News
Given the ever-increasing risks of cyber attacks, the EU is strengthening the IT security of financial entities such as banks, insurance companies and investment firms. Today the Council adopted the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) which will make sure the financial sector in Europe is able to stay resilient through a severe operational disruption.
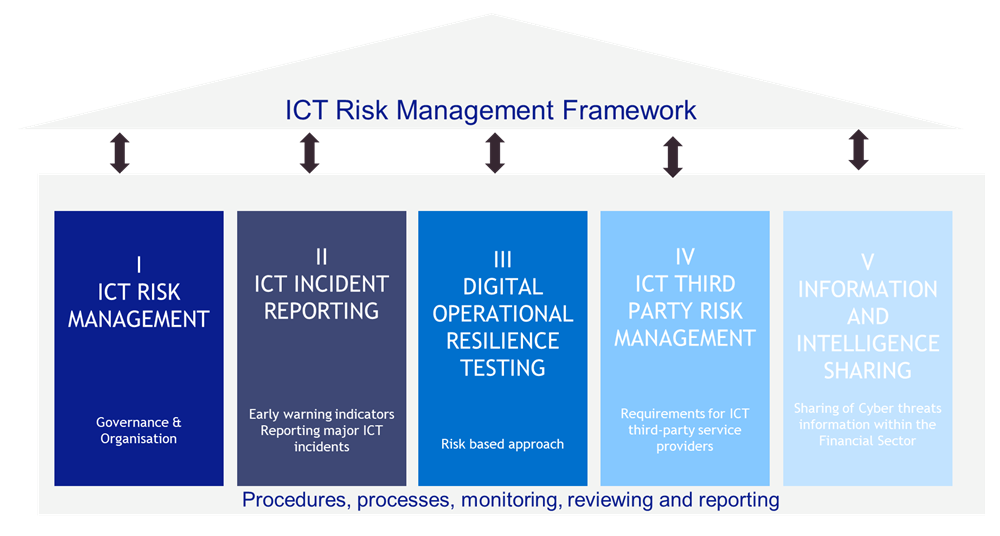
DORA sets uniform requirements for the security of network and information systems of companies and organisations operating in the financial sector as well as critical third parties which provide ICT (Information Communication Technologies)-related services to them, such as cloud platforms or data analytics services. DORA creates a regulatory framework on digital operational resilience whereby all firms need to make sure they can withstand, respond to and recover from all types of ICT-related disruptions and threats. These requirements are homogenous across all EU member states. The core aim is to prevent and mitigate cyber threats.
Now that the DORA proposal is formally adopted, aspects that require national transposition will be passed into law by each EU member state. At the same time, the relevant European Supervisory Authorities (ESAs), such as the European Banking Authority (EBA), the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) and the European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority (EIOPA), will develop technical standards for all financial services institutions to abide by, from banking to insurance to asset management. The respective national competent authorities will take the role of compliance oversight and enforce the regulation as necessary.
Background
The Commission came forward with the DORA proposal on 24 September 2020. It was part of a larger digital finance package, which aims to develop a European approach that fosters technological development and ensures financial stability and consumer protection. In addition to the DORA proposal, the package contained a digital finance strategy, a proposal on markets in crypto-assets (MiCA) and a proposal on distributed ledger technology (DLT).
This package bridges a gap in existing EU legislation by ensuring that the current legal framework does not pose obstacles to the use of new digital financial instruments and, at the same time, ensures that such new technologies and products fall within the scope of financial regulation and operational risk management arrangements of firms active in the EU. Thus, the package aims to support innovation and the uptake of new financial technologies while providing for an appropriate level of consumer and investor protection.
The Council adopted its negotiating mandate on DORA on 24 November 2021. Trilogues between the co-legislators started on 25 January 2022 and ended in a provisional agreement on 10 May 2022. Today’s adoption is the final step in the legislative process.
Source: EU
The world’s most trusted cybersecurity platform now secures more than 25 million devices!
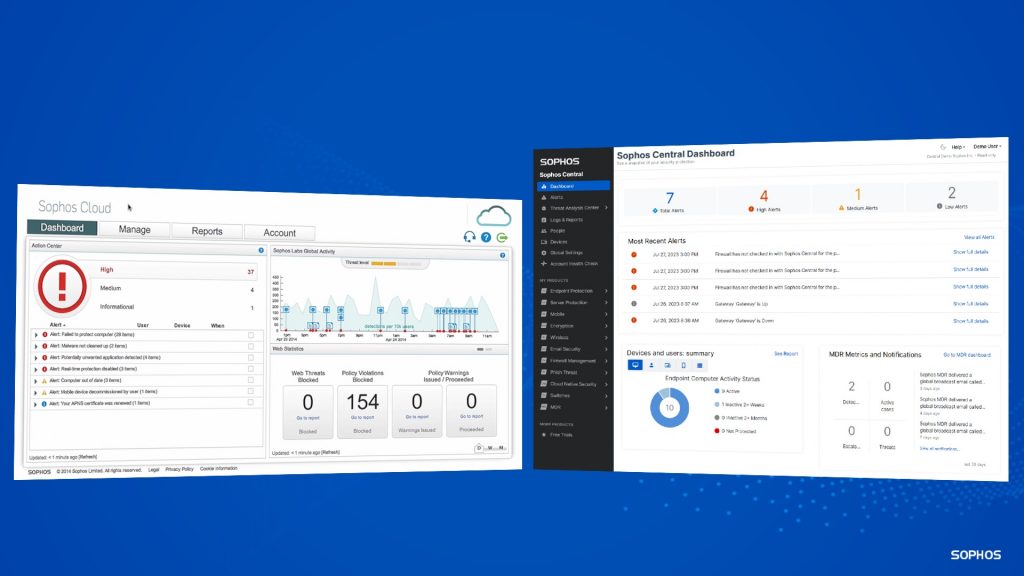
July 29, 2023, is a very exciting milestone for all of us at Sophos as it marks the tenth birthday of Sophos Central, the world’s most popular cloud-based security platform.
