave your own review of Keeper Password Manager visiting this link!
Source: Keeper Security
Sophos Firewall v21.5 adds a top requested feature: Entra ID single sign-on (SSO) integration with Sophos Connect and the VPN portal.
SSO for Remote Access VPN
Adding single sign-on integration with Sophos Connect and the firewall VPN portal makes remote access VPN easier for end-users, enabling them to use their corporate network credentials with the Sophos Connect client and the firewall VPN portal when working remotely.
It provides cloud-native integration over the industry standard OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect protocols for a seamless experience. It fully supports Entra ID MFA to protect against identity theft and brute force hacks.
Demo Video
Watch this quick demo video for a look at how it works:
Helpful Documentation
Check out the online documentation for full details.
Get Started Today
Start taking advantage of this great new capability in Sophos Firewall v21.5 by participating in the Early Access Program. Simply register for the program, click the link in your email to download the firmware update package, and install it on your Sophos Firewall.
Source: Sophos
Sophos Firewall v21 offers an innovative industry first: Network Detection and Response (NDR) integrated with your firewall.
What is NDR?
Network Detection and Response (NDR) is a category of network security products designed to detect abnormal traffic behavior to help identify active adversaries operating on the network.
Skilled attackers are very effective at evading detection, but they ultimately need to move across or communicate out of the network to carry out an attack. NDR typically sits within the network, utilizing sensors that monitor and analyze network traffic to identify this kind of suspicious activity.
NDR products have been around for many years, and Sophos NDR has been part of our MDR/XDR portfolio of products since early 2023. However, with SFOS v21.5, we are integrating NDR with Sophos Firewall – an industry first – at no extra charge for Sophos Firewall customers with Xstream Protection.
Integrating NDR with a Next-Gen Firewall may seem like an obvious choice, but the challenge is doing it in a way that doesn’t impact the performance of the firewall since NDR traffic analysis requires significant processing power. As a result, we’ve taken the novel approach of deploying an NDR solution in the Sophos Cloud to offload the heavy lifting from the firewall.
Sophos NDR Essentials
Sophos Firewall v21.5 introduces our new NDR Essentials cloud-delivered Network Detection and Response platform. It utilizes the latest AI detections to help identify active adversaries and shares that information using the Sophos Firewall threat feeds API as part of Active Threat Response to keep you informed of any detections and their relative risks.
Watch this quick demo video for a look at how it works or read on for full details:
How it works
Sophos Firewall captures meta data from TLS-encrypted traffic and DNS queries and sends that information to NDR Essentials in the Sophos Cloud.
There, the data is analyzed using multiple AI engines. It can detect malicious encrypted payloads without performing TLS decryption as well as new and unusual domains generated through algorithms that are often a key indicator of compromise.
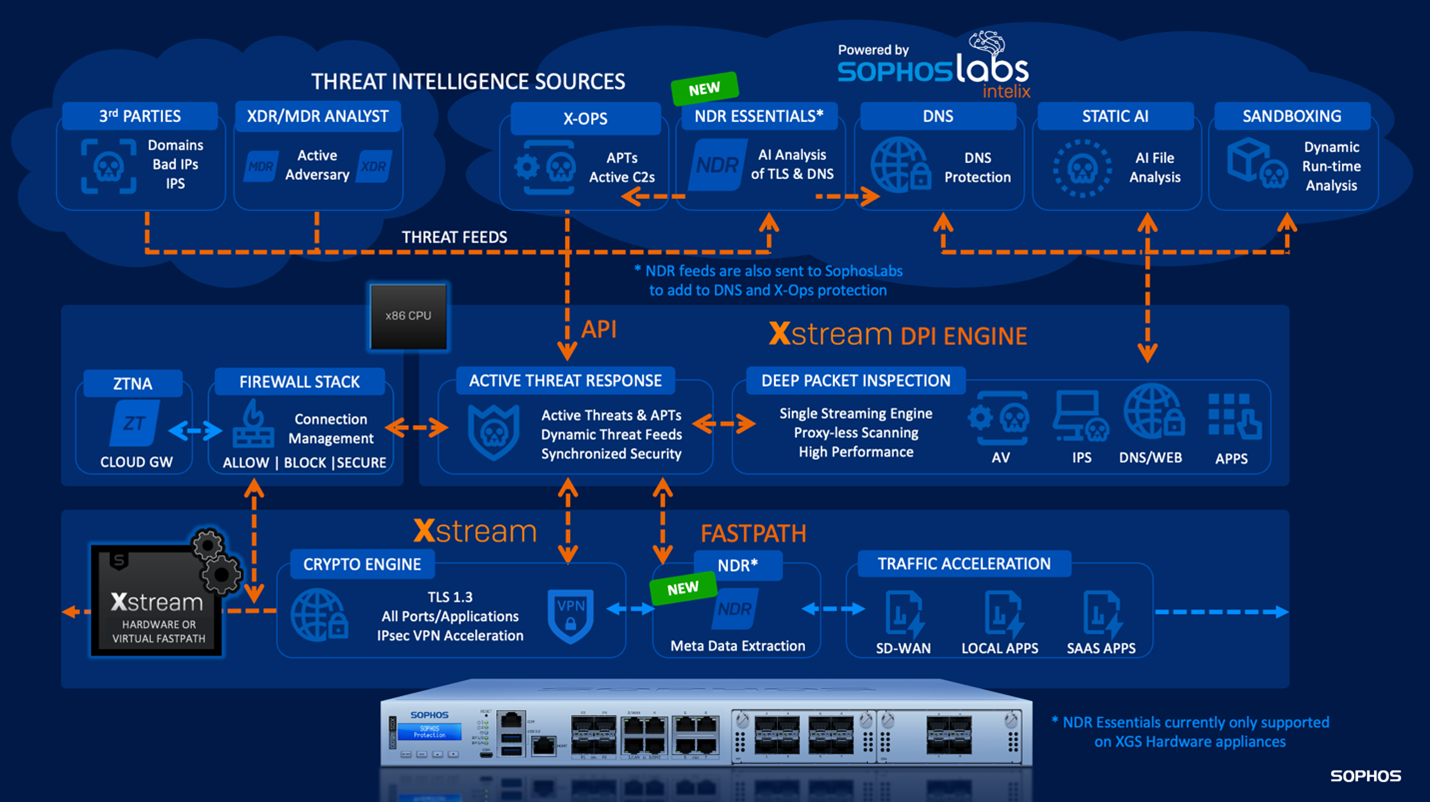
The meta data extraction is performed by a new lightweight engine implemented on the Xstream FastPath and, as a result, one caveat with this new capability is that it is only available on XGS Series hardware firewalls. Virtual, software, and cloud firewalls may get this NDR integration capability in the future, but not in v21.5.
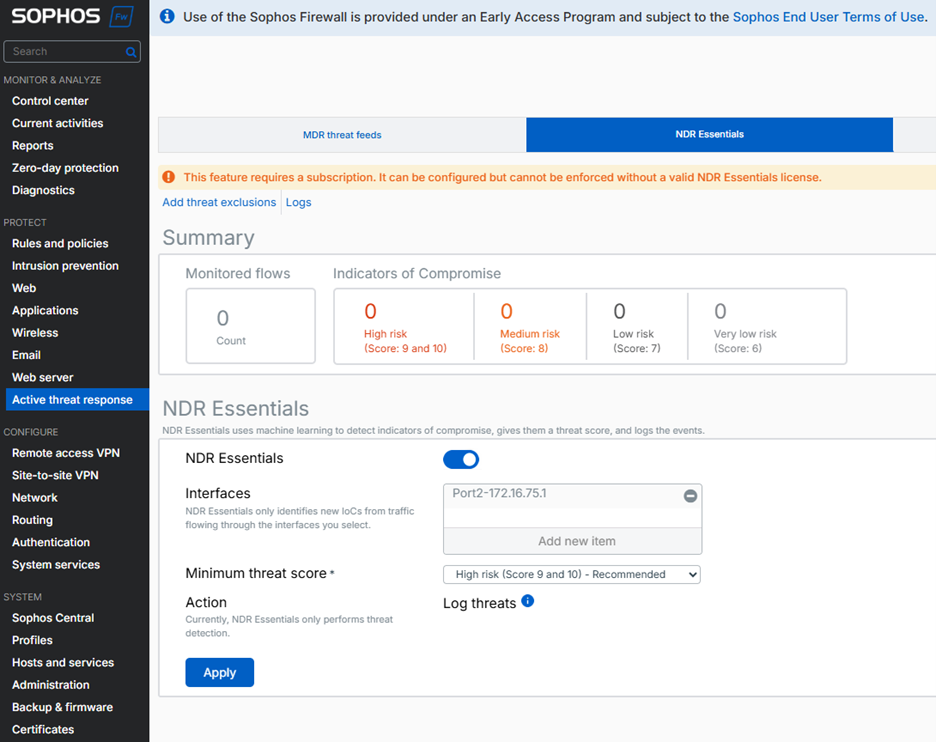
NDR Essentials detections are scored on a range from 1 (low risk) to 10 (highest risk). You decide which risk score sets the threshold for an alert based on your particular environment. The recommended default is high-risk (9-10).
All detections that are scored greater than or equal to 6 are logged but only those meeting or exceeding your threshold trigger notifications and are shown as alerts on the new Control Center dashboard widget.
Detections scored less than 6 may be false positives and are not logged as a result. No NDR Essentials detections are blocked at this time, but this maybe an option in the future. All detections are fully accessible via the Active Threat Response report available both on-box and via Sophos Central Firewall Reporting.
How does NDR Essentials compare to Sophos NDR?
To put it simply, Sophos NDR Essentials is a “lite” version of Sophos NDR.
Sophos NDR is designed to sit deep inside the network so it can effectively monitor and detect suspicious activity and traffic flows heading both north-south (or inside-outside) as well as east-west flows that are traversing the LAN internally.
As you know, a firewall is designed to sit at the network gateway and inspect north-south traffic. Thus, NDR Essentials doesn’t have the same visibility at the network gateway as a full NDR solution sitting inside the network.
Our full Sophos NDR solution has five different AI detection engines. In this initial version of NDR Essentials, we’ve implemented the two engines that have the most relevance and impact at gateway traffic inspection: the Encrypted Payload Analysis engine, and the Domain Generation Algorithm engine. At this point, with its added engines, Sophos NDR provides deeper coverage and greater detection capabilities than NDR Essentials.
In summary, NDR Essentials provides an excellent additional layer of active threat detection to Sophos Firewall, and it does so at no extra charge and no performance impact. However, it is not a replacement for a full Sophos NDR implementation for any of our customers taking advantage of our XDR platform or MDR service.
If you want further detection insights and threat hunting capabilities, you are strongly encouraged to check out Sophos Extended Detection and Response (XDR) with the full implementation of Sophos NDR and the new NDR Investigation Console.
You may also wish to consider our full 24/7 Managed Detection and Response service. All of these products and services work better together with your Sophos Firewalls.
Get started today
Start taking advantage of this great new capability in Sophos Firewall v21.5 by participating in the early access program. Simply register for the program, click the link in your email to download the firmware update package, and install it on your Sophos Firewall.
