News
Sophos announced the launch of Intercept X Advanced for Server with EDR, bringing the power of Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) to Intercept X for Server.
EDR gives you the ability to proactively hunt down evasive threats across your server estates (and endpoints with Intercept X Advanced with EDR), understand the scope and impact of security incidents and to confidently report on your security posture at all times.
EDR also allows you to:
- Search for indicators of compromise across the network
- Prioritize events for further investigation
- Analyze files to determine if they’re potentially unwanted or true threats
- Answer tough compliance questions in the event of a breach.
Evolving EDR
EDR is designed to investigate the grey area of files that are suspicious but cannot be immediately identified as malicious or benign. That’s fantastic in theory, but the reality for many organizations is that EDR tools require a level of knowledge and time investment that simply cannot be met.
At Sophos we take a different approach. We start with the strongest layer of protection that blocks the latest threats like ransomware and exploits, and also reduces the grey area of suspicious files that need investigation. In effect this means there is less to investigate and it is easier and faster to find the needle in the haystack.
On top of that you get the latest threat intelligence from SophosLabs helping you to make an informed decision on whether a file is benign or malicious.
Download the datasheet to learn more and then try it for free. If you’re a Sophos Central user, you can start a trial directly from the console.
It’s now one year on since the GDPR came in to effect – a regulation with an aim to standardise data protection laws across the EU, increase the privacy and protection of personal data and extend the rights of the data subject. So what has happened since GDPR go-live this past year, and what have we learnt?
According to IAPP research, since go-live, over 500,000 organisations have a registered Data Protection Officer in place – a new required position under the regulation for organisations meeting certain criteria that oversees compliance and data protection obligations.
The new regulation has prompted over 200,000 cases to have been created by data protection authorities and over 94,000 complaints received, ranging from right to erasure to unfair processing.
The GDPR overhauled and detailed new requirements for data breach notifications, which has seen a major increase in reported data breaches – estimated at over 64,000, and in some countries more than double the previous year’s amount.
The hottest topic related to GDPR was how infringements would equate to fines for organisations at fault – to date over €56,000,0000 fines have been issued as GDPR enforcement actions, however, the largest single fine was issued to Google and contributed to the majority of the global total at over €50m.
GDPR and the rest of the world
It should not to be forgotten that the GDPR is applicable not only to EU countries, but any country that holds EU citizen data and although only a small proportion of the total number, this past year has seen almost 300 cross-border cases raised.
Although described as an evolution rather than revolution, the GDPR has ushered in similar data protection regulation proposals across the globe. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) has been signed in to law with further deadlines to agree and adopt the legislation, although currently only at state level, it’s looking likely the U.S will adopt a GDPR style regulation nationally in the future.
Brazil, Latin America’s largest economy and its Lei Geral de Proteçao de Dados (LGPD) regulation has been modelled directly after the GDPR for 2020, and Australia have solidified data breach notification requirements since 2018 with the Australian Privacy Act amendment.
What have we learnt?
The data is enough to show a turn of the tide on the protection of personal data and enforcement for those who fall short, still – year one is a transition year and with that, we should expect a lot more movement in following years.
The positive note is that it’s not only organisations who are waking up to the need to protect personal data, but other countries now who are adopting similar style approaches for their own citizens personal data.
We have learnt that since the GDPR has been enforced, the majority of businesses have had an enormous amount of resource and investment required to offer the level of protection of personal data, which the average citizen may have been surprised hadn’t previously been in place.
The general consensus is that there is still a long way to go until a GDPR style approach to data protection is realised globally.
Data classification and GDPR compliance
If you want to learn more about how data classification supports GDPR compliance by visual labelling, enhanced workforce awareness of the value of the data used and metadata labels facilitating data security, data management and retention policies, then download our resource: EU GDPR – Protect Sensitive Personal Data On EU Citizens Fact Sheet or request a data classification demo.
Discovering that you’ve been the victim of a breach is never pleasant. Perhaps your customers’ data was stolen and now sits in the wilds of the internet. Maybe your intellectual property and trade secret were compromised. Or you could be concerned the adversaries are still actively lurking on your network.
If this is you, you should have a couple of things already in place, including a well-rehearsed response plan and a digital forensics and incident response (DFIR) retainer. Both help prevent you from having to mobilize a strategy and find expert help during a time of unfolding chaos.
That said, if you’re at the point where the rubber meets the road, it’s time to get moving. Here is what you can expect will be necessary to accomplish in the hours, days, weeks and months following a breach discovery. Part of the burden will naturally fall on you, but outside help is available to amplify your efforts or compensate for any internal resource shortfalls.
1) Make the call.
If you can’t handle the full spectrum of breach response yourself, get in touch with a DFIR investigator immediately. The faster they can begin their investigation, the better.
2) Document the situation.
Back in my university days, I was a Canadian Navy Reserve officer. A useful lesson from training school that applies here is that before starting any mission, document your situation. Write down the systems/data that have been impacted by the breach, methods that could contain the situation, and how those methods might affect your operations, data, and evidence.
3) And document some more.
Time will speed up as you’re investigating a breach. You’ll be working on it, while also providing updates to others and figuring out next steps. Because of the pressure, it’s easy to forget steps if you’re not recording them. Keep a record of what actions are being taken and when. This detail will help immensely when you’re restoring systems and tracking evidence.
4) Make copies.
Back up systems and data before making any changes. You might need that data later if changes don’t go well, or you might want to further study any malware or viruses on affected systems.
5) Identify what else might be affected.
When an incident is identified, determining which systems are affected is the easy part. More difficult is tracking how those systems interact with the rest of the network, what information may be on them and how that information could enable an attacker to pivot to other systems. It’s better to be wrong and assume the worst than assume attackers got no further than the initial target.
6) Implement containment.
Many options exist to stop the bleeding. Remove compromised systems, update firewall rules, change passwords and more. These steps probably won’t constitute a final resolution, but they will give you time to put a more comprehensive solution in place.
7) Review breach notification requirements.
Ideally you already have this information available in your incident response plan, but if you don’t, you should know that requirements vary by state, country and even industry. And in some cases, you will have to provide notification for a region even if the affected systems weren’t in that region (e.g., if personnel in that region were impacted).
8) Consider legal counsel.
Lawsuits are a common outcome following breaches, but your liability can be managed. Depending on the systems and data affected, you might want assistance from a law firm that specializes in cyber law.