Originally called Sophos Cloud, the platform initially supported Sophos Endpoint and Server solutions for customers in the U.S. and UK.
Today Sophos Central manages all Sophos’ market-leading next-gen security services and products for our customers and partners across the world. Users can deploy and manage all their security solutions in one place: from our MDR service and XDR security operations tools, to our endpoint, email and cloud security solutions, and our full network stack.
Central by the Numbers
For those of you who, like me, enjoy putting numbers to things, I’d like to share some current usage stats.
- Over 432,000 organizations currently use Sophos Central to secure their organization – more than the population of the Bahamas or Iceland
- 7 million devices are hosted in Sophos Central – greater than the combined populations of Sweden, Singapore, and New Zealand!
- 120 terabytes of data are uploaded to the Sophos data lake every single day – equivalent to 1MB for every person in Japan
Data sovereignty is an important customer consideration with all cloud-based tools. As demand for Sophos Central has grown, so have our data centers: from our initial three in 2013 we now have nine across the EU (x2), U.S. (x2), Canada, Australia, Japan, India, and Brazil.
Delivering Superior Cybersecurity Outcomes
While the numbers demonstrate the popularity of our platform, what I’m most proud of are the tremendous cybersecurity outcomes that Sophos Central delivers for our customers and partners. Organizations running Sophos Central to manage their defenses consistently report protection and efficiency benefits that make a real day-to-day impact, including:
- 85% reduction in the number of cybersecurity incidents the team needs to deal with
- 90% reduction in time spent on day-to-day cybersecurity management
- Doubling the efficiency of the IT team
Sophos Central enables IT teams to stop console-hopping and manage all their security in one place. Should an alert need investigating, you can follow the trail seamlessly across protection technologies to quickly get to the root of the issue and remediate appropriately. User-based policies make it quick and simple to apply consistent approaches across endpoint and network security tools.
We recognize that each organization is different and Sophos Central is a flexible tool that adapts to customer needs. The intuitive dashboards and one-click fixes support stretched IT teams while enterprise-grade features and granularity provide the depth and control security specialists require.
Looking Ahead
While our interface and breadth and depth of capabilities has changed hugely over the last ten years, our passion to elevate usability, utility, and scalability has not.
Over the coming year our dedicated Sophos Central engineering team, partnering with our outstanding product and services teams, will be delivering further leaps forward in customer delighting usability, capability and function; ensuring that we continue to give organizations the very best tools for managing their defenses.
As we celebrate this milestone anniversary, be assured that Sophos Central will continue to be at the heart of Sophos innovation and product and service delivery for the decade to come.
Source: Sophos
Sophos Firewall has received Frost & Sullivan’s prestigious Competitive Strategy Leadership Award in the next-generation firewall (NGFW) industry. Frost & Sullivan applies a rigorous analytical process to evaluate multiple vendors for each award category before determining the final award recipient.
We are very honored that Sophos Firewall was awarded this distinction based on strategic innovation and customer impact.
Frost & Sullivan praised our focus on delivering a turn-key cybersecurity solution that enables organizations to scale their security operations without increasing IT complexity. They also praised us for enabling organizations to reduce TCO, strengthen their security posture, enhance visibility, and improve compliance.
 They noted that we are uniquely positioned to provide a holistic cybersecurity platform through Sophos Central, which eliminates blind spots in increasingly complex network environments while not forcing customers to compromise on performance for better firewall security:
They noted that we are uniquely positioned to provide a holistic cybersecurity platform through Sophos Central, which eliminates blind spots in increasingly complex network environments while not forcing customers to compromise on performance for better firewall security:
“Sophos’ firewall offering removes the burden of choosing between security and performance with its Xstream acceleration engine, which balances data traffic between CPUs to optimize performance and keep the network secure.”
Frost & Sullivan concluded that Sophos Firewall aligns with customer needs for better price/performance and value, a great ownership experience, and the option to easily scale or adapt as their needs change or grow.