Source: Sophos
We’re pleased to announce that the early access program (EAP) is now underway for the latest Sophos Firewall release. This update brings exciting industry-first enhancements and top-requested features, including…
Sophos NDR Essentials integration
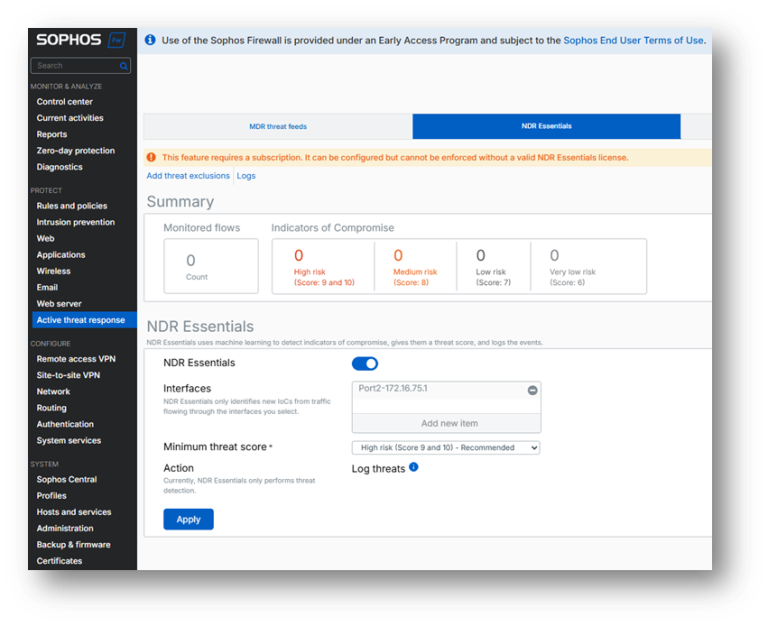 Sophos Firewall customers with Xstream Protection now get Sophos NDR Essentials in the cloud, for no extra charge, significantly bolstering network protection:
Sophos Firewall customers with Xstream Protection now get Sophos NDR Essentials in the cloud, for no extra charge, significantly bolstering network protection:
Sophos NDR Essentials can detect active adversaries using encryption without using TLS decryption thanks to AI Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) analysis. Sophos NDR Essentials can also detect advanced domain generation algorithms that try to evade normal DNS and web filtering.
Sophos NDR Essentials delivers a new layer of protection, and since it’s cloud-hosted by Sophos, it doesn’t impact your firewall performance at all – further strengthening our industry leading performance and protection. Review the What’s New Guide for full details.
Entra ID (Azure AD) single sign-on for remote access VPN
One of your top requested features makes remote access VPN easier for end users, enabling them to use their corporate network credentials with the Sophos Connect client and the firewall VPN portal:
- Entra ID (Azure AD) single-sign on integration with Sophos Connect and the VPN portal is now included in SFOS v21.5
- It provides cloud-native integration over the industry standard OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect protocols for a seamless experience
- Supported with Sophos Connect client 2.4 (and later) on Microsoft Windows
Other VPN and scalability enhancements
- User interface and usability enhancements: Connection types have been renamed from “site-to-site” to “policy-based,” and tunnel interfaces have been renamed to “route-based” to make these more intuitive
- Improved IP lease pool validation: Across SSLVPN, IPsec, L2TP, and PPTP remote access VPN to eliminate potential IP conflicts
- Strict profile enforcement: On IPsec profiles that exclude default values to ensure a successful handshake, eliminating potential packet fragmentation and tunnels failing to establish properly
- Route-based VPN scalability: Route-based VPN capacity is doubled with support for up to 3,000 tunnels
- SD-RED scalability: Sophos Firewalls now support up to 1,000 site-to-site RED tunnels and up to 650 SD-RED devices.
Sophos DNS Protection
Last year, we launched our DNS Protection service and made it free for all Xstream Protection-licensed firewall customers. With this release, Sophos DNS Protection gets further integration with Sophos Firewall:
- New control center widget to indicate service status
- New troubleshooting insights via logging and notifications
- New guided tutorial on how to set up Sophos DNS Protection easily
Streamlined management and quality-of-life enhancements
As with every Sophos Firewall release, this version includes several quality-of-life enhancements that make day-to-day management easier:
- Resizable table columns: A long-requested feature, many firewall status and configuration screens now support resizable column widths that are retained in browser memory for subsequent visits. Many screens such as SD-WAN, NAT, SSL, Hosts and services, and site-to-site VPN, all benefit from this new feature.
- Extended free text search: SD-WAN routes now enable searching by route name, ID, objects, and object values like IP addresses, domains, or other criteria. Local ACL rules also now support searching by object name and value, including content-based search.
- Default configuration: By popular demand, the default firewall rules and rule group previously created when setting up a new firewall have been removed with only the default network rule and MTA rules provided during initial setup. The default firewall rule group and the default gateway probing for custom gateways are both set to “None” by default.
- New font: The Sophos Firewall user interface now sports a new lighter, cleaner, sharper font for added readability and improved performance
Other enhancements
- Virtual, software, cloud licensing: In case you missed it, all Sophos Firewall virtual, software, and cloud licenses (BYOL) no longer have RAM limits. Licenses are now strictly limited by core count and have no RAM restrictions.
- Larger file size limit in WAF: Supports a configurable request (upload) file size limit for Web Application Firewall (WAF), which can now scan files up to 1 GB
- Secure by design: We are continually improving the security of Sophos Firewall, and in this release are adding real-time telemetry gathering to flag any unexpected changes to core OS files using secure hash validation. This will enable our monitoring teams to proactively identify potential security incidents early before they can become a real problem.
- DHCP prefix delegation relaxation: Now supports /48 to /64 prefixes, improving interoperability with ISPs. Router advertisements (RA) and the DHCPv6 server are also now enabled by default.
- Path MTU discovery: This will resolve TLS decryption errors due to the latest ML-KEM (Kyber) key exchange support in browsers. The Sophos Firewall deep packet inspection engine will now automatically detect and adjust the MTU for each flow, ensuring optimal performance based on specific network conditions.
- NAT64 (IPv6 to IPv4 traffic): NAT64 is supported for IPv6 to IPv4 traffic in explicit proxy mode. In this mode, IPv6-only clients can access IPv4 websites. The firewall also supports IPv4 upstream proxy for IPv6-only clients.
Get the full details
Download the full What’s New Guide for a complete overview of all the great new features and enhancements in v21.5.
Get started today
You can download the upgrade package or installer for v21.5 from the Sophos Firewall v21.5 EAP Registration Page. Simply submit your details and the download links will be emailed to you straight away.
All support during the EAP will be through our forums on the Sophos Firewall Community.
Please provide feedback using the option at the top of every screen in your Sophos Firewall as shown below or via the Community Forums.
Source: Sophos
According to the 2024 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, 75% of cyber attacks involve exploiting compromised privileged credentials, making privileged access one of the most sought-after attack vectors. Additionally, 60% of organizations cite insider threats as the primary cause of data breaches (2023 Cybersecurity Insiders – Insider Threat Report), highlighting the critical need to secure privileged accounts against both external and internal threats.
However, a vast majority of organizations – both big and small – don’t have the platforms and processes in place to secure the privileged accounts of every user, on every device, from every location. That’s where a modern Privileged Access Management (PAM) solution comes into play.
The growing need for modern privileged access management
Organizations that fail to implement a robust PAM solution face significant financial and operational risks. The 2024 IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report found that the average cost of a breach rose to $4.88 million. However, 80% of organizations that have adopted a PAM solution report a significant reduction in cyber attack success related to credential theft and misuse.
With the increasing complexity of IT environments, including hybrid cloud infrastructures, passkey adoption, DevOps pipelines and remote workforces, legacy PAM solutions often fail to provide seamless security and usability. Today’s modern infrastructure needs to be accessible at all times, from anywhere in the world, while still maintaining Just-In-Time (JIT) access, zero trust and least privilege.
Introducing KeeperPAM: A groundbreaking approach to privileged access management
Keeper Security is pleased to announce the next generation of its privileged access management platform, KeeperPAM, a patented cloud-native, zero-knowledge platform. KeeperPAM enables seamless infrastructure access through a secure vault. Simply log in with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for one-click, passwordless access to servers, databases, web apps and SaaS platforms.
Unlike legacy PAM solutions, KeeperPAM is zero-knowledge and zero-trust, meaning Keeper never has access to your network, infrastructure or secrets. With a lightweight, containerized gateway, Keeper eliminates agents and on-premises complexity while providing full auditing, session logging and flexible access through User Interface (UI), Command-Line Interface (CLI) or isolated web browsing.
Keeper’s engineers are the original creators of Apache Guacamole and experts in browser-based remote session protocols covering SSH, RDP, VNC, HTTPS, MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server and more.
What makes KeeperPAM groundbreaking?
- Cloud-native, not cloud-adapted – Unlike legacy PAM providers that have adapted on-premises products to the cloud, KeeperPAM was built from the ground up to be cloud-native, scalable and easy to deploy across any environment.
- Multi-protocol access – Instant passwordless sessions to remote servers, databases and web-based applications – without exposing credentials or requiring firewall changes.
- Zero-trust and zero-knowledge security – With end-to-end zero-knowledge encryption, only you can decrypt your data and remote sessions, ensuring absolute privacy and security.
- Agentless, seamless deployment – Unlike legacy PAM solutions that require complex network configurations, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) or on-prem appliances, KeeperPAM simplifies access by using a lightweight Keeper Gateway service, which eliminates network vulnerabilities and significantly reduces IT overhead.
- All-in-one platform – KeeperPAM integrates enterprise password management, secrets management, privileged session management, remote browser isolation and zero-trust network access into a single, unified solution. You can choose whether users have only an enterprise password manager license or a full PAM license.
With KeeperPAM, businesses no longer need various cybersecurity platforms cobbled together that leave them exposed. Everything is managed from a single pane of glass.
Core benefits and capabilities of KeeperPAM
KeeperPAM offers all of the functionality organizations need to prevent breaches, ensure compliance and enable easy and secure access to resources.
Some of the core capabilities include:
- Password Management – Protect and manage passwords, passkeys and confidential files in a zero-knowledge vault.
- Secrets Management – Protect API keys, CI/CD pipelines and developer tools, while eliminating secrets sprawl, by removing hard-coded credentials from source code.
- Session Management – Provide passwordless remote access to any resource using a web browser.
- Database Management – Control access to databases, either on-prem or cloud, using interactive UI sessions, CLI sessions or tunneling with your favorite front-end tools.
- Remote Browser Isolation – Lock down internal web-based apps, cloud apps and admin panels, while preventing data exfiltration and controlling browsing sessions, with auditing, session recording and password autofill.
- Admin Console – Manage and deploy Keeper to users, integrate with identity providers, monitor activity and establish role-based enforcement policies.
- Control Plane – Orchestrate and monitor the various components and activities related to privileged access, session management, policies and workflow.
How is KeeperPAM deployed?
KeeperPAM uses a zero-trust gateway service to access each environment. No firewall updates or ingress changes are needed, thereby enabling seamless, secure access without complexity.
There are three simple steps to deploy KeeperPAM, which will take under an hour to complete:
- Deploy the vault with your SSO and provision through SCIM, SAML or AD
- Set policy
- Install a Keeper Gateway in the target environments
Deploying KeeperPAM is fast, flexible and designed to scale with your organization’s needs. Whether you’re a small business or a global enterprise, Keeper’s innovative cloud-native architecture ensures rapid implementation with minimal IT overhead. Professional services are never required, unlike legacy PAM platforms.
The future of PAM is here
As cyber threats continue to escalate and regulatory requirements become more stringent, businesses need a modern PAM solution that is secure, scalable and simple to deploy. KeeperPAM redefines privileged access security by eliminating outdated architectures, reducing complexity and delivering an all-in-one, zero-trust security platform.
By combining enterprise password management, secrets management, connection management, zero-trust network access and remote browser isolation into a single, easy-to-use interface, KeeperPAM empowers businesses of all sizes to proactively prevent breaches, streamline compliance and simplify security.
Ready to take control of privileged access and eliminate standing privilege? Request a KeeperPAM demo today.
Source: Keeper Security
Sophos, a global leader of innovative security solutions for defeating cyberattacks, today released the 2025 Sophos Active Adversary Report, which details attacker behavior and techniques from over 400 Managed Detection and Response (MDR) and Incident Response (IR) cases in 2024. The report found that the primary way attackers gained initial access to networks (56% of all cases across MDR and IR) was by exploiting external remote services, which includes edge devices such as firewalls and VPNs, by leveraging valid accounts.
The combination of external remote services and valid accounts aligns with the top root causes of attacks. For the second year in row, compromised credentials were the number one root cause of attacks (41% of cases). This was followed by exploited vulnerabilities (21.79%) and brute force attacks (21.07%).