9) Notify stakeholders.
In addition to your requirements to provide breach notifications, you will likely want to proactively notify customers, partners or other interested parties if their data was affected or potentially affected. In your notification, you’ll want to include what actions they should take to protect their own systems and data.
Serving as the storekeeper of your most sensitive assets, from college admissions applications to resumes of executives, databases are relied upon by organizations worldwide to warehouse and make accessible their information.
They are your modern-day treasure chest, essential in helping you manage your data in a world where bits and bytes are growing at staggering rates. Contemporary database systems are rich in features that enable fast, convenient and flexible entry, storage and retrieval.
Of course, the value that databases bring in managing large quantities of information also lead to arguably their biggest downside: security concerns. Between the allure of huge data sets sitting all in one place and the potential security risks that default-enabled features bring – not to mention increasing cloud deployments and the risk that patching will break something – databases require their own specific security attention. If not, something bad may happen, as I alluded to at the start of this post with references to college applications and executive resumes.
To help you avoid similar adverse fate, let’s discuss the primary threats facing databases and some quick reminders of how you can keep them safeguarded from both attacks and mistakes.
1) Credential Threats
Weak password management and authentication schemes allow attackers to assume the identity of legitimate database users. Specific attack strategies include brute force attacks and social engineering, namely phishing.
2) Privilege Threats
When a user accidentally misuses access rights that were granted properly, or when an admin grants a user excessive access rights by oversight or out of negligence, it can result in privilege abuse, or more malevolent, privilege escalation.
- Privileged account abuse occurs when the privileges associated with a user account are used inappropriately or fraudulently: maliciously or accidentally, or through willful ignorance of policies.
- Privilege escalation involves attackers taking advantage of vulnerabilities in database management software to convert low-level access privileges to high-level access privileges. Privilege escalation requires more effort and knowledge than simple privilege abuse.
3) System Threats
A myriad of other things could trip up database security. These include:
- SQL injections: a perennially top attack type that exploits vulnerabilities in web applications to control their database.
- Missing patches: Once a vulnerability is published, which typically happens around the time a patch is released, hacking automation tools start to include exploits for it. For context, 119 vulnerabilities were patched in five of the most common databases in 2017, according to the 2018 Trustwave Global Security Report.
- Audits: Databases are key components in breach investigations and compliance audits. Audit logs are mandated by the General Data Protection Regulation, Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, Sarbanes-Oxley, Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act and more, yet it is still a significant issue. And following an incident, you don’t want to be in a position where you can only tell that something bad happened, but you cannot get detailed information about what exactly happened.
- Cloud: Purchasing third-party database systems can lead to a lack of visibility, control and transparency because they will most likely not be provided with a full-service description detailing exactly how the platform works and the security processes the vendor operates.
As a complement to the database security methodology detailed here, here are some quick tips to remember when setting up strategy for locking down your information repositories.
- ✔ Inventory existing installations.
- ✔ Make sure everything is properly patched.
- ✔ Disable unused functionality.
- ✔ Drop unnecessary privileges.
- ✔ Use strong encryption.
- ✔ Enable auditing.
- ✔ Validate application code.
For more information on how real-life CISOs are constructing their database security programs, check out this e-book.
GlobalSign (www.globalsign.com), a global Certificate Authority (CA) and leading provider of identity and security solutions for the Internet of Things (IoT), today announced that its popular Digital Signing Service (DSS) supports 2014/55/EU, the newly implemented European Union directive regarding electronic invoicing. The directive defines a common standard for e-invoices to reduce the complexity and legal uncertainty around e-invoicing and make cross-border trade relations easier. As a result of the new regulation, which came into force on April 18, all EU public sector contracting authorities are required to receive and process e-invoices that comply with the standard.
In Europe, the need to guarantee “authenticity of origin” (i.e., the identity of the invoice issuer) and “integrity of content” (i.e., the content of the invoice has not been changed from the moment of issuance) for e-invoices was first established in EU Directive 2006/112/EC on Value Added Tax (VAT). Per the regulation, all VAT registered entities had to meet the requirement in order to maintain compliance. The “VAT Directive” specified advanced electronic signatures as one method for meeting this. Advanced electronic signatures guarantee authenticity and integrity of content by uniquely identifying the sender of the invoice, as well as creating a tamper-evident seal on the invoice contents, such that any changes made to the document after it was signed will be detectable.
“DSS provides the throughput, availability, and fault tolerance needed to support high volume electronic invoice generation. With it, we are easily able to meet the new requirements in the EU. In addition, DSS makes it easy to build advanced electronic signatures directly into existing e-invoice generation workflows without requiring significant development time, PKI expertise, hardware investment or ongoing management,” said Lila Kee, General Manager, Americas, GlobalSign. “Global companies need to plan ahead and apply thought around their current invoicing standards moving forward should there be a requirement to meet cross-border standards into Europe.”
To learn more about GlobalSign’s electronic invoicing capabilities, visit https://www.globalsign.com/en/lp/e-invoicing-directive-dss/.
As organizations learn that sophisticated attackers are dwelling unnoticed on their networks for months – or even years – on end, you may be seeing the need to move beyond basic threat prevention and become more proactive in identifying and eradicating threats.
With 83 days the median time between when attackers gain unauthorized access to victim networks and when incidents are first detected, according to the 2018 Trustwave Global Security Report, your adversaries are having ample time to cause real damage. But a defense activity known as threat hunting has emerged in recent years as a key way to counter that seemingly interminable window of time when intruders can operate untrammeled within your borders.
Threat hunting is broadly defined as the manual practice of applying tools, tactics, procedures and intelligence to uncover advanced network attacks that have slipped past existing defenses. Threat hunting’s growing popularity is, in part, because:
- Increasingly sophisticated attackers continue to bypass traditional security prevention technologies.
- The threat hunting toolset is more efficient, with mature endpoint detection and response (EDR) with integrated threat intelligence and use behavior analytics available.
- There are a growing number of security professionals with a deep understanding of threat hunting tools and techniques.
With more interest – and more vendors pushing threat hunting services – you should carefully consider when to invest in proactive threat hunting and how to go about doing the threat hunt. Let’s look at some of the most common reasons for doing a proactive threat hunt. In a future article, we’ll talk about how to decide to do them using in-house or outsourced resources.