“Sophos has capitalized on opportunities to simplify its product portfolio, solidifying its position as one of the leading NGFW vendors in the market. For its strong overall performance, Sophos earns Frost & Sullivan’s 2023 Global Competitive Strategy Leadership Award in the next-generation firewall (NGFW) industry.”
Download the full Frost & Sullivan Award Report and check Sophos.com/Firewall for more information.
Source: Sophos
The evolution of businesses and IT infrastructures over the last few years has been staggering, resulting in data disparately distributed throughout the business ecosystem. This makes it difficult to monitor both the data and the server carrying it. That’s why it is crucial for managed service providers (MSPs) like you to be well-prepared to protect and recover your critical server workloads regardless of where they are located.
Due to data sprawl, it gets quite challenging for MSPs to provide complete data protection to “edge cases,” which include small businesses with individual servers, servers situated in very remote or inhospitable places, or servers distributed over multiple sites. It also gets incredibly complicated and time-consuming to implement and manage the backup infrastructure of the server workloads, especially when there’s a need to implement a separate on-site backup appliance at each location. Added to this is the heavy cost incurred by MSPs to carry out the entire operation.
Hence, most MSPs tend to avoid rolling out or managing backup infrastructures.
Putting MSPs at risk
The reluctance to manage backup infrastructures can be costly for MSPs since it leaves their clients’ data unprotected. Not backing up data creates data loss risks and possible exposure to ransomware attacks, resulting in business downtime and reputation loss for the MSP. This can directly impact the MSP’s profitability and must be addressed smartly.
Direct backup to the cloud
A dedicated backup infrastructure in a data center isn’t always the solution. Complementing your tech stack with a direct backup to the cloud would be the ideal choice. With the help of a unified, direct-to-cloud business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) solution, you can bolster your data protection and take it beyond the boundaries of primary data centers. You can do away with all the complexities associated with the implementation and management of modern IT infrastructure, in turn saving technician time and energy and focusing on helping your clients grow their business.
Another reason to amplify your stack and opt for direct-to-cloud backup is the possibility of new revenue and healthy margin opportunities. It allows the backup services to expand beyond their spheres of influence and include the protection of clients’ systems, eliminating the risk of data loss and the possibility of downtime — at great operating margins.
A game changer for MSPs
Datto Endpoint Backup for Servers offers compact, direct-to-cloud BCDR solutions for servers anywhere. Purpose-built for MSPs, this solution combines its direct cloud backup feature with ransomware protection and powerful disaster recovery (DR) capabilities and can be managed via a unified management portal. It eliminates the need to put hardware on-site.
Let’s take a look at what it brings to the table.
Enhancing your and the clients’ reputation
Ransomware attacks are on the rise owing to their late detection. Such a threat can result in unplanned downtime and jeopardize your company’s reputation. Datto’s latest solution, with its unique ransomware detection capabilities, scans for early warnings and regularly checks immutable backups stored in the Datto Cloud with Cloud Deletion Defense™ — protecting your customers’ businesses from IT disasters. This goes a long way towards preserving and enhancing your reputation as well as that of your clients. The same technologies as Datto SIRIS and Datto Continuity for Microsoft Azure are used here to eliminate ransomware threats.
Expanding your BCDR services
Datto Endpoint Backup for Servers helps create new revenue streams for your business and expands the scope of your BCDR services by offering complete protection for “edge case” servers. Despite the expansion of services, the costs involved in providing complete protection (backup, DR and DR testing) follow a flat-fee structure and are lower than “do-it-yourself” (DIY) vendors, whose costs are often high and unpredictable. The solution comes with the lowest total cost of ownership (TCO), without any hidden/variable fees. No extra charges for cloud storage, computing, DR or DR testing are incurred. Such a cost-effective pricing model enables predictable business growth for you and your clients.
Simplifying the backup business
The recent shift to a hybrid business model has led to increased complexity within the IT landscape, with data and servers scattered across multiple sites. Datto Endpoint Backup for Servers comes with a centralized management portal that simplifies the data backup workflow while saving time and eliminating complexity in just a few clicks. The portal is connected with both Datto BCDR solutions and Datto Continuity for Microsoft Azure. Hence, managing the full backup stack from a single, unified interface is now a reality. The MSP-centric architecture of the solution delivers optimal technician efficiency and minimum overhead costs compared to solutions designed for enterprise IT.
Best-in-class tech support
Datto-certified experts are there to quickly help you with proven, direct-to-tech, 24/7/365 support. This ensures proper monitoring of your backup and DR services and pushes you and your clients to succeed.
Built to scale MSPs
With Datto Endpoint Backup for Servers, you get appliance-less, direct-to-cloud backup managed via a client-centric view for consistent data protection across remote servers, data centers, Azure and SaaS. Due to this single-pane-of-glass management, there’s a streamlining of daily operations, increasing overall BCDR efficiency with smart features like screenshot verification, automated testing and email alerts. As a result, MSPs like you get a much simpler and smarter BCDR solution.