Understanding The Speed of Attacks
When analyzing MDR and IR investigations, the Sophos X-Ops team looked specifically at ransomware, data exfiltration, and data extortion cases to identify how fast attackers progressed through the stages of an attack within an organization. In those three types of cases, the median time between the start of an attack and exfiltration was only 72.98 hours (3.04 days). Furthermore, there was only a median of 2.7 hours from exfiltration to attack detection.
“Passive security is no longer enough. While prevention is essential, rapid response is critical. Organizations must actively monitor networks and act swiftly against observed telemetry. Coordinated attacks by motivated adversaries require a coordinated defense. For many organizations, that means combining business-specific knowledge with expert-led detection and response. Our report confirms that organizations with proactive monitoring detect attacks faster and experience better outcomes,” said John Shier, field CISO.
Other Key Findings from the 2025 Sophos Active Adversary Report:
- Attackers Can Take Control of a System in Just 11 Hours: The median time between attackers’ initial action and their first (often successful) attempt to breach Active Directory (AD) – arguably one of the most important assets in any Windows network – was just 11 hours. If successful, attackers can more easily take control of the organization.
- Top Ransomware Groups in Sophos Cases: Akira was the most frequently encountered ransomware group in 2024, followed by Fog and LockBit (despite a multi-government takedown of LockBit earlier in the year).
- Dwell Time is Down to Just 2 Days: Overall, dwell time – the time from the start of an attack to when it is detected – decreased from 4 days to just 2 in 2024, largely due to the addition of MDR cases to the dataset.
- Dwell Time in IR Cases: Dwell time remained stable at 4 days for ransomware attacks and 11.5 days for non-ransomware cases.
- Dwell Time in MDR Cases: In MDR investigations, dwell time was only 3 days for ransomware cases and just 1 day for non-ransomware cases, suggesting MDR teams are able to more quickly detect and respond to attacks.
- Ransomware Groups Work Overnight: In 2024, 83% of ransomware binaries were dropped outside of the targets’ local business hours.
- Remote Desktop Protocol Continues to Dominate: RDP was involved in 84% of MDR/IR cases, making it the most frequently abused Microsoft tool.
To shore up their defenses, Sophos recommends that companies do the following:
- Close exposed RDP ports
- Use phishing-resistant multifactor authentication (MFA) wherever possible
- Patch vulnerable systems in a timely manner, with a particular focus on internet-facing devices and services
- Deploy EDR or MDR and ensure it is proactively monitored 24/7
- Establish a comprehensive incident response plan and test it regularly through simulations or tabletop exercises
Read the full It Takes Two: The 2025 Sophos Active Adversary Report on Sophos.com.
Source: Sophos
Customers have spoken, and the results are in. G2, a major technology user review platform, has just released its Spring 2025 Reports, where users rated Sophos as the #1 overall Firewall, MDR, and EDR solution.
Recognizing the power of our platform, Sophos is – once again – the only vendor named a Leader across the G2 Overall Grid® Reports for Endpoint Protection Suites, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), Extended Detection and Response (XDR), Firewall Software, and Managed Detection and Response (MDR). Based on user feedback, Sophos was also ranked the #1 solution in 53 individual reports spanning the Antivirus, EDR, Endpoint Protection Suites, XDR, Firewall, and MDR markets.
Managed Detection and Response
In addition to the #1 overall ranking among MDR solutions, Sophos MDR is also rated the top solution in four additional report segments for the category, including the Enterprise and Mid-Market Grids, and earning the Best Results and Best Usability distinctions among Enterprise customers.
We continue to extend Sophos MDR to support the more than 29,000 organizations that use our service. Recent updates include enhanced ability to fortify Microsoft defenses with new Sophos-proprietary detections for Office 365, an expanded ecosystem of turnkey integrations with third-party cybersecurity and IT tools includes a new Backup and Recovery integration category, and new AI-powered workflows to streamline the operational processes and drive better security outcomes for our customers.
Endpoint Detection and Response/Extended Detection and Response
Sophos EDR/XDR was named a Leader across nine different segments in the Spring 2025 Reports, including the Overall, Enterprise, Mid-Market, and Small Business Grids. The Sophos XDR platform was rated #1 for Best Usability and Best Relationship across all four segments (Overall, Enterprise, Mid-Market, and Small Business), reinforcing why it is the overall top-rated XDR solution.
Firewall
In addition to being named the #1 Overall Firewall solution, Sophos Firewall was also rated as the #1 firewall solution by Mid-Market and Enterprise users. All four user segments (Overall, Small Business, Mid-Market, and Enterprise) named Sophos Firewall a Leader in their respective G2 Grid Reports. For usability, Sophos Firewall is the top-rated solution in the Overall, Enterprise, and Mid-market segments in the Usability Index.
What Sophos customers are saying
“Sophos MDR: 360 degree MDR solution for endpoint security” said a user in the Enterprise segment
“Sophos MDR helps us sleep at night knowing our environment is monitored 24/7” said a user in the Mid-Market segment
“Sophos Firewall is a robust and user-friendly security solution that provides comprehensive protection through advanced threat detection, deep packet inspection, and synchronized security with other Sophos products” said a Head of IT in the Mid-Market segment
“Sophos Firewall automatically identifies and blocks active threats, prevents the lateral movement of attacks, and delivers immediate insights into compromised devices, users and application” said a user in the Small Business segment
“What stands out the most is how effortlessly Sophos Firewall streamlines security tasks, allowing users to focus on protecting their networks without getting bogged down in complex configurations” said a user in the Mid-Market segment
“We can rest easy knowing that Sophos Intercept X is continuously guarding our endpoints from ransomware assaults, which are the kind of thing that keep IT administrators up at night” said a SOC Analyst in the Mid-Market segment
For more information on our services and products, speak to your Sophos partner or representative and visit our website.
Source: Sophos
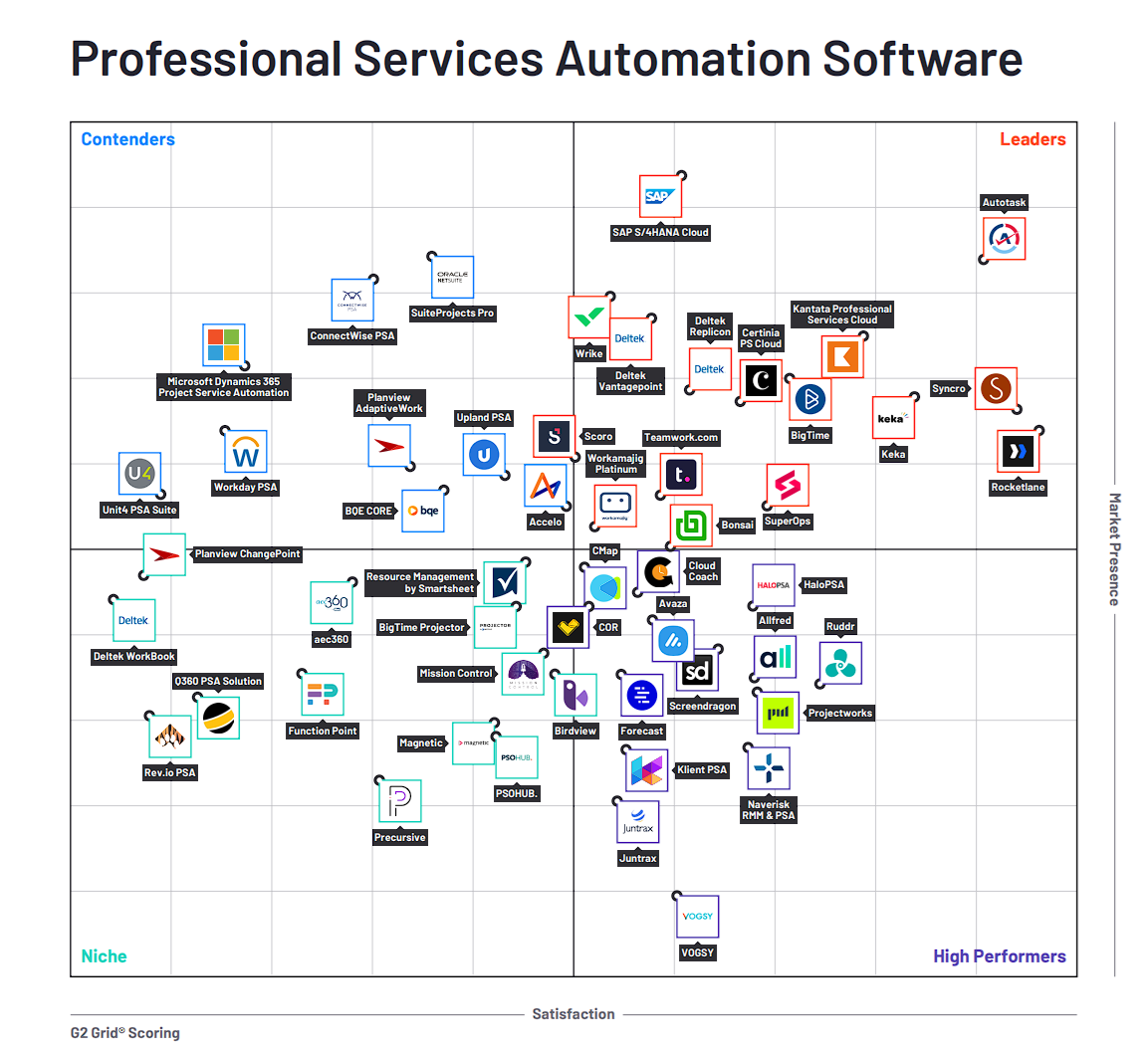
Discover key insights on why Autotask has been recognized as a leader in the G2 Grid® Report for Professional Services Automation (PSA) – Spring 2025.
Autotask PSA is a cloud-based platform that enables MSPs to run their business at peak profitability because it’s reliable, centralizes their operations, and enables quick data-driven decisions. Autotask provides real-time metrics that give full visibility into service delivery, customer satisfaction, sales pipeline, internal operations, resource utilization, profitability and more. As the central hub of an MSP’s business, it integrates with more than 170 industry-leading solutions. Autotask PSA has consistently delivered 99.99% uptime over the last 10 years.
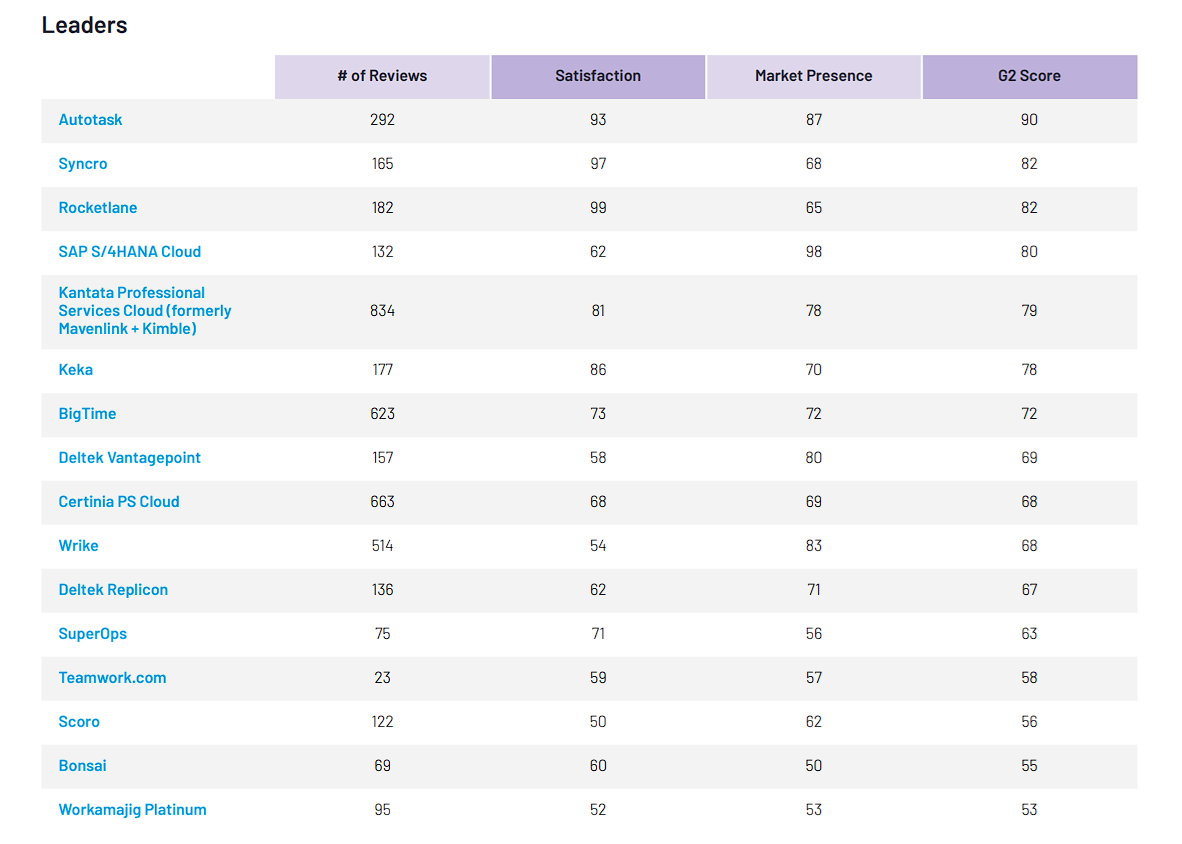
Autotask earned its place on the G2 Leader Grid® Report for Professional Services Automation thanks to exceptional customer satisfaction and a strong market presence. With 86% of users giving Autotask 4 or 5 stars, 85% believing it is headed in the right direction and 83% saying they would recommend it, Autotask stands out as a reliable solution for streamlining service delivery and project management.