Sometimes the decision to invest in a threat hunt is easy. If you know your organization is breached, a reactive threat hunt may ensue, when incident responders look for the cause and extend of the breach. Determining when to invest money and resources proactively can be more difficult, though in the following situations, a proactive threat hunt is a security best practice.
- You’re partaking a merger or acquisition: Companies involved in M&A activities should make evaluating the security posture and controls of an acquisition part of their due diligence process. A proactive threat hunt should be a part of this process to ensure that when the two company networks connect, it doesn’t give an attacker already on one network easy access to the other.
- You’ve experienced a breach: When discovering a data breach, companies will go through their IR plan to determine the who, what, when, where and how details of the breach and remediate issues. A few weeks or months after resolution is a good time to invoke a proactive threat hunt to double check that the threat is really gone. Even the most thorough IR team can miss an indicator of compromise or some other weakness that attackers can leverage to strike again.
- Your partner has experienced a breach: Sometimes a breached supplier, contractor or other third-party firm may indicate that your business has been hit as well. If you get notification from a partner that they’ve sustained a compromise, a proactive threat hunt can help determine if their misfortune extends to your network.
- You are (or your organization has hired) a new CISO: Industry studies vary, but most suggest the average chief security tenure is somewhere between 12 and 24 months. New CISOs, responsible for protecting and enabling your business, should have a proactive threat hunt done to ensure that along with their new position, they haven’t inherited any unknown attackers.
- Your risk tolerance is low: If your organization is not willing to take on significant risk, it requires a highly mature security program. Organizations like these should include regular proactive threat hunts as part of their security program to validate environmental integrity and uncover advanced threats dwelling in their environment.
Aside from finding unknown malicious actors or threats pestering across your IT infrastructure, threat hunting can also provide visibility into previously unknown weaknesses in your environment, such as outdated and vulnerable software, violations to policy, insider threats and unprotected databases. Finding and fixing any or all issues identified help increase security and reduce risk.
SC Media recently reviewed XG Firewall and awarded it their top 5-star rating across all areas including features, documentation, performance, support, ease of use, and value.

In the course of the review, they highlighted many of XG Firewall’s advantages over competing firewall products.
The SC Labs Review team examined key areas of the product including the Control Center and reporting capabilities, noting:
“At a glance visibility shows traffic light style indicators of hidden risk on the network such as top risk users, suspicious payloads, endpoint health, advanced threats, network attacks and more“.
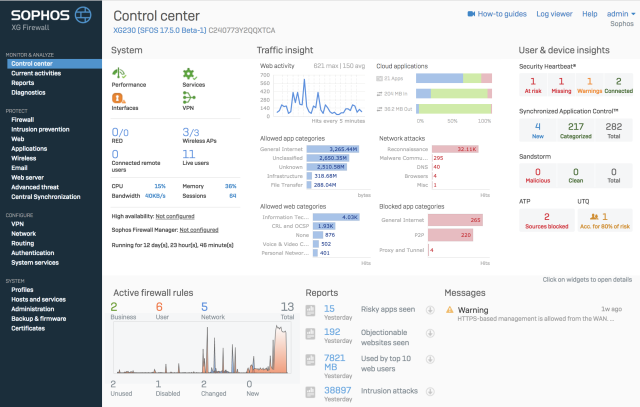
They also highlighted the important threat visibility, protection and response benefits that Security Heartbeat provides:
“Administrators do not need to do anything to automatically isolate threats as a result of the dynamic firewall rules and lateral movement protection coordinated with the endpoints“.
The reviewers also noted the importance of Synchronized Application Control:
“Integrating the endpoint with the firewall also allows for the identification of applications that would not otherwise be identified“.
They also noted many of our unique XG Series appliance benefits:
“Hardware advantages include flexible connectivity, business continuity and easy management, high performance solid-state storage on every model“.
Overall, the SC Labs review team was super impressed with the product’s many visibility, protection, and response benefits.
Learn more about XG Firewall at Sophos.com/XGFirewall.
This month, SophosLabs has been examining a new ransomware attack called MegaCortex that uses layers of automation, obfuscation, and a variety of other techniques to infect victims and spread throughout an environment without detection.
Fortunately for Sophos customers, Intercept X leverages multiple layers of defense to stop MegaCortex, including:
- Blocking PsExec from executing the batch script remotely
- Deep Learning to quarantine the malware before it executes
- Tamper Protection to stop the attacker from disabling Sophos
- CryptoGuard to identify the ransomware’s malicious encryption and roll back any impacted files
How it works
You can learn more about the attack and how Intercept X stops it in this short video:
Learn more
For a technical analysis of MegaCortex, check out the SophosLabs Uncut article.
To find out more about Intercept X, visit the Sophos website, or sign up for a free trial.
The UK’s Information Commissioner stressed in a speech that nearly one year into GDPR, the regulation is at a critical stage.
There have been tremendous strides in data protection since the implementation of the General Data Protection Regulation last May but there’s still plenty more to be done from an accountability perspective, according to the UK’s Information Commissioner.
Elizabeth Denham, Britain’s Information Commissioner since 2016, reflected on the GDPR, data protection achievements and challenges in a keynote speech at the Data Protection Practitioners’ Conference in Manchester, and stressed that she hasn’t seen data protection, as a culture, shift from compliance to accountability.
“I think even so early in the new law’s lifespan, we’re finding ourselves at a critical stage,” Denham said, “For me, the crucial, crucial change the law brought was around accountability. Accountability encapsulates everything the GDPR is about.”
Because of this deficiency, Denham told the crowd she thinks there’s a real opportunity for data protection professionals to bridge that gap and “have a real impact on that cultural fabric of [their] organization, beyond bolt on compliance work.”
In Denham’s eyes, the next wave of GDPR needs to look past compliance and zero in on comprehensive data protection, a concept that embeds what the Commissioner calls sound data governance into business processes.
The Commissioner gave three examples of data protection professionals who are going above and beyond in the industry and satisfying this rationale.
The shortlist includes legal experts who double as business analysts and can comprehend how data protection fits with the vision of the organization, “where it can be imperative, positive and transformative,” professionals who coach and have built a network of ambassadors within the business that understand what needs to be done, along with marketers, who have mastered ways to “get people to look up from their day jobs and realize they all need to buy-in.”
While not a new concept, it’s the second time in the last several weeks that Denham has harped on the theme of accountability – one of the seven key principles of GDPR – as it relates to data protection.