A sign of such an evolved, smarter BCDR process is the hourly backup of your clients’ servers directly to the secure and private Datto Cloud, ensuring rapid recovery during downtime, cyberattacks and outages. This sets the standard for a secure cloud infrastructure and paves the way for unhindered business growth.
Source: Datto
Even with a well-guarded IT infrastructure, business disruptions are inevitable regardless of the size or industry of a company. This is especially true for organizations operating in harsh or highly uncertain environments, such as oil rigs, mines and factory floors. From cyberthreats to natural disasters and hardware failure, many factors could halt industrial and manufacturing production. One such factor is excessive vibration, which could cause data errors in hard disk drives (HDDs) and hamper operational continuity.
Challenges MSPs face serving clients operating in complex and risky environments
Managed service providers (MSPs) often struggle to deliver robust disaster recovery (DR) solutions to clients in the industrial and manufacturing sectors. This is due to the risk of low DR success rate and extended downtime because of the damage caused by excessive vibration to DR infrastructures relying on spinning HDDs.
In addition, MSPs face thinning margins implementing business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) solutions for clients with stringent recovery time objectives (RTOs). MSPs need premium hardware to deliver superior BCDR services and meet shorter RTO goals, which require high capital expenditure (CapEx).
Why HDDs aren’t ideal for disaster recovery in harsh environments
HDDs have many moving parts that operate with incredibly high precision. The mechanical components, read/write heads and platters or magnetic disks are delicate and sensitive, making them vulnerable to physical damage. The platter and heads rotate at high speeds of 10,000 to 15,000 rotations per minute (RPM) to store and retrieve information. Because of the delicate nature of its components and the rates at which it works, a sudden jerk or strong vibration could easily damage a hard disk drive and cause read-write errors. Data recovery from a damaged hard disk drive platter can be tedious and time-consuming.
HDDs vs. SSDs
HDDs are inexpensive compared to solid-state drives (SSDs) and provide more storage space. However, rotating HDDs have many mechanical parts that are prone to wear and tear after a few years of regular use, increasing the risk of hardware failure. SSDs, on the other hand, utilize flash memory to store information, have no moving mechanical components and can withstand bumps and vibrations. SSDs are highly durable and reliable storage mediums, even in harsh environments like manufacturing plants and factories. They are much lighter, faster, quieter and consume less energy than HDDs.
Minimize risks and expand margins with Datto SIRIS NVMe SSD Models
A crucial part of running a successful MSP business is having the right set of tools in your tech stack.
The new Datto SIRIS models, built using NVMe SSD, minimize risks by decreasing DR hardware failure rates caused by vibrations in harsh environments, like oil rigs, mines and factory floors. Our solutions allow you to increase your BCDR service profitability even for demanding clients and workloads since Datto SSD models come at one simple flat fee — no upfront CapEx costs or hidden or extra charges.
Datto’s flat-fee subscription model eliminates surprises by including DR/backup cloud, hardware, software, storage and technical support, even for the premium high-cost hardware based on NVMe SSD technologies.
Most Datto BCDR implementations deliver immediate return on investment (ROI) with larger margins and zero CapEx investment required.
Source: Datto
When ransomware strikes, files become encrypted. That’s the hallmark signature of most ransomware attacks. Even if you pay the ransom, there’s no guarantee that you’ll get the keys to unlock your encrypted files. Bottom line, when ransomware hits you are likely to lose important data.
This ends with Ransomware Rollback. Ransomware Rollback is a new, innovative feature included with Datto Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) that gives you peace of mind knowing that when a ransomware attack hits you’ll be able to get your files back, intact as they were before the incident.
Datto EDR includes Ransomware Detection, a unique and powerful antimalware technology that identifies known and unknown types of ransomware and kills the encryption process once an attack begins. As fast as Ransomware Detection is, the attacker’s encryption process always strikes first, meaning some files become encrypted before Ransomware Detection can kill the process and isolate the endpoint.
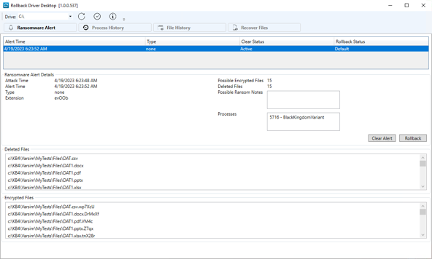
To address this, Datto created Ransomware Rollback, a lightweight application that tracks changes on endpoint disk space, providing rollback functionality for files and databases impacted by ransomware attacks. It consists of software that runs silently in the background, as well as a desktop application used for monitoring and managing the rollback process.
The solution works by intercepting file system calls made by applications and then performs tracking of the changes made. For example, if a file is renamed, deleted, or updated, the system records these changes and stores them in a designated tracking directory on the user’s disk.
For database applications like SQL Server or QuickBooks, Ransomware Rollback saves the data being written on an operation-by-operation basis, allowing the entire update to be rolled back if it is compromised by ransomware.