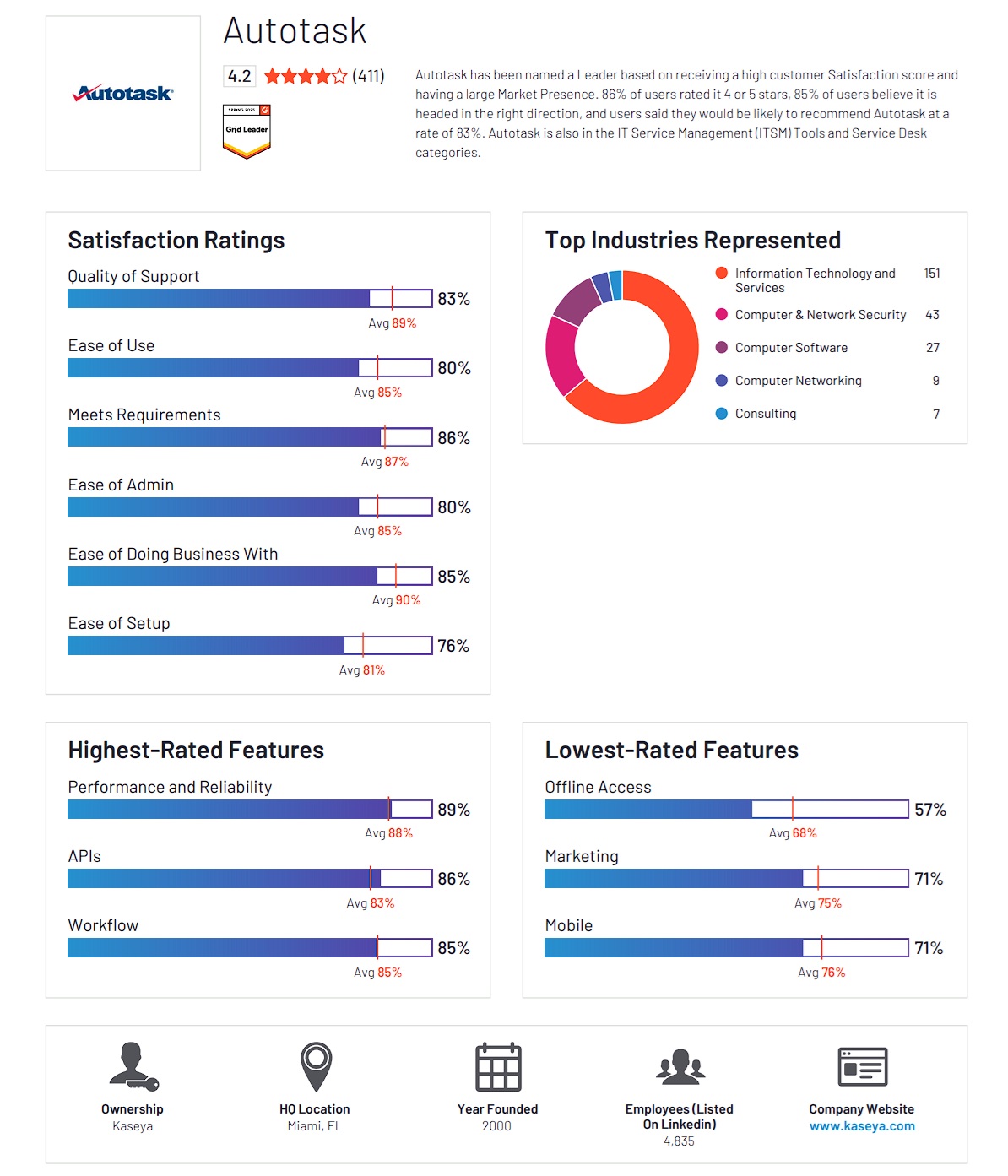
Backed by robust features and a proven ROI, Autotask continues to provide IT professionals with seamless workflows, visibility and control over their operations.
Download the report to discover how Autotask is leading the way:
- User satisfaction and overall performance.
- Feature comparisons.
- User adoption and ROI.
- Autotask, also recognized in the ITSM Tools and Service Desk categories, brings powerful automation and service management under one unified platform.
Join thousands of IT service providers around the world who rely on Autotask to power their businesses.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, addressing cybersecurity challenges is more urgent than ever. Traditional passwords, long considered foundational to digital security, are increasingly vulnerable to sophisticated attacks like phishing and credential stuffing. With cybercriminals becoming more adept, businesses need more secure and reliable authentication methods. Enter passkeys – an innovative step forward in authentication technology.
Recent research from Keeper Security reveals a major shift in the industry: 80% of organizations have either adopted or plan to implement passkeys. But the transition is not without hurdles.
Why passkeys are the future
While passwords have long been the foundation of online security, they come with significant flaws. For example, 32% of employees admit to reusing passwords across multiple accounts, making them easy targets for cybercriminals. Combined with the pervasive threats of phishing and brute force attacks, it’s clear that traditional passwords are no longer sufficient.
Passkeys address these vulnerabilities by leveraging public key cryptography. Unlike passwords, which can be stolen or exposed, passkeys don’t require users to transmit sensitive information. Instead, they use a cryptographic key pair: One key is stored securely on the user’s device, and the other is stored on the authentication server, ensuring that credentials remain secure, private and resistant to phishing attacks.

A phased approach to passkey adoption
Transitioning to passkeys is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Businesses need a structured plan that addresses legacy systems, cost considerations and user adoption challenges. Here is a phased approach to ensuring a smooth and secure transition.
1. Conduct a risk assessment
Identify high-risk systems and prioritize their migration to passkeys. Focus on accounts that store sensitive data or have a history of security breaches. Keeper’s dark web monitoring tool, BreachWatch, can help detect exposed credentials and guide where to start.
2. Upgrade infrastructure
Evaluate authentication tools for compatibility with passkey technology. Hybrid authentication systems, which support both traditional passwords and passkeys, provide a seamless way to transition. Keeper’s password manager supports this hybrid approach, helping organizations secure existing credentials while preparing for a future with passkeys. This dual support enables gradual adoption, ensuring compatibility with legacy systems and minimizing disruption. By integrating passkeys at a manageable pace, organizations can enhance security without sacrificing functionality or user experience.
3. Drive user adoption
Successful implementation depends on user adoption. To support this, organizations must provide clear guidance, comprehensive training materials and hands-on demonstrations that highlight the benefits of passkeys. Keeper’s user-friendly interface and seamless autofill technology simplify the transition, encouraging widespread adoption. Establishing clear policies on when and how to use each authentication method helps ensure users feel confident in their choices. Hybrid solutions not only reduce resistance but also build trust, making the shift to passkeys smoother and more effective across the organization.
4. Launch a pilot program
Introduce passkeys to a smaller group before expanding company-wide. Gather feedback, refine processes and address concerns to optimize the user experience. Keeper’s enterprise-grade security tools ensure seamless integration with existing Identity and Access Management (IAM) frameworks to facilitate user adoption.
5. Execute an organization-wide rollout
Expand passkey usage across all systems, prioritizing high-value accounts and critical users before gradually including other platforms and the broader organization. Ongoing monitoring is essential for maintaining long-term security and user satisfaction.
A vision for the future
Passkeys mark a paradigm shift in authentication. As businesses strengthen their cybersecurity posture, adopting passkeys will be a crucial step toward eliminating credential-based attacks and enhancing the user experience.
Keeper is here to help organizations navigate this transformation. With enterprise-grade security solutions, seamless integrations and expert guidance, businesses can embrace the future of authentication with confidence.
Secure your future today
The journey to passkey adoption begins now. Download Keeper Security’s latest insight report, Navigating a Hybrid Authentication Landscape, for a deeper dive into emerging trends, challenges and solutions.
Source: Keeper Security
Over the years the industry has tied itself in knots in its attempts at augmenting (or upgrading) the password, using all sorts of confusing terminology such as two-factor authentication (2FA), two-step authentication, multifactor authentication (MFA), and the more modern confusion of universal second factor (U2F), Fast IDentity Online 2 (FIDO2), WebAuthn, and passkeys.
Up until now, most of us were happy enough to get someone to adopt any of the above. Anything more than a password is an improvement, but we have now reached the point where we need to raise the minimum bar of acceptability. In this post I’ll look at the current state of bypassing “stronger” authentication methods – and, I believe, point out the best path forward.
Not two smart
Too many of the simplest “2FA” options are not true to what two-factor authentication is really meant to be. Ideally the two factors are two of the following three types: something you know (like a password or PIN), something you have (like a USB/Bluetooth token, SmartCard or public/private keypair), or something you are (like a fingerprint or faceprint). Unfortunately, most of the early solutions boil down to something you know and . . . something else you know.
Take the RSA token, SMS text message, or TOTP (time-based one-time passwords; e.g., Google Authenticator or Authy) styles of “2FA,” where in most cases you are presented with a 6-digit code that rotates every 30 seconds. While people have criticized SMS implementations of this due to the possibility of SIM swapping, the reality is they are all weak and susceptible to interception.
Here’s the problem. Imagine you are sent a well-crafted (perhaps AI-generated?) phishing email. For the scammer to succeed in compromising you at this stage, you must believe the email is legitimate, whether you are using multifactor authentication or not. This is where challenging someone for two different things they know (their password and a secret code that is dynamically generated) ends in tears: If you really think you are logging into your bank, email, or corporate account, you will happily disclose not just your password, but the secret code as well. This type of authentication is only in a single direction; the scammer is verifying your identity, but you have not verified the identity of the entity asking for the proof.
There are in fact freely available tools to automate this deception. One of the more popular is called evilginx2. Originally based on the popular web server nginx, it is now a standalone Go application that serves as an all-in-one tool to phish knowledge-based multifactor authentication and steal session cookies to bypass authentication. This has lowered the barrier for malfeasance to new depths.
How did we get here?
If we consider the history of credential compromise, it all began with sniffing unencrypted Wi-Fi or performing other network-based attacks before things were encrypted. Back in 2010 there was an infamous tool called FireSheep that was designed to allow attackers to visit a cafe and passively steal people’s logins due to the lack of encryption on the web.
In response to these attacks, and to Edward Snowden’s leaks in 2013, we moved to encrypting nearly everything online. That change secured us against what are referred to as machine-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks. We now have nearly ubiquitous use of HTTPS across the web and even in our smartphone apps, which stops any random passersby from capturing everything you might see or do online.