In South Africa, at a speech at the International Conference of Information Commissioners (ICIC) last month, Denham said the ICO as a group is committed to the advancement of transparency, accountability, and democracy, acknowledging the themes unite everyone and are the basis for collaboration and combating challenges.
The concept of accountability essentially requires organizations to take responsibility for what they do with personal data. The concept, per the EU’s Data Protection Supervisor, requires orgs to put in place the appropriate technical and organizational measures to be able to demonstrate what they did and its effectiveness when requested.
With the impacts and repercussions of the looming California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) on the minds of many privacy professionals, new research from MediaPRO shows more work is needed to train U.S. employees of this first-of-its-kind privacy regulation.
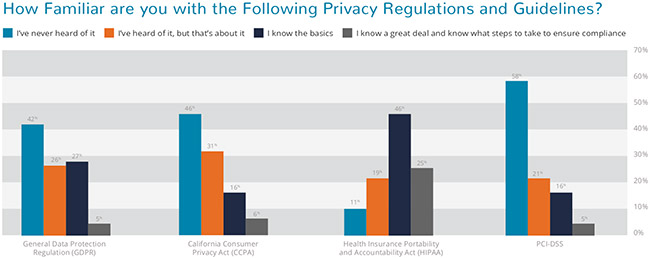
MediaPRO’s 2019 Eye on Privacy Report reveals 46 percent of U.S. employees have never heard of CCPA, which sets specific requirements for the management of consumer data for companies handling the personal data of California residents.
Passed last year and going into effect in January 2020, the CCPA has been referred to as a U.S. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for its scope and focus on data rights. Privacy experts expect the law to apply to more than 500,000 U.S. companies. The 2019 Eye on Privacy Report findings suggest that raising employee awareness should play a key role in preparing for this new regulation.
Data privacy and the public
The CCPA awareness findings come from MediaPRO’s 2019 Eye on Privacy Report, a survey of more than 1,000 U.S.-based employees. The survey tested knowledge on data privacy best practices and privacy regulations in addition to gauging opinions on a variety of different privacy topics.
The survey presented participants with questions concerning when to report potential privacy incidents, what qualifies as sensitive data, how comfortable respondents were with mobile device apps having specific permissions, and the most serious threats to the security of sensitive data.
Additional findings from the report
- 58 percent of employees said they had never heard of the PCI Standard, a global set of payment card industry (PCI) guidelines that govern how credit card information is handled.
- 12 percent of employees said they were unsure if they should report a cybercriminal stealing sensitive client data while at work.
- Technology sector employees were least likely to identify and prioritize the most sensitive information. For example, 73 percent of those in the tech sector ranked Social Security numbers as most sensitive, compared to 88 percent of employees in all other industries ranking this type of data as most sensitive.
- Employees were more comfortable with a mobile device app tracking their device’s location than with an app accessing contact and browser information, being able to take pictures and video, and posting to social media.
- Theft of login credentials was considered the most serious threat to sensitive data, with disgruntled employee stealing data and phishing emails coming next.
The findings give weight to the vital role employees play in a strong data privacy posture and the continuing need for privacy awareness training in protecting sensitive information. Working toward a “business-as-usual” approach to data privacy, with best practices embedded into all employee actions, is increasingly becoming a must for companies of all sizes.
“We’re at a pivotal time in history for privacy, and more people than ever are paying attention to privacy and data protection,” MediaPRO’s Chief Learning Officer Tom Pendergast said.
“Some of our survey results might make you think that people are starting to get it—but until everybody gets it, we in the privacy profession really can’t rest. In today’s world, protecting personal information really is everyone’s responsibility, and that’s why it’s up to us to champion year-round privacy awareness training programs that aim to create a risk-aware culture.”
Security teams need to consider the possibility of internal as well as external threats
While high-profile cybersecurity breaches originating from malicious insiders are on the rise, many cybersecurity professionals continue to focus exclusively on external threats, forgetting that a threat could be sat right beside them.
It’s easy to put the notion of an insider threat to the back of our minds, however looking at the spate of cybersecurity breaches last year, many of them had one thing in common – they originated from a malicious insider.
Motivations and behaviours of an insider threat
Many security teams assume that their employees would not compromise the reputation, operations, or even existence of the business. However, the truth is that no one is immune.
There are various type of insider threats; malicious insiders often seek financial gain, look for revenge, or can even result from insider collusion, where a relationship with an organisation or hacker group has been formed. Unintentional insider threats on the other hand are more well-meaning but are no less dangerous as these employees fall victim to social engineering techniques or phishing emails – something that needs to be addressed proactively by security professionals.
Key behavioural traits of an insider threat that businesses can look out for, include:
Resignation: Individuals leaving on bad terms are important to monitor as they often maintain access to intellectual property initially. It is highly possible that they could – and often will – sabotage intellectual property. However, it’s important to note that an employee could be leaving the company on great terms, but still have less-than-honourable intentions regarding their access to IP. It’s sadly not uncommon for someone to take data to their next gig to sweeten the deal.
Ignorance: These individuals were never trained on their personal responsibility over company data and have little knowledge of the company’s security practices. As such, they are highly susceptible to phishing and other similar attacks. A clear warning sign of this is if you see someone walk away from their computer or laptop without locking their screens first.
Discontent: These individuals often voice their grievances and dissatisfaction in the office, display combative behaviour and a resistance to change. A sure warning sign is if this is done with little regard to the audience, whether it includes new hires, interviewees, management or even media. They feel wronged by the company and feel like they have something to gain; this is often in the form of IP theft.
Personal life: These individuals are easy to influence due to personal reasons and are often the ones who get blackmailed into handing over intellectual property. Sometimes financial motivation is also a factor, where employees can see gains by selling company confidential information. Warning signs can include unusual working hours, frequent absence from work, or general suspicious activity at the workplace such as someone covering something up when you are walking over to say hello.
Why insider threats are dangerous
1. They are hard to identify
Since insider threats already have access to the network with authorised credentials, their access does not flag on a traditional monitoring system. They also often already have access to sensitive data and awareness of the existing security measures in place and how to get around them. Combine this all with a lack of visibility into user access and data activity, and the difficulty of identifying threat actors is incredibly challenging.