Unlike other EDR applications that offer similar rollback capabilities, Datto EDR with Ransomware Rollback does not rely on Windows shadow copy, which is often targeted by ransomware attacks. This ensures that your files and data are safe from even the most advanced cyberattack.
What’s more, Ransomware Rollback solves the problem of “wiper” attacks. Data wipers are one of the fastest growing categories of malware. Here, the objective of a wiper attack is to delete and destroy files and data.
Ransomware Rollback even restores deleted files, such as those hit by a wiper attack or files deleted by accident. Through the creation of hard links in a tracking directory, Ransomware Rollback ensures that users can restore deleted files, no matter the circumstance.
Ransomware Rollback is an integral component of Ransomware Detection, which is included with Datto EDR. With one click, you can quickly revert encrypted data and files back to their previous state, which makes the recovery process easy, efficient and effortless.
To get a demo of Datto EDR with Ransomware Rollback, click here.
Source: Datto
The European Union works on various fronts to promote cyber resilience, safeguarding our communication and data and keeping online society and economy secure.
Cybersecurity Strategy
The European Commission and the High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy presented a new EU Cybersecurity Strategy at the end of 2020.
The Strategy covers the security of essential services such as hospitals, energy grids and railways. It also covers the security of the ever-increasing number of connected objects in our homes, offices and factories.
The Strategy focuses on building collective capabilities to respond to major cyberattacks and working with partners around the world to ensure international security and stability in cyberspace. It outlines how a Joint Cyber Unit can ensure the most effective response to cyber threats using the collective resources and expertise available to the EU and Member States.
Legislation and certification
Directive on measures for a high common level of cybersecurity across the Union (NIS2 Directive)
Cybersecurity threats are almost always cross-border, and a cyberattack on the critical facilities of one country can affect the EU as a whole. EU countries need to have strong government bodies that supervise cybersecurity in their country and that work together with their counterparts in other Member States by sharing information. This is particularly important for sectors that are critical for our societies.
The Directive on security of network and information systems (NIS Directive), which all countries have now implemented, ensures the creation and cooperation of such government bodies. This Directive was reviewed at the end of 2020.
As a result of the review process, the proposal for a Directive on measures for a high common level of cybersecurity across the Union (NIS2 Directive) was presented by the Commission on 16 December 2020.
The Directive was published in the Official Journal of the European Union in December 2022 and entered into force on 16 January 2023. Member states will have 21 months from the entry into force of the directive in which to incorporate the provisions into their national law (actual date: 18 October 2024).
NIS2 Directive
The NIS2 Directive is the EU-wide legislation on cybersecurity. It provides legal measures to boost the overall level of cybersecurity in the EU.
The EU cybersecurity rules introduced in 2016 were updated by the NIS2 Directive that came into force in 2023. It modernised the existing legal framework to keep up with increased digitisation and an evolving cybersecurity threat landscape. By expanding the scope of the cybersecurity rules to new sectors and entities, it further improves the resilience and incident response capacities of public and private entities, competent authorities and the EU as a whole.
The Directive on measures for a high common level of cybersecurity across the Union (the NIS2 Directive) provides legal measures to boost the overall level of cybersecurity in the EU by ensuring:
- Member States’ preparedness, by requiring them to be appropriately equipped. For example, with a Computer Security Incident Response Team (CSIRT) and a competent national network and information systems (NIS) authority,
- cooperation among all the Member States, by setting up a Cooperation Group to support and facilitate strategic cooperation and the exchange of information among Member States.
- a culture of security across sectors that are vital for our economy and society and that rely heavily on ICTs, such as energy, transport, water, banking, financial market infrastructures, healthcare and digital infrastructure.
Businesses identified by the Member States as operators of essential services in the above sectors will have to take appropriate security measures and notify relevant national authorities of serious incidents. Key digital service providers, such as search engines, cloud computing services and online marketplaces, will have to comply with the security and notification requirements under the Directive.
ENISA – the EU cybersecurity agency
ENISA (European Union Agency for Cybersecurity) is the EU agency that deals with cybersecurity. It provides support to Member States, EU institutions and businesses in key areas, including the implementation of the NIS Directive.
The Cyber Resilience Act
The proposal for a regulation on cybersecurity requirements for products with digital elements, known as the Cyber Resilience Act, bolsters cybersecurity rules to ensure more secure hardware and software products.
The proposal for a regulation on cybersecurity requirements for products with digital elements, known as the Cyber Resilience Act, bolsters cybersecurity rules to ensure more secure hardware and software products.
EU Cyber Resilience Act – For safer and more secure digital products
Hardware and software products are increasingly subject to successful cyberattacks, leading to an estimated global annual cost of cybercrime of €5.5 trillion by 2021.
Such products suffer from two major problems adding costs for users and the society:
- a low level of cybersecurity, reflected by widespread vulnerabilities and the insufficient and inconsistent provision of security updates to address them, and
- an insufficient understanding and access to information by users, preventing them from choosing products with adequate cybersecurity properties or using them in a secure manner.