Criminals then moved on to credential theft, and to a large degree most of us have moved on to some variation of multifactor authentication, but again, usually merely the cheapest and easiest variation — something we know, plus an ephemeral something-else we know. This is an ineffective speed bump, and we must move on once again.
Industry consensus has, after many a committee meeting and standards body creation, settled on a widely agreed-upon standard known as the Web Authentication API, or WebAuthn. If you want to dive deeply into the confusion over the various bits and pieces, there is a Reddit thread for that, but I won’t go too deeply into those weeds here.
A walk through WebAuthn
WebAuthn/passkeys make multifactor authentication close to phish-proof. Nothing is perfect, of course, and recent research has discovered a limited-but-interesting MitM attack vector involving specialized hardware devices and a since-patched CVE, but from here forward we are referring to it as phishing-resistant multifactor authentication.
Let’s walk through the process. I want to create an account on a popular social media site. Using my smartphone or computer with passkey support, I choose to create a new account with a passkey. The site prompts me for my desired username (usually my email address). My device sends the username to the site, and it responds back with my username, a challenge, and the site’s domain name. My device generates a unique cryptographic keypair, stores it safely alongside the site name and username, signs the challenge from the site, and attaches the associated public key for the site to now use as my identifier.
Next time I go to this site, I will no longer need or use a password, which by this definition is just a shared secret and could be stolen or replayed. Instead, as shown in Figure 1, I send the username that is matched to that site’s domain name. The site responds with a challenge. My device looks up the key for that domain name and uses it to sign the challenge, proving my identity.
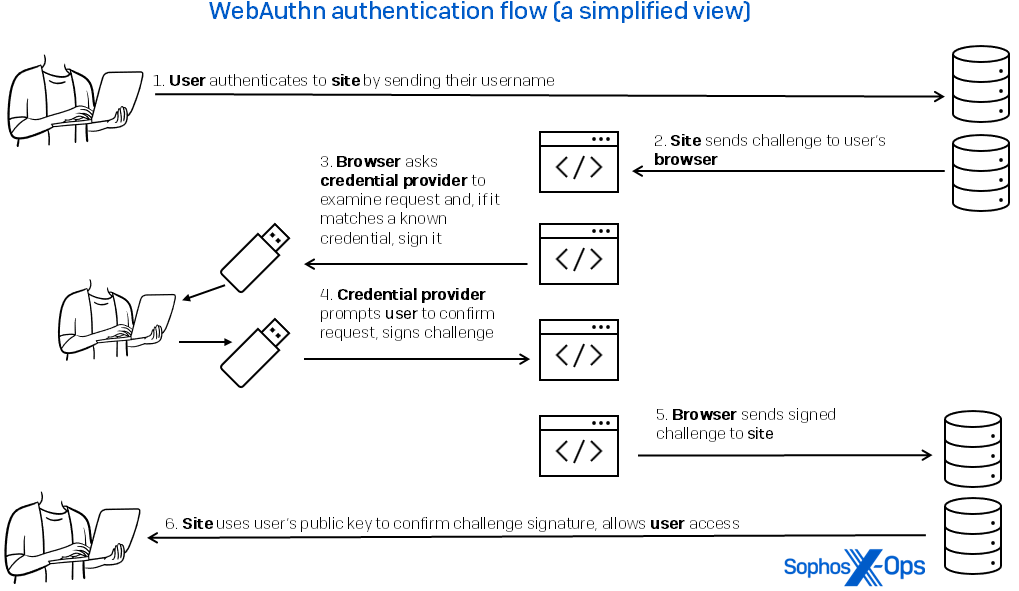
For more information, vertx.io has a developer-centric dive into the mechanics of the process.
What could possibly go wrong?
With this combination of data points, the key can’t easily be stolen or reused, and I can’t be tricked into trying to sign into an imposter site with a lookalike domain name. (There is a small attack surface here as well: If you add a passkey for zuzax.com and I can create a subdomain under my control as an attacker, phish.zuzax.com, I can get you to sign a replayed challenge.)
Beyond my device, where the keys are stored determines their safety against theft and abuse. Using hardware U2F tokens, like a YubiKey or SmartCard, ensures the keys are locked to that device and cannot be extracted and physical theft is the only practical option. Some hardware tokens require a biometric, PIN, or passphrase to unlock as well. With the advent of passkeys, the secret keys can be synchronized across your OS vendor’s cloud (iCloud, Google Drive, OneDrive) or through your password manager (Bitwarden, 1password, etc.) making them more susceptible to theft if your account is compromised.
And, of course, it has to be implemented. The burden of implementation lies with the sites (where we have made reasonably quick progress on this in the past year) and, as ever, with enterprises that must enable and use it in their specific environments. This isn’t so different to our constant advice to security practitioners to treat MFA as basic hygiene (along with patching and disabling unnecessary RDP), but it still has to be budgeted for and done.
The last remaining weakness is the session cookie that gets set upon login, but that’s a topic for another article.
It goes both ways (and moves us forward)
As a user, I should be able to prove my identity to my device by using a PIN, fingerprint, or faceprint, and have the device do the work of authenticating both parties. That’s the most important part of this transaction — its bidirectionality.
We all know password theft is a problem, and we have really only extended their lifetimes by trying to augment them with other flavors of knowledge-based authentication. Information can be and will be stolen, intercepted, and replayed. If we truly want to have multifactor authentication, we must move beyond knowledge and demand stronger proof.
This is an opportunity to move beyond security being a source of friction for users; in fact, it actively improves security while diminishing the friction. Today’s passkey implementations can be finicky and awkward, but I am convinced those who embrace it will benefit the most and that in short order we will solve the user interface challenges. We don’t have a choice. It is the best solution available to us and the criminals won’t wait for us to argue the merits.
Source: Sophos
Sophos X-Ops’ research, presented at Virus Bulletin 2024, uses ‘multimodal’ AI to classify spam, phishing, and unsafe web content.
At the 2024 Virus Bulletin conference, Sophos Principal Data Scientist Younghoo Lee presented a paper on SophosAI’s research into ‘multimodal’ AI (a system that integrates diverse data types into a unified analytical framework). In his talk, Lee explored the team’s novel empirical research on applying multimodal AI to the detection of spam, phishing, and unsafe web content.
What is multimodal AI?
Multimodal AI represents a significant shift in artificial intelligence. Rather than traditional single-mode analysis, multimodal systems can process multiple data streams simultaneously, synthesizing data from multiple inputs.
In the context of cybersecurity – and particularly when it comes to classifying threats – this is a powerful capability. Rather than analyzing textual and visual content separately, a multimodal system can process both, and ‘understand’ the intricate relationships between them.
For example, in phishing detection, multimodal AI examines the linguistic patterns and writing style of the text alongside the visual fidelity of logos and branding elements, while also analyzing the semantic consistency between textual and visual components. This holistic approach means that the system can identify sophisticated attacks that might appear, to more traditional systems, to be legitimate. Moreover, multimodal AI can learn from, and adapt to, the correlations between different data types, developing a sense of how legitimate and malicious content differs across multiple dimensions.
Capabilities
In his research, Lee details some of the detection capabilities of multimodal AI systems:
Text analysis and natural language understanding
- Analysis of linguistic patterns, writing style, and contextual cues to identify manipulation attempts
- Detection of social engineering tactics such as manufactured urgency and unusual requests for sensitive information
- Maintenance of an evolving database of phishing pretexts and narratives
Visual intelligence and brand verification
- Comparison of logos, corporate styling, and visual layouts to legitimate templates
- Detection of subtle differences in brand colors, fonts, and layouts
- Examination of image metadata and digital signatures
Advanced URL and security analysis
- Identification of deceptive techniques like typosquatting and homograph attacks
- Analysis of relationships between displayed link text and actual destinations
- Detection of attempts to obscure malicious URLs with styling and formatting tricks
Case study: A fake Costco email
The below image is a genuine phishing attempt, designed to trick recipients into thinking that they have won a prize from Costco. The email looks official, complete with imitated Costco logo and branding.
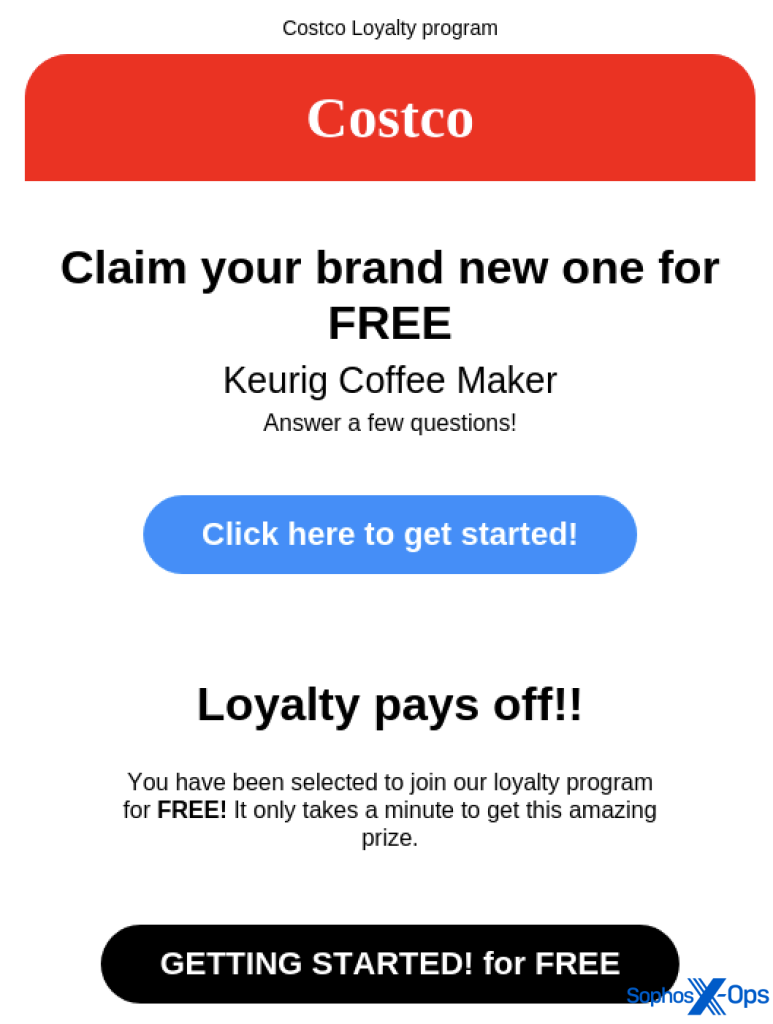 Figure 1: A screenshot of a phishing email, purportedly from Costco
Figure 1: A screenshot of a phishing email, purportedly from Costco
Multimodal AI can identify several suspicious aspects of this email, including:
- Phrases used to incite urgency and action
- The sender’s email domain not matching legitimate domains
- Inconsistencies with logos and images
As a result, the system assigns a high score to the email, flagging it as suspicious.
SophosAI also applied multimodal AI to NSFW (not safe for work) websites containing content relating to gambling, weapons, and more. As with the classification of phishing emails, detection leverages a number of capabilities, including the evaluation of keywords and phrases (agnostic of language), and analysis of imagery and graphics.
Experimental results
To test the efficacy of multimodal AI compared to traditional machine learning models such as Random Forest and XGBoost, SophosAI conducted a series of empirical experiments. The full results are available in Lee’s whitepaper and Virus Bulletin talk – but, briefly, traditional models performed well when detecting known threats, and struggled with new, unseen phishing emails. Their F1 scores (a measure that balances precision and recall to give an overall representation of accuracy between 0 and 1) were as low as 0.53 with unseen samples, reaching a high of 0.66. In contrast, multimodal AI (using GPT-4o) performed very well in detecting new phishing attempts, achieving F1 scores up to 0.97 even on unseen brands.
It was a similar story with NSFW content; traditional models achieved F1 scores of around 0.84-0.88, but models with multimodal AI embeddings achieved scores of up to 0.96.