2. They are expensive
Like a traditional threat actor, the longer they go undetected and are free to roam the network, the more damage they can do. Even with baselining, often threat actor activity can get caught in a baseline, making it much more difficult to identify their rogue behaviour. The fact that they are not raising alarms means you are talking some serious potential damage. Indeed, the Ponemon Institute revealed that the average cost of insider threats per year for an organisation is $8.76 million.
3. They risk compliance
Data protection and compliance should also be considered because an insider threat will often make the exfiltration of data their objective. Last year, Coca Cola suffered an insider threat attack which saw the personal information of about 8000 of its employees leave the building. Not only this, but the dwell time of the incident was extended. They didn’t realise it had happened until law enforcement informed them of the data breach.
4. They cause operational disaster
As seen with Tesla, an insider threat can sabotage operations and risk an organisation’s competitive edge. In this instance, a disgruntled employee who lost out on a promotion made ‘direct code changes to the Tesla Manufacturing Operating System under false usernames and exported large amounts of highly sensitive data to unknown parties’ according to a letter addressed to employees.
Mitigating insider threats
Insider threats take many forms and companies must ensure they evaluate the risk. Policy is needed to reduce insider threats. Employee handbooks that are easily accessible can detail how employees can protect customers data, for example the do’s and don’ts with company laptops. It’s also important that employees fully understand all information in the handbook.
Awareness and training is critical. Companies should put a programme in place and make sure that senior management continuously reinforce that programme. Businesses should consider having a security culture improvement programme. Again, it should be supported by senior management, but perhaps with ways to measure the success of the programme.
Ultimately, companies must invest in technology that will help them to respond to and prevent insider threats from moving data externally. Organisations can identify what data has left their network, and how to prevent data leaving in the future by looking for similar information on all other data assets.
You can read the original article, here.
In May, it will be a year since the enforcement of the EU GDPR began. In the midst of continued and ever growing confusion within the EU caused by the Brexit process, a recent report around another high profile EU issue may have gone unnoticed. DLA Piper recently released a paper looking into incidents reported — both GDPR breach notification and other kinds of notification — fines enforced and how reports and fines are spread out across EU members.
From the time GDPR was introduced to the point when the report was released, 59,000 incidents were reported to the various regional “Data Commissioners,” such as the CNIL in France. The numbers were built upon on data reported by EU members (which still includes the UK as I write this) and collected by DLA, but, it is important to note that not all countries expose such information.
Firstly, before discussing these numbers, we need to be clear that these incidents do not imply 59,000 data breaches. Because GDPR is concerned not only with data breaches, but also with the inappropriate handling and processing of data,EU countries are required to engage in more than just GDPR data breach notification. The reported number of incidents, therefore, cover data abuse as well as data loss, whether accidental or maliciously derived. A separate source, directly from the EU commission, places the data breach related incidents as coming to 41,500 for both malicious and accidental events.
The effects and legalities of GDPR are still rippling their way through data processing services. As a recent example, lobbyists from several countries launched a petition to their respective regional Data Protection Authorities on how EU personal data is used in the fast growing space of Real-Time Bidding, which is the process that determines which adverts are shown to you online. Real-Time Bidding is driven by the data advert companies have about you, since this is what allows them to make the most informed decision as to which advertisement you would find most appealing. The decision of which advert to show you is made in a split second and, therefore, clearly, there is no possible way for the user to ‘opt-in’ to the processing of their data. This is separate from the 50m EURO fine placed on Google by the French CNIL earlier this year.
One very interesting element of the DLA Piper report is the breakdown by country of the number of incidents filed. The Netherlands tops the list with around 15,400 reported incidents. Strangely, despite having a population nearly three times that of the Netherlands and a similar difference of scale in GDP, France only reported 1,300 incidents – over 14,000 less! This, perhaps, highlights an inconsistency between EU members as to what needs to be reported. For example, reported incidents have included simple notification that an email was accidentally sent to the wrong recipient. It would appear, although not confirmed, that the Dutch are playing it safe and reporting any infringement, whereas the French and Italians (with 610 incidents reported in Italy), have a narrower interpretation of what a data incident is.
Potentially, the reporting of even mild infringements could explain why only 91 fines have resulted from the 59,000 reported incidents. However, the report from DLA Piper does concede that there is likely to be a backlog within the EU commission to process GDPR breach notification and other types of incidents, which could mean that more fines will be forthcoming. The backlog may also be a sign that the EU underestimated the initial volume of incidents it would receive.
The main thing that is evident from this report is that the effect of the GDPR is still not fully understood. This is reflected by the huge variance in reported incidents per country and the ongoing arguments around the interpretation of legal data processing. The implications and interpretations will continue to play out for the foreseeable future.
One thing remains clear, organisations (with a deliberate UK spelling) who are the controller or processor of EU related data need to protect this information and its usage with a specific mind-set. The data is not theirs; it belongs to the individuals to whom it is linked. Organisations must treat the data as something they are borrowing or looking after, not something they own. It needs to be locked away with the right protection to ensure only those who should use it or see it can do so. It may seem like an obvious shift of perception, but it’s vital in terms of the importance we place upon protecting EU-related data.
CyberArk is honored to be named a 5-Star Security Vendor – the highest rating in CRN’s 2019 Partner Program Guide. This marks the second consecutive year that CyberArk has received this prestigious designation. This recognition highlights the importance of privileged access management (PAM) as a top security control and enterprise priority. Organizations that are extending PAM to users and applications across the enterprise, in the cloud, throughout the DevOps pipeline and at the endpoint are realizing rapid risk reduction and strong business impact.
CyberArk received a 5-Star rating based on an in-depth assessment of channel program offerings, partner profitability, partner training, education and support, marketing programs and resources, sales support and communication.
CyberArk has built a powerful channel partner community to help customers around the world to reduce risk, protect against advanced cyber threats and securely embrace digital transformation strategies. This recognition comes on the heels of CyberArk’s Scott Whitehouse being named a CRN Channel Chief.
We believe that protecting high-value assets and data in today’s increasingly complex business environment requires high levels of innovation and collaboration. Our partner ecosystem brings together the strengths of advisory consultants, global systems integrators and regional solutions providers to deliver the industry’s most complete privileged access security solution. We’re honored to be recognized by CRN for our commitment to cybersecurity innovation and channel partner empowerment.
CRN’s annual guide identifies the strongest and most successful partner programs offered by the top IT products and services suppliers. Solution providers have come to rely on this world-class guide as they evaluate security providers they work with or are considering working with in the future. The 5-Star rating recognizes an elite subset of companies that empower solution providers with the best partner program offerings.