While existing internal market legislation applies to certain products with digital elements, most of the hardware and software products are currently not covered by any EU legislation tackling their cybersecurity. In particular, the current EU legal framework does not address the cybersecurity of non-embedded software, even if cybersecurity attacks increasingly target vulnerabilities in these products, causing significant societal and economic costs.
Two main objectives were identified aiming to ensure the proper functioning of the internal market:
- create conditions for the development of secure products with digital elements by ensuring that hardware and software products are placed on the market with fewer vulnerabilities and ensure that manufacturers take security seriously throughout a product’s life cycle; and
- create conditions allowing users to take cybersecurity into account when selecting and using products with digital elements.
Four specific objectives were set out:
- ensure that manufacturers improve the security of products with digital elements since the design and development phase and throughout the whole life cycle;
- ensure a coherent cybersecurity framework, facilitating compliance for hardware and software producers;
- enhance the transparency of security properties of products with digital elements, and
- enable businesses and consumers to use products with digital elements securely.
Cybersecurity Act
The Cybersecurity Act strengthens the role of ENISA. The agency now has a permanent mandate and is empowered to contribute to stepping up both operational cooperation and crisis management across the EU. It also has more financial and human resources than before. On 18 April 2023, the Commission proposed a targeted amendment to the EU Cybersecurity Act.
Cyber Solidarity Act
On the 18 April 2023, the European Commission proposed the EU Cyber Solidarity Act, to improve the response to cyber threats across the EU. The proposal will include a European Cybersecurity Shield and a comprehensive Cyber Emergency Mechanism to create a better cyber defence method.
Certification
Our digital lives can only work well if there is general public trust in the cybersecurity of IT products and services. It is important that we can see that a product has been checked and certified to conform to high cybersecurity standards. There are currently various security certification schemes for IT products around the EU. Having a single common scheme for certification would be easier and clearer for everyone.
The Commission is therefore working on an EU-wide certification framework, with ENISA at its heart. The Cybersecurity Act outlines the process for achieving this framework.
The EU cybersecurity certification framework
The EU cybersecurity certification framework for ICT products enables the creation of tailored and risk-based EU certification schemes.
Certification plays a crucial role in increasing trust and security in important products and services for the digital world. At the moment, a number of different security certification schemes for ICT products exist in the EU. But, without a common framework for EU-wide valid cybersecurity certificates, there is an increasing risk of fragmentation and barriers between Member States.
The certification framework will provide EU-wide certification schemes as a comprehensive set of rules, technical requirements, standards and procedures. The framework will be based on agreement at EU level on the evaluation of the security properties of a specific ICT-based product or service. It will attest that ICT products and services that have been certified in accordance with such a scheme comply with specified requirements.
In particular, each European scheme should specify:
- the categories of products and services covered;
- the cybersecurity requirements, such as standards or technical specifications;
- the type of evaluation, such as self-assessment or third party;
- the intended level of assurance.
The assurance levels are used to inform users of the cybersecurity risk of a product, and can be basic, substantial, and/or high. They are commensurate with the level of risk associated with the intended use of the product, service or process, in terms of probability and impact of an accident. A high assurance level would mean that the certified product passed the highest security tests.
The resulting certificate will be recognised in all EU Member States, making it easier for businesses to trade across borders and for purchasers to understand the security features of the product or service.
As for the implementation of the certification framework, Member State authorities, gathered in the European Cybersecurity Certification Group (ECCG) have already met several times.
Stakeholder Cybersecurity Certification Group
Following the entry into force of the Cybersecurity Act in 2019, the European Commission launched a call for applications to select members of the Stakeholder Cybersecurity Certification Group (SCCG).
The SCCG will be responsible for advising the Commission and ENISA on strategic issues regarding cybersecurity certification, and assisting the Commission in the preparation of the Union rolling work programme. This is the first stakeholder expert group for cybersecurity certification launched by the European Commission.
Depending on how you create your passwords, such as the length or including letters, numbers and symbols, the time it would take a cybercriminal to crack it varies. Understanding what makes it easy for cybercriminals to crack your passwords is critical to keeping yourself safe from becoming a victim of this type of attack.
Read on to learn how long it would take to crack your password and what you can do to strengthen your passwords so they’re not easily cracked by a cybercriminal.
What’s Password Cracking?
Password cracking is when cybercriminals use tools and programs to retrieve passwords saved in a computer system or sent via a network. Using these programs, cybercriminals can crack your passwords and get into your accounts in a matter of seconds, minutes, hours, days or years depending on how complex your passwords are. The less complex your passwords are, the faster a password-cracking program can successfully crack them and compromise your accounts.
How Long It Would Take to Crack Your Password
To give you an idea of how long it takes to crack passwords, here are a few examples from the Statista chart below.

According to Statista, passwords with at least one uppercase letter, number, symbol and at least 12 characters will take the longest for a password cracking program to crack – Statista estimates 34,000 years for a password that includes all of those criteria.