Conclusion
The digital landscape is in a state of constant evolution, bringing with it an array of new threats – including the use of generative AI to deceive users. Phishing emails now meticulously, and routinely, mimic legitimate communications, while NSFW websites conceal harmful content behind deceptive visuals. While traditional cybersecurity methods remain important, they are increasingly inadequate on their own. Multimodal AI offers an innovative layer of defense that enhances our comprehension of content.
By effectively detecting sophisticated phishing emails and accurately classifying NSFW websites, multimodal AI not only protects users more effectively but also adapts to new threats. The experimental results Lee presents in his paper show significant improvements over traditional methods.
Going forward, incorporating multimodal AI into cybersecurity strategies is not just beneficial; it is crucial for ensuring the protection of our digital environment amid growing complexities and threats.
For further information, Lee’s full whitepaper is available here. A recording of his 2024 Virus Bulletin talk is available here (along with the slides).
Source: Sophos
The World’s Most Innovative Companies Award by Fast Company is the definitive source for recognizing organizations that transform industries and shape society. Today, we’re celebrating that Fast Company has named Silverfort a 2025 Most Innovative Company. We are honored to be listed in the security category alongside others who are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible to create a more secure world.
More than 1,000 enterprises trust Silverfort, and our gross customer retention rate remains high at 94%. We’ve raised more than $220M in funding from leading investors, and we’ve grown to over 450 team members worldwide, with revenue increasing by nearly 100% year over year for the last five years. The entire Silverfort team deserves this honor for working tirelessly to build a platform that delivers maximum security with minimal effort. Thank you to our employees, customers, and investors for all your hard work, loyalty, and unwavering support. And special thanks to our incredible Research, Engineering and Product teams for continuously delivering unmatched innovation that pushes the identity security market forward.
2024 was a big year for Silverfort. In the last six months alone, we acquired Rezonate, an impressive cloud identity security company, we released an incident response solution that flips the script on the traditional IR process, and our product team released an entirely new product—one that helps businesses go beyond managing privileged accounts to securing them (Privileged Access Security). We can proudly say our platform analyzes over 10B authentications daily, detects an average of 34K identity exposures and threats per customer, and is 17 times faster to deploy than traditional solutions.
Silverfort’s journey began with a mission to address a glaring—and growing—weakness we saw years ago in the security industry: identity. Determined to close this gap, the founding Silverfort team pioneered unique, patented Runtime Access Protection (RAP) architecture, which connects seamlessly to an organization’s existing identity stack. It provides unparalleled visibility into all identities and environments, leverages AI for adaptive authentication and threat detection, and even protects what used to be unprotectable, like non-human identities (NHIs), legacy systems, and command-line tools.
Over the last several years, we have worked continuously to build the identity security platform companies deserve. Unlike other solutions that solve one piece of the security puzzle or require overly complicated maintenance and deployments, Silverfort breaks down silos to eliminate security gaps and blind spots with one easy-to-deploy platform.
The result? Identity security without limits.
The Silverfort Identity Security Platform is the only solution that truly goes everywhere to deliver unparalleled protection, context, and visibility, without compromising on productivity. Today, over 1,000 organizations worldwide trust us to protect all identities, all resources, and all environments, all the time—and we look forward to seeing that number grow as we continue to take identity security where it has never gone before.
Thank you to Fast Company for the recognition, and congratulations to the team that got us here. This is identity security done right.
Source: Silverfort
We’re thrilled to announce that Datto RMM has taken home top honors in the G2 2025 Awards. Among thousands of solutions, it stood out as a top choice, securing wins in multiple categories.
Out of 125,912 products in the contest pool, Datto RMM rose to the top, earning top honors across several categories:

- Top 100 in the Best Software Products
- Top 50 in the Best Products for Small Business
- Top 50 in the Best Software for Mid-Market Business
- Top 50 Best Security Software Products
- Top 100 in Highest Satisfaction Products
These high-level rankings highlight how Datto RMM empowers IT professionals with seamless management, from multitenant visibility and automated monitoring to patch management and remote control.
With round-the-clock support, you can count on Datto RMM for:
- Ease of use – An intuitive, user-friendly experience
- Automation – Streamlining tasks and job scheduling
- Seamless integrations – Connecting multiple tools and platforms effortlessly
- Efficient monitoring – Proactive management to prevent issues before they arise
Built with a security-first approach, Datto RMM also delivers robust endpoint and data security through native ransomware detection, mandatory 2FA and agent encryption — helping IT professionals deliver the best experience to their customers and end users.
Milestones That Matter: Our Community’s Success
In addition to Datto RMM’s standout success, Datto earned several other awards worth celebrating.
- Datto BCDR: Known for its user-friendly interface, easy navigation and reliable support functions, Datto BCDR secured a position among the Top 50 IT Management Products and has been credited as the “3rd Easiest to Use” product in the Server Backup software category.

The key aspects of BCDR that stood out for users include:
- Ease of Use
- Customer Support
- Recovery Ease
- Cloud Backup
- Autotask has also ranked in the Top 50 IT Management Products. It secured the Leading Product within the Professional Services Automation category among 5,003 products for the Best IT Management Software Products 2025.

With real-time metrics that give full visibility into service delivery, customer satisfaction, sales pipeline, internal operations, resource utilization, profitability and more, Autotask PSA has consistently delivered 99.99% uptime over the last 10 years.
Explore More:
These awards reflect our strong standing with customers worldwide. If you’re seeking a proactive approach to endpoint protection, now is the perfect time to explore the world of Datto RMM and beyond.
Try for free in our 14-day t/rial!
Source: Datto
Have you ever thought how many accounts in your environment operate outside of your visibility and control? One of the biggest identity security blind spots, often ignored by organizations but frequently used by attackers – is Local Accounts.
Unlike domain-based accounts that security teams can easily detect and monitor, local accounts are left in the dark with limited to no visibility into their activity and privileges. This gap has become such a critical issue that the FBI recently issued a warning, urging organizations to disable local administrator accounts to reduce the risk of cyberattacks.
In this blog, we’ll explore the different security risks posed by local accounts, and how Silverfort’s new local authentications visibility feature helps organizations to close the blind spot.
Understanding local accounts: what they are and how they work
Local accounts exist in 2 main types: local user accounts and local administrator accounts. Let’s describe each type in more detail:
- Local user accounts
These are standard accounts with limited access permissions, typically used for basic access to an endpoint. Local users can log in and operate a system but lack administrative privileges to make any system-wide changes.
- Local administrator accounts
These accounts have full control over an endpoint, allowing users to install software, modify system settings and create new accounts. Built-in local admin accounts (for instance, default Microsoft Windows “Administrator” account) are often under high risk as they can be exploited by attackers for compromise and privilege escalation.
While domain accounts are centrally managed through Active Directory (AD) or an Identity Provider (IdP), local accounts exist only on individual endpoint. From an identity management perspective, the key difference between local and domain accounts is who manages them:
- Local accounts exist and are controlled on the individual endpoint. The user has full control on the system, including privilege access to critical settings, with no visibility from the security teams.
- Domain accounts, on the other hand, are managed centrally by domain administrators within Active Directory (AD) or an Identity Provider (IdP). Security teams have more visibility into domain accounts and the ability to enforce security controls on each user, with specific policies and restrictions configuration.
Local accounts are often used for administrative tasks or legacy systems to provide access to a specific computer or device, but lack of monitoring and advanced security controls offered by domain-based accounts.
The hidden risks of local accounts
From a security perspective, local accounts by themselves won’t cause major security risks. But not managing them properly can have serious impact on the organization. Main of these risks are lack of visibility, limited centralized management, and weaker security controls. These challenges make local accounts a prime target for attackers looking to move laterally and escalate privileges undetected.
Let’s focus on the identity security risks of local accounts in more detail:
1.Lack of visibility: a blind spot in authentication monitoring
One of the biggest risks of local accounts is that security teams can’t see what they can’t track. Unlike domain-based authentications, which are centrally logged and stored, local accounts’ activities are isolated into individual endpoints and do not have any records in AD or IdP logs. This means that any malicious activity, including failed logins, unusual access patterns or compromised credentials, makes it nearly impossible to detect it before it’s too late.
2.Limited centralized management: a security and operational nightmare
Local accounts are stored outside of the directory-based identity management scope. And security teams struggle not only on enforcing policies but even on tracking who has access to what. Many organizations rely on default passwords or static credentials for local accounts without proper credential rotation, which increases the risk of unauthorized access. Without any central authentications management, organizations have fragmented security controls that attackers can easily exploit for compromise.
3.Weaker security controls: an open door for attackers
Local accounts are rarely secured with strong security controls, like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) or other security controls, resulting in an easy target for attackers. Once a local account is compromised, it can be used to escalate privileges or move laterally across the environment without triggering any security alerts. This makes local accounts a critical blind spot in organization’s identity security posture.
How Silverfort enables local accounts visibility
With Silverfort you can now enhance your visibility into local accounts authentications, starting from Silverfort for Windows Logon version 2.1.3.
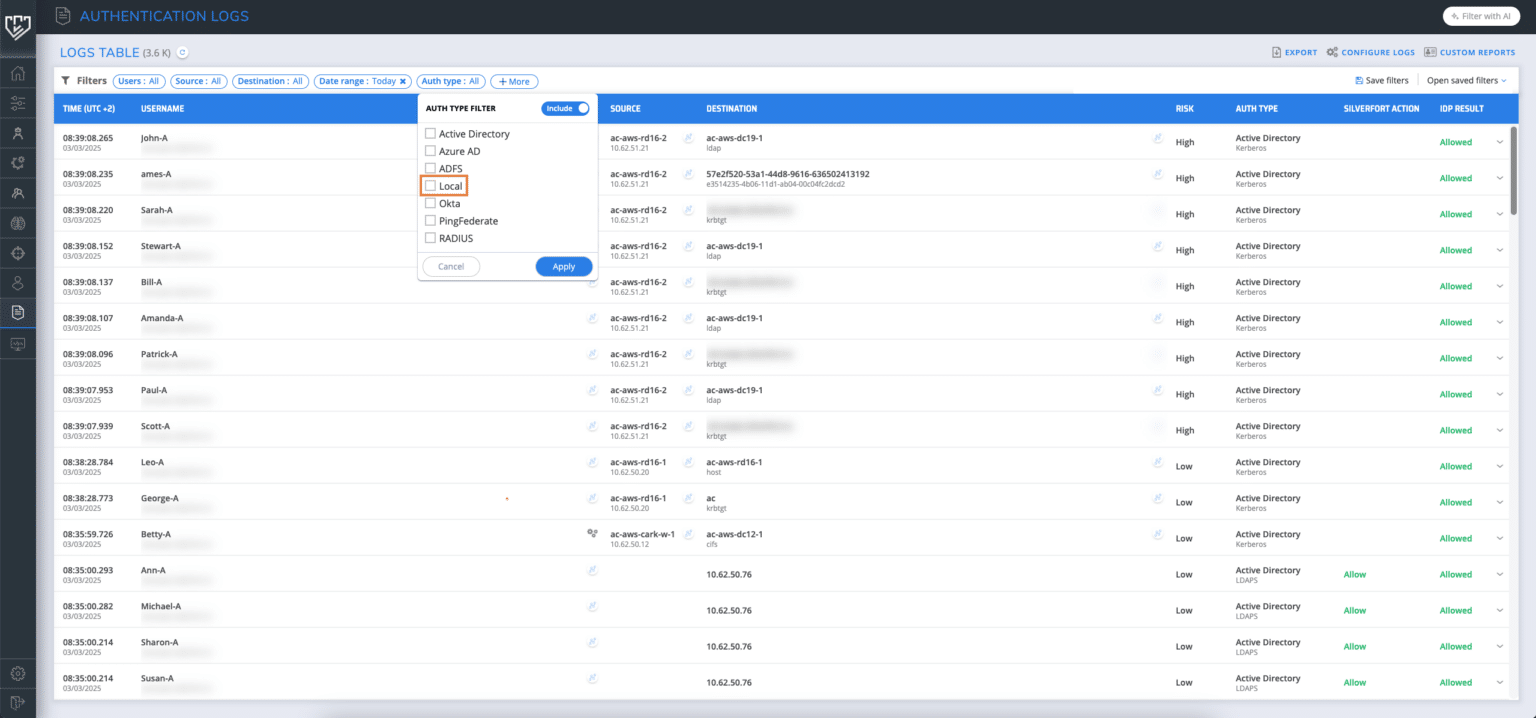
When a local user accesses a Windows machine with Silverfort for Windows logon installed, the authentication will be recorded with the auth type “Local”, and you will gain complete visibility into these access attempts from Silverfort Logs screen by filtering by Auth type = “Local”.