The 2019 Partner Program Guide will be featured in the April issue of CRN and is available online here. To learn more about the CyberArk Global Partner Program, visit here.
Is PowerShell bad? Not necessarily. In fact, most PowerShell executions are not malicious, but PowerShell can be (and often is) taken advantage of.
The new Sophos EDR capabilities offer the ability to track down malicious executions that otherwise may remain hidden. For example, executions which use the encoded command argument are more likely to be associated with bad behavior and are less common in good executions.
With Intercept X Advanced with EDR 1.1, analysts can easily search for PowerShell commands, including encoded command arguments.
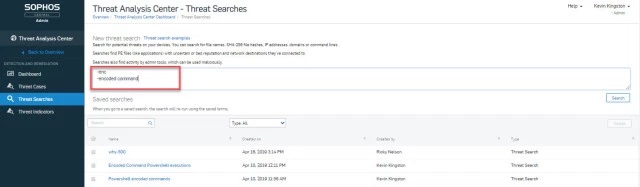
You can look for other suspicious PowerShell executions besides encoded commands such as policy bypass (-Exec Bypass), missing information (-NoLogo, -NoProfile), and more.
These new capabilities have also been added to the Intercept X Advanced for Server with EDR Early Access Program (EAP) so participants can start using these new features on their servers.
PowerShell features previously included in Intercept X
Intercept X already blocks known malicious PowerShell activity. The Application Lockdown feature automatically terminates a protected application based on its behavior. For example, when an Office application is leveraged to launch PowerShell, access the WMI, run a macro to install arbitrary code, or manipulate critical system areas, Sophos Intercept X will block the malicious action – even when the attack doesn’t spawn a child process. It will also prevent malicious PowerShell code executions via Dynamic Data Exchange too. Learn more about exploit protection with Intercept X.
Finally, if PowerShell appears to be involved with a detection it is referenced in a Threat Case where the command line executed can be analyzed.
Few terms in networking have generated as much buzz recently as SD-WAN (or Software Defined Networking in a Wide Area Network). All that buzz has been accompanied by equal doses of useful information and confusing rhetoric. As a result, SD-WAN has grown to mean a lot of different things to different people, while some are still trying to figure out exactly what it means.
Fundamentally, SD-WAN is usually about achieving one or more of these networking objectives:
- Reduce connectivity costs: Traditional MPLS connections are expensive, and organizations are shifting to multiple more affordable broadband WAN options
- Business continuity: Organizations require solutions that will elegantly handle WAN failures and outages, and are looking for redundancy, routing, fail-over and session preservation
- Simpler branch office VPN orchestration: VPN orchestration between locations is often complex and time-consuming, so organizations are looking for tools to simplify and automate deployment and setup
- Quality of critical applications: Organizations are seeking real-time visibility into application traffic and performance in order to maintain session quality of mission-critical business apps
What’s most important to you?
XG Firewall includes all the common SD-WAN features and capabilities you need to achieve these goals. Check out our XG Firewall and SD-WAN Solution Brief for the full details, but here’s a quick summary of how XG Firewall can help you achieve your SD-WAN objectives:
Multiple WAN links: XG Firewall offers support for multiple WAN links, including a variety of copper, fiber, and even cellular interface options. XG Firewall can terminate MPLS circuits using Ethernet handoff and VDSL through our optional SPF modem. XG Firewall also offers essential WAN link monitoring, balancing, and fail over capabilities.

Branch office connectivity: Sophos has long been a pioneer in the area of zero-touch branch office connectivity with our unique SD-WAN RED devices. These affordable devices are super easy to deploy by a non-technical person, and provide a robust secure Layer 2 tunnel between the device and a central XG Firewall. XG Firewall also supports site-to-site RED tunnels, as well as a variety of standard VPN solutions and easy orchestration wizards and tools to make inter-office connectivity quick and painless.

VPN support and orchestration: XG Firewall offers support for all the standard site-to-site VPN options you would expect including IPSec, SSL, and even our own unique RED Layer 2 tunnel with routing that is very robust and proven to work reliably in high-latency situations such as over-satellite links. Sophos Firewall Manager or Central Firewall Manager also offer centralized multi-site VPN orchestration tools to easily set up a mesh of VPN SD-WAN connections. XG Firewall also offers a flexible failback option to automatically fail back to the primary VPN connection when a WAN link is restored.

Application visibility and routing: You can’t route what you can’t identify, so accurate, reliable application identification and visibility is critically important. This is one area where XG Firewall and Synchronized Security provide an incredible advantage. Synchronized Application Control provides 100% clarity and visibility into all networked applications, providing a significant advantage in identifying mission critical applications, especially obscure or custom applications.
XG Firewall also includes application-based routing and path selection in every firewall rule as well as policy based routing (PBR), making it easy to direct important application traffic out the optimal WAN interface. Additionally, it includes predefined Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) objects for popular SaaS cloud services with thousands of FQDN hosts definitions included out of the box with the option to easily add more.
What’s Next for SD-WAN with XG Firewall?
XG Firewall includes many innovative solutions to help organizations reach their SD-WAN objectives – from great WAN connectivity options to our unique RED SD-WAN appliances, to our unmatched application visibility and great routing options.
XG Firewall offers a powerful, flexible network connectivity and security solution for every type of network and Sophos is continuing to invest in SD-WAN capabilities in upcoming releases, with new features for link monitoring and management, VPN orchestration, and application routing.
Check out our XG Firewall and SD-WAN Solution Brief, to get further insights into how XG Firewall is solving the top challenges with SD-WAN and helping organizations achieve their important SD-WAN goals.
NSS together with CyberArk and Sophos will inform you of the latest cyber threats and will suggest ways to address them at the 9th Infocom Conference on 17th and 18th of April – Dais Conference Center.
The concept of Industry 4.0 (aka the 4th Industrial Revolution), has begun to be reported more and more, reflecting the utmost modernization and rapid development of all the levels of the production, services and procedure, with the main pillar of all the new and advanced technologies that bring us a revolution in the way that private businesses, public organizations and societies operate.
The basis for Industry 4.0 is the combination of the natural and digital world. The interconnection of machines with information and communication systems and the complete digitization of physical procedures through the combination of existing and emerging technological trends such as Cyber Physical Systems, Artificial Intelligence, Augmented Reality, and the Cognitive computing, as well as Big Data, cloud computing and cryptocurrencies.