On the contrary, passwords that are 6 characters or less will be cracked instantly even when incorporating an uppercase letter, number and symbol. If you find that your password matches up to the criteria in the red, it means your passwords can be cracked instantly or in a matter of minutes, which is a risk to your online security.
The Importance of Random and Strong Passwords
It’s evident from the findings above that using weak passwords that don’t follow password best practices will make them easier for cybercriminals to crack. When you follow password best practices, the ability to crack your password becomes more difficult because of the complexity and length.
Password best practices include:
- Not using sequential numbers (e.g. 12345)
- Not including personal information (e.g. home address)
- Not using dictionary words (e.g. Dog)
- Not reusing passwords across multiple accounts
- Creating passwords with at least 12 characters
Oftentimes, people rely on themselves to create all their passwords. This results in using weak passwords because they are easier to remember or it leads to the reuse of passwords across multiple accounts. Reusing passwords is a dangerous practice as it makes it easier for cybercriminals to compromise more than just one of your accounts.
So, how can you go about creating passwords that are random, strong and difficult for cybercriminals to crack?
How to Create Strong Passwords That Are Hard to Crack
Here are a few ways you can create strong passwords that cannot be easily cracked.
Use a password generator tool
A password generator is a tool that aids you in creating unique passwords. When using a password generator, all you have to do is click a button and it’ll generate a unique string of characters based on how long you want your password to be. This is the easiest solution to strengthening your passwords since you won’t have to create them yourself. Keeper has its own password generator tool that is free to use. However, using a password generator tool alone is risky because you’re still left with the problem of having to remember them all – and the more complicated they are, the harder that is to do.
This is where a password manager can help.
Store your passwords in a password manager
A password manager is a cybersecurity tool that aids in generating passwords and storing them securely. Keeper’s password manager securely stores your passwords and allows you to access them on any platform, from any device. All you have to do is create a strong master password and Keeper Password Manager does the rest.
With Keeper, rest assured that your passwords will be almost impossible for a cybercriminal to crack.
Make sure your passwords are at least 12 characters long
Even when using a password generator tool or password manager, you’re still allowed the option to choose how long you want your passwords to be. Keep in mind that passwords less than 12 characters are not as secure as passwords that are at least 12 characters in length. The longer the password, the longer it’ll take for a cybercriminal to crack. The same goes for the complexity of the password.
Prevent Your Passwords From Being Cracked With Keeper
As technology advances, password cracking becomes easier for cybercriminals to successfully do. It’s important to understand the criteria to follow when creating strong, complex passwords and tools you can use to help create them.
Start a free 30-day trial of Keeper Password Manager to see how Keeper helps you create strong, unique passwords.
Source: Keeper
In a 2023 study commissioned by Datto, Forrester Consulting surveyed 421 cloud strategy decision-makers at small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) about their organizations’ current IT infrastructures and how leveraging external partnerships streamlines operations, saves money and contributes to organizational success.
Although the past five years have posed many different challenges for small businesses, the most notable among these organizations has been the move to the public cloud. While the 2020 pandemic accelerated this move as businesses adapted to work-from-home needs, it was not the primary reason for its adoption. In fact, many organizations were already looking to the public cloud for potential cost savings and as a solution to meeting tougher global compliance regulations prior to the pandemic shutdowns.
Today this adoption continues, and according to the study’s findings, many IT professionals expect 61% of their workloads to be in the cloud within the next two years. Interestingly, the other 39% of infrastructure and applications were still expected to operate on-premises, with many respondents not expecting a full cloud transformation. In this blog we will further examine what has led to this adjustment.
Public cloud: expectations vs. reality
Streamlining operations and increasing speed, modernizing existing apps and services, and cost-effectiveness are three of the top expectations businesses cite when positioning a transition of their IT infrastructure into the cloud. For many survey respondents, it appears the cloud has had less of an impact than once thought.
Potential cost-effectiveness was cited as the primary decision for the transition by 93%. But for many SMBs migrating to the cloud is a significant undertaking, and our study found only 47% of respondents said their organization had seen greater cost optimization. Additionally, respondents cited other challenges that have offset the benefits of migration. Only 33% reported seeing increased speed of setup or buildouts and only 31% saw improved ability to meet compliance regulations. With cloud service costs continuing to rise, more SMBs will need to consider the expected benefits of migration. Furthermore, many organizations will need to ask if this lackluster performance is due to the cloud or the limitations of their IT organizations.
Complex technology and a skill set challenge
SMBs had painted the cloud as a “promised land,” and at first glance this study shows us that few of the cloud’s expectations have been met. The question we ask is — is it the capabilities and structure of the cloud that has not met our expectations or is it something else?
The harsh reality is that cloud infrastructures are complex, and as mentioned earlier, 39% of many SMBs’ infrastructure remains on-prem, meaning that many of these cloud migrations are hybrid, leading to even further complexity. Decision-makers noted that one of their biggest challenges was maintaining interoperability between cloud and on-prem infrastructures. This creates a complex disjointed hybrid environment and opens concerns around security.