Video: Example of how to filter local user authentications in Silverfort’s logs screen
This new product capability allows you to track local logons for Windows. By filtering local account access attempts, you can quickly identify any malicious activities, including potential credential misuse.
Shining a light on local accounts: the first step to protection
Local accounts have always been seen as a security blind spot which attackers can utilize to create an easy entry to compromise an environment and stay unnoticed. Without visibility into the accounts’ authentication activities, you could not detect or respond to any of these malicious activities before they escalate.
With Silverfort’s real-time visibility into local accounts’ authentications, you can finally unlock new hidden layer of identity security from being completely unseen to monitor, track and investigate these identities. This is a solid ground to start towards complete security and protection of local accounts.
Ready to explore hidden local accounts in your environment? If you are an existing customer, please reach out to your customer success manager or schedule a call with one of our experts.
Source: Silverfort
A password generator is an online tool that automatically creates strong, random passwords at the click of a button. To create unique passwords, a password generator combines a variety of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols. Password generators dramatically ease the process of creating strong passwords by automatically producing random, lengthy ones – two qualities that make passwords more challenging for cybercriminals to crack.
Keep reading to learn why you should use a password generator and how you can use it to strengthen your online security.
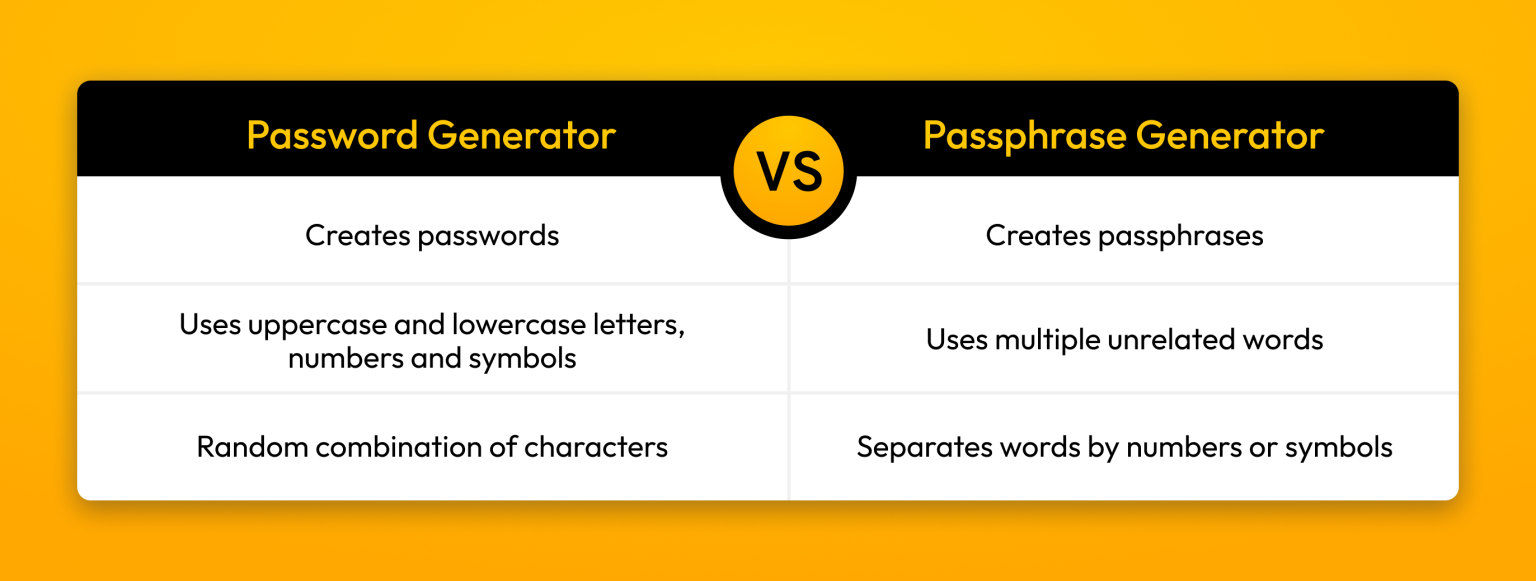
Password vs passphrase generator: What’s the difference?
The main difference between a password generator and a passphrase generator is that a password generator creates a password, while a passphrase generator creates a passphrase. Password generators create strong passwords, which contain at least 16 characters, including uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols. For example, this would be a strong password produced by a password generator: B^F<>8=>56qXUQCkhN?$.
A passphrase is a combination of words separated by numbers or symbols that are used as a password. Therefore, a passphrase generator produces multiple unrelated words, making passphrases more difficult for cybercriminals to crack. An example of a strong passphrase created with a passphrase generator could look something like this: Leaf-Banana0-Joy_Friend4-Sunlight.
Why use a password generator?
You should use a password generator because it guarantees strong and unique passwords, eliminates the chances of using weak or reused passwords and makes updating your passwords convenient.
It ensures your passwords are always strong
Password generators naturally create strong passwords by randomly combining letters, numbers and symbols. This random combination of characters contributes to the strength and uniqueness of any password you create with a password generator. Strong passwords are essential in reducing your chances of a cybercriminal hacking into your online accounts, which, in turn, minimizes your risk of becoming a victim of fraud or identity theft.
You don’t have to rely on yourself to create passwords
Maybe you believe that you can come up with strong passwords on your own just fine. However, a recent study commissioned by Keeper® found that 41% of people admit to reusing the same password across multiple accounts. Password generators eliminate dangerous human tendencies by creating passwords that are completely random and unrelated to personal information, such as a pet’s name or birthdate. If you only rely on yourself to create strong and memorable passwords, you will likely start to reuse the same password or slight iterations of the same password on multiple accounts. Using weak or reused passwords increases the likelihood of a cybercriminal cracking your passwords and stealing your private information.
It makes changing your passwords easy
If you need to change your password following a data breach or hacking, using a password generator makes updating your passwords simpler while ensuring the new ones are secure. All you have to do is hit a button to receive a new, strong and random password that will be very difficult for a cybercriminal to crack. Rather than racking your brain to come up with a password you haven’t used before, a password generator makes this process quick and convenient.
It helps you avoid dictionary attacks
A dictionary attack targets passwords that use common words or phrases found in dictionaries. Since common words or phrases are easy for a cybercriminal to crack in a password, using a password generator combats dictionary attacks because your password will contain a random combination of letters, numbers and symbols rather than easy-to-guess words or phrases. If each of your passwords to your many online accounts is a 16-character password with unique letters, numbers and symbols, a cybercriminal will have a very difficult time cracking them.
How to use a password generator
You may be wondering how simple it is to use a password generator after hearing all its benefits. Follow the steps below to learn how you can use a password generator to create strong and unique passwords.
1. Find a secure password generator to use
Luckily, there are many free password generators you can use online to create passwords. However, you should consider the benefits of using a password manager with a built-in password generator, like Keeper Password Manager. Having a built-in password generator makes it easy to create or update passwords that are strong and unique. Then, you can save your randomly generated passwords directly in your Keeper Vault to ensure your passwords are encrypted and protected from cybercriminals.
2. Adjust the password generator settings
After finding the best password generator for you, you can customize its settings to fit a specific website or app’s password requirements. For example, if an online account requires your password to contain both uppercase and lowercase letters, at least two numbers and one symbol, you can adjust your password generator’s settings so it creates a password based on those criteria. An app might require your password to contain at least 16 characters, which means your password must contain a minimum of 16 letters, numbers and symbols combined. Regardless of what requirements a website or app may have for your password, you can change your password generator’s settings to suit your password needs.
3. Generate your strong password
Once you’ve set your password generator’s settings, you can create your random password. After the password generator produces a strong and unique password, you can either try to remember it or save it in a password vault. Saving your passwords in a password vault like Keeper ensures your passwords are protected and saves you the hassle of remembering the password. Keeper has an autofill feature that works on all devices and browsers, so the next time you need to input your password, Keeper will do it for you.
Generate strong, unique passwords with Keeper
Using a password generator is not only convenient but also safe for strengthening your passwords and protecting your private information. Keeper Password Manager’s built-in password generator is easy to use and eliminates the risk of using weak or reused passwords.
Start a free 30-day trial of Keeper Password Manager to experience the ease of a built-in password generator and a safe place to store your passwords.
Source: Keeper Security
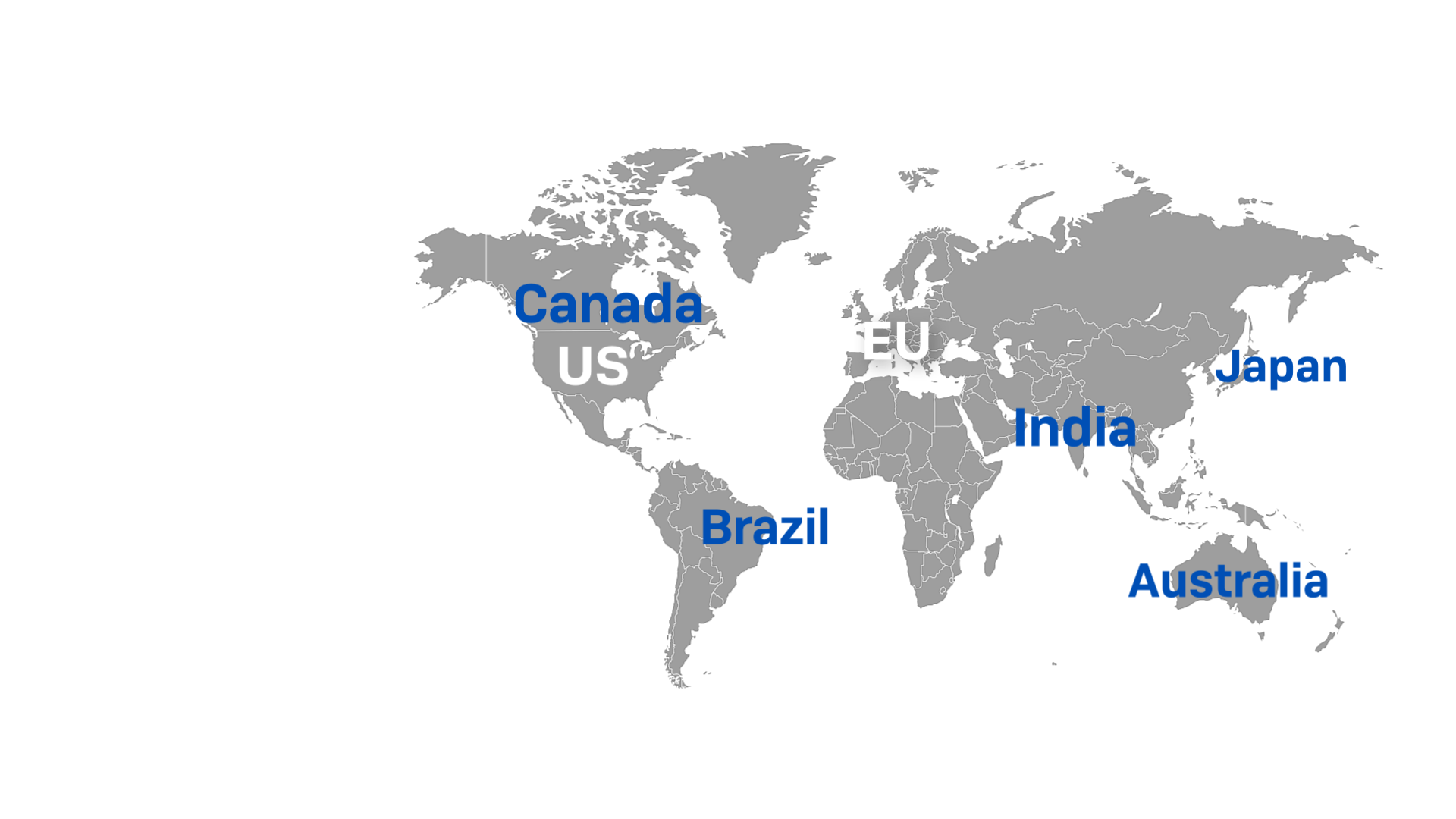
Sophos DNS Protection is now available for Sophos Firewall customers with Sophos Central accounts outside of the standard US and EU regions, adding five new management regions: Australia, Brazil, India, Japan, and Canada.