In this new era, the Digital Security sector, if we include Information Security, Networks and IT infrastructures also Data Protection, is to have a very important role, creating new challenges and new opportunities that we will present at the 9th Infocom Security Conference, to be held on 17 and 18 April at the Dais Conference Center at Maroussi Athens.
Cyber Security, in all aspects, is vital importance to the effective understand and use all the new technologies that can lead us to the 4th generation Digital Revolution, and that’s why all the professionals should be fully informed about the evolution of cyber-threats, the trends and the strategies that are developed in the field of security, new technologies and new generation protection solutions.
This need for information on Digital Security – with a business-oriented approach, but also scientific, research and technological interest – the Infocom Security Conference will fill for one more year. Infocom Security Conference is the reference point for the security specialist and the place of their annual meeting.

Speeches
17th April 13:30 “Anatomy of a cyberattack – forensics made simple with Artificial Intelligence”, Sophos Sales Engineer Peter Skondro
18th April 14:30 “Are the apps that run your business also your Achilles’ heel”, Cyberark Account Executive Roee Abaiov
Security Workshops
During the 9th Infocom Security, parallel workshops will take place, offering techniques and practical presentations by specialists about information security issues.
Workshop-room D1
17th April 14:00-15:00 “EDR in Action – Forensics and automatic containment of threats with Sophos Synchronized Security”, Sophos Sales Engineer Peter Skondro
Workshop-room D2
18th April 15:00-16:00 “Learn how to Protect your business Apps in the Age of Industry 4.0”, Cyberark Customer Success, David Kellermann
Sponsor companies’ expo
During the 9th Infocom Security -like every year- there will be an expo for sponsor companies, giving visitors the opportunity to get in touch with businesses active in the country, in the sector of information security services and solutions, in order to stay informed face-to-face about all developments in this area, as well as their own activities.
You move to the public cloud with the dream of infrastructure cost savings, added agility, and taking full advantage of devOps process to speed up development and product delivery. A move to Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure or Google Cloud Platform can bring all that good stuff. But soon you’ll meet your new challenge of increasingly complex attacks targeting a more dispersed multi-cloud network.
That’s exactly what we found in the most recent Sophos research study of 10 cloud honeypots placed worldwide. Once the honeypots were live, it took attackers no time at all to discover the SSH service and for login attempts to start. In one instance, a honeypot was attacked less than one minute after it was deployed. And once the login attempts started, the attacks were relentless and continuous.
Put that smile back on your face
To solve the problem of public cloud security and get you back to spending your time on projects that move your business forward, rather than security worries, we’re pleased to announce the launch of Sophos Cloud Optix.
The latest addition to the Sophos Public Cloud Security line up, Cloud Optix is a powerful new tool that allows you to accurately see what you have running in the cloud at all times, while combining the power of AI and automation to simplify compliance, governance and security monitoring in the cloud. And you can have it up and running in less than 10 minutes.
You can’t secure what you can’t see
Running multiple cloud environments, potentially across multiple providers, you’re going to have a tough time visualizing what your actual cloud network and assets look like. This means you can easily spend days or weeks preparing accurate diagrams to ensure they are configured correctly in order to prepare for audits. Cloud Optix is an agentless solution that does this in seconds with complete network inventory, topology visualization and continuous asset monitoring. But don’t just listen to us, here’s why HubSpot chose Sophos:
Sophos Cloud Optix provides us a comprehensive network topology diagram with real-time traffic of our cloud environment. I have better insight into our cloud network security posture than ever before.
– Jessica Mazzone, Security Engineer, HubSpot Inc.
Changing environments need continuous compliance
In an ever-changing, auto-scaling public cloud environment, automatically detecting changes to your cloud environments in real time is a life saver. Cloud Optix continuously monitors compliance, with custom or out-of-the box templates for standards such as SOC2, HIPAA and GDPR, and reports generated in seconds.
It only takes one open door
The biggest issue in cloud security is not necessarily some new kind of malware, it’s about making sure your architecture is secure and you have the right visibility of it.
In our report, we found that, on average, cloud servers were subjected to 13 attempted attacks per minute, per honeypot. So if you accidentally leave your Amazon S3 storage buckets set to public, or leave a MongoDB database open to the public internet, you’re risking hitting the headlines for the wrong reasons.
Cloud Optix has a range of threat response and alerting capabilities to help. From detection of suspicious traffic patterns on the network (i.e. a data breach in action) and shared access keys to your cloud provider account, to data storage left open to the public internet and more.
For more information on our research findings, please read the full Sophos report, or for the highlights you can read the Naked Security article.
And to learn more about Sophos Cloud Optix and how it can help simplify visibility, compliance and threat response for you, visit www.sophos.com/cloud-optix.
Earlier this week, news broke that a Chinese woman attempted to sneak a USB stick loaded with malware into Mar-a-Lago, President Trump’s main place of residence outside of the White House.
The news made international headlines due to the nationality of the alleged attacker and the location of the attempted attack.
Using an external device like a thumb drive to deliver malware is not a new attack method – it has been around for years.
But this somewhat old-school delivery mechanism is still very effective today. Why? Because many endpoint protection products only focus on “next-gen” approaches to endpoint security and skip over proven foundational techniques that have worked for years.
Those techniques include “device control” or “peripheral control” which protects external hard drives.
The USB stick incident at Mar-A-Lago is a perfect example of why you need endpoint protection that combines modern/next-gen techniques *and* foundational techniques like device control. Fortunately, with Intercept X Advanced you get both.
How does Intercept X Advanced protect against this type of attack?
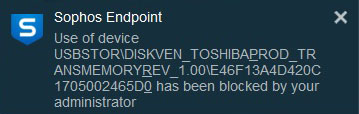
Intercept X Advanced administrators have the ability to control access to removable storage devices (like USB sticks), mobile devices (iPhone, various Androids, Blackberry), Bluetooth, and other peripheral devices.
They can choose to either block the use of peripheral device types altogether, monitor devices, allow in read only mode, or block/allow specific devices.
If a person was able to sneak a USB drive into an environment, they would receive a message similar to this when trying to use it:
But that’s not it…
Even if this feature had not been enabled, Intercept X would be able to detect the malware before it executed using the industry’s best malware detection engine, powered by deep learning technology. Find out more about Intercept X Advanced here.
You can read the original article, here.
XG Firewall v17.5 recently delivered several new innovations including Lateral Movement Protection, management via Sophos Central, and a variety of new features focused on education.
With Maintenance Release 4 (MR4) announced earlier this week, there are a few new important features I want to ensure everyone is able to get the most out of.
While we always encourage all our customers and partners to keep their firewall up-to-date with the latest firmware release, MR4 is the perfect time to update if you haven’t been keeping current to take advantage of the latest security, performance, and many other enhancements.
Email notifications
Several new email notifications have been added to inform you about important system and threat related activity including:
- Started SFOS
- Sign-in failed for web admin console, SSH, or CLI console
- Advanced threat protection alert or drop actions
- Installed new firmware
- System restart initiated through web admin console
- System shutdown initiated through web admin console
To receive these new alerts, simply ensure you have these boxes checked in the Notification Settings tab of your XG Firewall:
Backup encryption
Backup files now use a personal password key for enhanced security. You’ll be required to take advantage of this new feature going forward to protect your backups.
The new options are part of the workflow for scheduling and performing backups and restoration of your XG Firewall configuration on the Backup & Firmware main menu option, on the first tab for Backup & Restore:
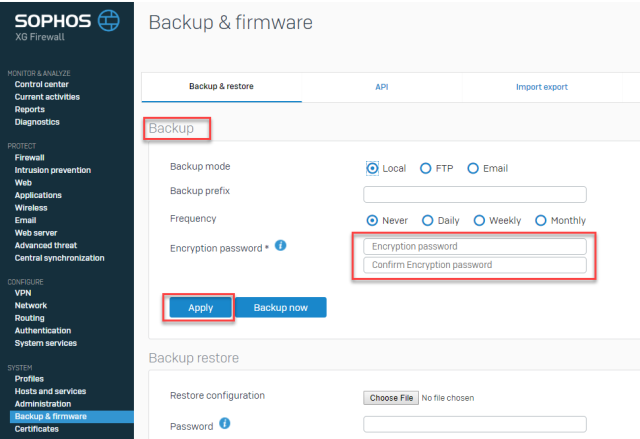
Υou’ll notice new entries for an “Encryption password” for the backup and restore process.
You should update your backup settings to utilize a strong password that’s 12 characters or more in length. Once you’ve typed in your password, click “apply”.
All backups from that point onwards, will use the new password as the encryption key. You can change the password at any time, and even at the time of doing a local backup. Of course, we suggest you use a password manager so you don’t need to worry about remembering all your passwords, but if you forget your encryption password, you can change it at any time and create a new backup.
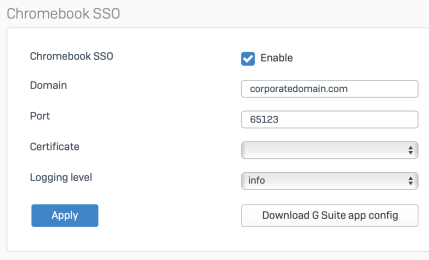
Chromebook authentication
If you’re one of the many XG Firewall customers enjoying the new Chromebook authentication support, there’s now a new option to generate the application configuration file from within the XG Firewall console to import into Google GSuite.
This option can be found under Authentication > Services > Download GSuite App Config, as shown below:
Other enhancements
XG Firewall v17.5 MR4 also introduces a number of performance, reliability and stability enhancements. You can check out the full release notes for more details.
How to get it
As with every XG Firewall firmware update, it will appear in your console automatically at some point in the near future, but if you want to start taking advantage of these enhancements right away, you can download the firmware update immediately from the MySophos Portal.
If you need a refresher on how to update your firmware, watch this short how-to video:
You can read the original article, here.
The age of digital transformation is upon us. Cloud, virtualization and containerization are becoming mainstream. With all of the buzzwords and technology hype, it is easy to forget the real business drivers behind this age of innovation. Established industries like finance and healthcare are being disrupted by new and nimble startups who have leap-frogged established players with new technologies that bring tremendous competitive advantage with speed to market, flexibility and resiliency. Now, established enterprises are adopting these new technologies to ensure and recapture their market leadership positions. It truly is an exciting time in B2B technology, but what about the engine of the enterprise? Business critical applications are the motor that keep firms running. They too are seeing change with the adoption of cloud and SaaS applications, but are often overlooked when it comes to their security.
Business critical for a reason
Consider the vast information and applications within your organization. Depending on your line of work and industry you will have your own list of critical business applications and related data that if compromised or lost, put your business at a stand-still. These can include applications like financial transaction apps and their related sensitive customer data; enterprise resource planning (ERP) applications that help manage crucial inventory for retailers or hospitals or critical electronic health record (EHR) applications storing vital electronic personal health information (ePHI) for health care providers, hospitals and insurers.
But how do organizations secure all of this sensitive information and the applications that store and manage it? Unfortunately, many business and IT stakeholders are finding themselves in a risky position. While they are doing a great job curating the right applications for their needs, they are missing the boat on protecting these costly investments that run their enterprises – and drive customer relationships.
According to a recent CyberArk Business Critical Application survey of 1,450 business and IT decision makers conducted across eight EMEA countries, 61% indicated that even the slightest downtime affecting their business critical applications would be massively disruptive and severely impact the business. Yet, 70% of these enterprises do not prioritize the security of business critical applications. So what can you do to help bridge this gap? CyberArk just released an eBook, “The Age of Digital Transformation: 5 Keys to Securing Business Critical Applications,” to answer your questions. Here is a preview of the first two points.
1. Identify what apps are truly business critical
As a security leader, it goes without saying that you need to be one with the business. Get to know your line of business leaders and the leaders of key functions such as finance, human resources and marketing. Once you have a handle on important business initiatives, you will be in a better place to identify the business apps that are truly critical. These could be SaaS applications or even custom applications built using DevOps tools and methodologies.
2. Get comfortable with the cloud (and securing it)
Understand what your cloud strategy, migration plan and timelines are for on-premises applications that are moving to the cloud or new cloud-native applications. Partner with cross-functional stakeholders to ensure privileged access security is a front-and-center consideration when you’re looking to migrate applications to the cloud or to adopt new cloud applications.
To learn about keys three through five and find out more about securing business critical app, download the eBook here.

