This matches similar regional expansions for other Sophos Central managed products including ZTNA, Sophos Switch, and our AP6 Wireless line. For a full list of Sophos Central products and which regions are supported, see this article.
If you currently manage Sophos Firewalls in one of these regions, you can now easily add Sophos DNS Protection to your account. Your Sophos Firewalls with Xstream Protection include DNS Protection at no extra charge (see below for how to get started).
Note that Sophos DNS Protection already provides a global network of DNS resolver points-of-presence (POPs) and DNS traffic is automatically directed to the nearest location using unicast routing technology to ensure the fastest response. This new release now enables management of DNS Protection from all Sophos Central locations as well.
Get started with Sophos DNS Protection
If you are a Sophos Firewall customer with Xstream Protection and are not already using Sophos DNS Protection, you can get started for free. Check out our online documentation and video resources.
Source: Sophos
Juggling daily demands can make it difficult to keep up with the renewal dates on your Sophos subscriptions. To help you avoid any gaps in your protection, we are improving expiration alerts in Sophos Central so you can enjoy seamless protection against the latest threats.
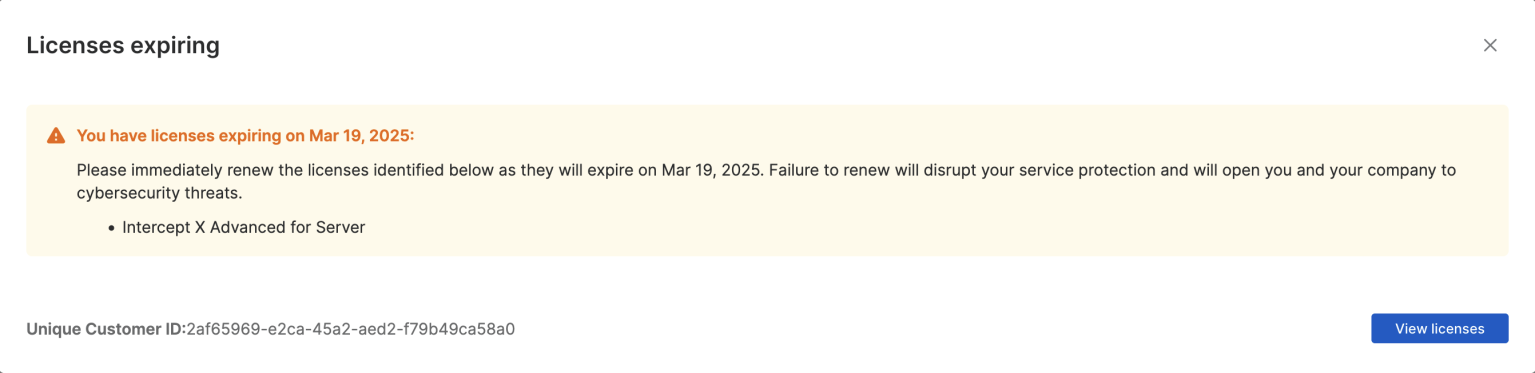
What to expect?
30 days before your renewal date we will begin notifying you of your upcoming license expiration when you log-in to Sophos Central. Expect to see a pop-up message like the image above that shows:
- Which license(s) are due for renewal
- The license expiry date(s)
Select “View licenses” to go to the “Licensing” page where you can apply a new license key, access your partner’s contact details, find additional contact information, or dismiss the notification for that log-in session. The messages will stop displaying once you renew your license.
If you do not renew your license before it expires, the alerts will let you know that you do not have an active subscription and that access to your products and services will be restricted after a period of time. Should you have no active Sophos licenses, access to your Sophos Central account will be restricted as well.
Is there anything else I should know?
The new license expiry notifications:
- Are only available in Central Admin
- Do not apply to free trials
- Do not change the behavior of Sophos products when licenses expire i.e., they are notification only. Details on individual product behaviors can be found within the Licensing Guide
Source: Sophos
Sophos Firewall OS v21 MR1 brings several scalability, resiliency, and stability enhancements to your Sophos Firewall.
What’s new
- SSL VPN – Now supports key sizes of 3072 or 4096 bits for the Diffie-Hellman key exchange to enhance secure communication and compliance requirements. Enhanced UDP-based SSLVPN tunnel resiliency has also been added using a granular dead peer detection timeout configuration.
- IPsec VPN – Improved stability for offloaded policy-based VPN IPsec traffic that eliminates slow browsing issues.
- NAT64 – The firewall enables IPv6-only clients to access IPv4 websites through an explicit proxy. Also added support for an IPv4 upstream proxy for IPv6-only clients.
- DHCP – Implemented added resiliency to the DHCP service which now auto-restores if it gets into an error state.
- Cellular WAN – The firewall now offers enhanced cellular WAN monitoring by automatically setting “8.8.8.8” as the second probe target. This addresses the issue of ISPs blocking gateway pings, reducing the need for manual configuration.
- SD-RED support – SD-RED devices now support remote troubleshooting and diagnostics by Sophos Support.
How to get the firmware and documentation
Sophos Firewall OS v21 MR1 is a free upgrade for all licensed Sophos Firewall customers – including XGS Series, cloud, virtual, and software firewalls.
Note: XG Series devices are soon to be end-of-life and need to be upgraded to XGS Series devices immediately and are not supported by v21 or v21 MR1.
This firmware release will follow our standard update process. You can manually download SFOS v21 MR1 from Sophos Central and update any time. Otherwise, it will be rolled out to all connected devices over the coming weeks. A notification will appear on your local device or Sophos Central management console when the update is available, allowing you to schedule the update at your convenience.
You should update your Sophos Firewall firmware at your earliest opportunity.
Sophos Firewall OS v21 MR1 is a fully supported upgrade from all previous versions of v21, v20, v19.5 and v19.0. Please refer to the Upgrade Information tab in the release notes for more details.
Full product documentation is available online and within the product.
Source: Sophos
With the explosion of cloud computing, video streaming, AI, and other data-hungry technologies, traditional gigabit Ethernet (GE) networks are struggling to keep up. Bottlenecks and latency issues are hampering application performance and the overall user experience.
The newest addition to the Sophos Switch portfolio, CS1010-8FP, provides a cost-effective way to support the high-speed, low-latency requirements of modern networks and applications, such as:
- High-definition media streaming
- Large file content transfer, e.g., Computer-Aided Design (CAD), video editing
- Server-to-server and server-to-NAS data backups
- Communication with 10-gigabit servers
- Linking multiple 1-gigabit switches for improved performance
- Higher-speed LAN to reap the potential of high-speed internet, e.g., Fiber to the premises
Product highlights
For a brief overview of the new model, watch this video:
The CS1010-8FP offers eight 10-gigabit PoE-capable ports (PoE++/802.3bt) and four SFP+ interfaces. The 410W Power over Ethernet budget is sufficient to power up to six 60W devices or eight PoE++ devices with slightly lower power consumption, such as our AP6 840E access points
CS1010-8FP connectivity
- 8 x 1/2.5/5/10 GE multi-gigabit copper ports
- 4 x 1/10G SFP+ fiber ports
- 410W PoE budget [Ports 1-8 (max. 60W per port), 802.3bt/PoE++]
10 GE is fully compatible with earlier Ethernet standards, making it easy to integrate into existing networks (provided the required Cat6 cables are used).
Sophos multi-gig connectivity across your firewalls, access points, and switches gives you a future-proof solution to avoid network bottlenecks and the necessary throughput to handle evolving connectivity requirements. This allows you to scale your operations and seamlessly support emerging technologies, keeping your employees productive, and your business agile.
Find out more at Sophos.com/Switch.
Source: Sophos
In IT service management, every second counts. When you’re handling countless tickets, managing client relationships and overseeing intricate projects, an inefficient PSA tool can be your biggest roadblock.
If your system is slow, clunky or frustrating to use, it isn’t just an inconvenience -it’s a drain on your productivity and profitability. A PSA tool should work for you, not against you. But if navigating your current system feels like an uphill battle, it’s time to consider the impact of a poor UI.
10 reasons why your PSA needs a better UI
Here are the top reasons why upgrading your PSA’s interface is a necessity.
1. Faster workflows
An optimized UI minimizes unnecessary clicks, improves navigation and streamlines workflows so your team can accomplish tasks quickly and efficiently.
2. Reduced training time
A user-friendly interface ensures that new hires can learn the system faster, reducing the time and cost associated with onboarding and training.
3. Improved accuracy
A well-designed UI eliminates confusion, making key actions clear and logical, which helps reduce errors and misplaced data.
4. Increased technician satisfaction
Your team deserves a PSA tool that works with them, not against them. A modern UI reduces frustration, improves morale and keeps technicians happy and engaged.
5. Seamless multidevice use
Technicians aren’t always at their desks. A PSA tool with a responsive, mobile-friendly UI ensures productivity whether they’re in the office or on-site.
6. Enhanced customer interactions
When information is easy to find, your team can respond to customer or user inquiries faster and more effectively, improving service quality and satisfaction.
7. Greater customization
A PSA tool should adapt to your business, not the other way around. A flexible UI allows users to customize dashboards and layouts to fit their unique workflows.
8. Accessibility for all
A great UI ensures usability for everyone, including those who rely on keyboard navigation, screen readers or other accessibility tools.
9. Lower error rates
A cluttered or unintuitive UI leads to mistakes. A streamlined, well-designed interface helps prevent costly errors and miscommunications.
10. Future-proofing your business
Technology evolves fast, and so should your PSA tool. A PSA with a modern, continuously improving UI ensures you stay ahead of industry trends and efficiency standards.
Autotask PSA’s Next-Generation UI: A Case Study in Good UX
If you’re looking for a PSA tool that embraces all these UX principles, Autotask’s latest UI update is worth exploring. With the 2025.1 release, Autotask PSA is taking its user experience to the next level with:
- Enhanced navigation: A collapsible left navigation menu, cleaner top navigation and a revamped search bar for a smoother experience.
- Refreshed dashboards: Customizable layouts with resizable widgets to tailor the interface to your workflow.
- Streamlined Worklist panel: Pinned tickets and tasks remain front and center, reducing distractions and keeping priorities clear.
- Improved accessibility: Enhanced keyboard navigation, mobile usability and screen reader support to ensure everyone can work efficiently.
- Unified UI across Kaseya IT Complete: A consistent design across Autotask, IT Glue and other Kaseya tools for easy cross-platform navigation.
And this is just the beginning. Future updates will include in-line editing, bulk actions, preview panels for related items and even more ways to improve usability and efficiency.
Don’t let a poor UI hold you back
Your PSA tool should make your job easier, not harder. If your current system is slowing you down, frustrating your team or making simple tasks unnecessarily complicated, it’s time for a change.
Autotask’s next-generation UI is designed to maximize efficiency, accessibility and user satisfaction. If you’re ready to see how a modern PSA interface can transform your workflow, it’s time to experience Autotask for yourself.
Ready to stop wasting time? Learn more about Autotask’s new UI today by booking a one-on-one call with one of our PSA experts.
Source: Datto