Yet 52% of the respondents stated that a lack of in-house staff expertise is challenging their organization’s operations in the public cloud and 74% felt that their organization does not have the capability or capacity to train employees as the cloud grows in complexity. This may be the answer to why cloud migrations are not meeting business expectations.
Leveraging partnerships
Managing both public cloud and on-premises infrastructures is becoming increasingly complex and expensive for SMBs. The cloud can only enable transformative outcomes if organizations are willing to undertake careful groundwork and planning and accept expert advice. Without a skilled and experienced staff, SMBs will continue to struggle to get the most out of their hybrid deployments. Leveraging partnerships with managed service providers (MSPs) will enable SMBs to manage their hybrid IT environments with skilled partners, enhance performance, increase security and keep their costs more predictable.
To learn more, download the Forrester study “SMBs: The Future Is Co-Managed.”
Source: Datto
Sophos is excited to announce a new partnership with Cysurance, a next-generation risk mitigation company that insures, warranties and certifies security solutions.
The partnership provides unique, fixed-price cyber insurance to U.S.-based organizations using Sophos Managed Detection and Response (MDR). The policies are the first of their kind to recognize organizations for having a layer of threat detection and response services.
As cyberthreats increase in complexity and velocity, MDR is quickly becoming an essential requirement for organizations to manage their cybersecurity posture. Most organizations simply can’t keep up with the evolving threat landscape, as evidenced by the 59% of U.S. security defenders who say today’s threats are too advanced for their organizations to deal with on their own.
Cysurance recognizes this and the value that Sophos’ 24/7 threat detection and response experts provide to mitigate cyber risk. Cysurance’s fixed-price coverage is a testament to Sophos’ MDR capabilities and the effective security services we provide to organizations.
Kirsten Bay, co-founder and CEO at Cysurance, says:
“The lack of comprehensive and integrated security strategies largely explains why cyber insurance policy fees are rising while coverage limits are declining. Those without defense in depth strategies are at increased cyber risk. However, cybersecurity is a manageable challenge, and Sophos can help. Together, we’re focused on helping organizations take responsible steps to implement proper cybersecurity to protect their business and digital assets. Sophos’ proven MDR solution allows Cysurance to offer a range of best-in-class coverage plans that reward customers for their smart cybersecurity investments.”
The Cysurance policies for Sophos MDR users supports all industry sectors in the U.S., regardless of number of employees or endpoints. Four plans, ranging from $275,000 to $3.2 million in total coverage – including ransomware coverage – are available. To learn more and sign-up, visit https://enroll.cysurance.com/sophos/
This is the latest in a series of cyber insurance partnerships for Sophos, which already this year announced deals with Cowbell and Measured Analytics and Insurance. Its partnership with Cysurance uniquely benefits organizations using Sophos MDR, one of the industry’s most widely used services with more than 17,000 customers.
Source: Sophos
Combining the best of Kaseya Connect and DattoCon, the first joint event since the acquisition of Datto will showcase technical insights, solutions updates and growth strategies with the European IT community.
Kaseya, the leading global provider of unified IT management and cybersecurity software for managed service providers (MSPs) and small to mid-size businesses (SMBs), has commenced its first combined Kaseya DattoCon Europe event taking place at the Convention Centre Dublin, Ireland from 26-28 June.
Bringing together more than 1,000 IT industry leaders over three days of sessions, exclusive certified trainings and networking, the event is a key opportunity for attendees to learn in-depth about Kaseya’s IT service solutions – including the recently launched IT Complete 2.0, the industry’s only purpose-built platform for multi-functional IT professionals.
Leading industry experts will discuss current trends in IT and cybersecurity and share impactful growth strategies for the IT community. A plethora of networking opportunities, actionable sales and marketing advice and hands-on, expert-led product training complete the three-day programme.
New capabilities in IT Complete 2.0
“Organisations ‘powered by Kaseya’ are the most successful in their industries,” said Fred Voccola, CEO, Kaseya. “IT Complete is already the most integrated and comprehensive suite of solutions for IT professionals. With this latest version, we’ve taken its capabilities to the next level by adding another 350 integrations, including all Datto products. We are proud to present IT Complete 2.0 to our European partners.”
- Following the acquisition of Vonahi, Kaseya has added automated network penetration testing to its Security Suite and lowered the pricing for Vonahi solutions by 10%.
- Kaseya has also expanded its MSP Enablement Suite to include the audIT automated sales presentation solution, with five free licenses for every customer.
- The ConnectBooster integration is now available to European partners, simplifying billing processes for MSPs.
Other product updates within IT Complete 2.0 include:
- Datto Endpoint Backup for Servers, a highly anticipated solution giving MSPs the option to protect servers directly to the secure Datto Cloud – no local appliance or IT hands required – while still including all the advanced features Datto BCDR users have come to expect.
- Microsoft 365 Management in Datto RMM, a new feature combining user management and device management to simultaneously give new users everything they need during the onboarding phase. It also revokes access at once when they are offboarding.
- The relaunched Datto Networking Appliance (DNA), a high-performance network router for ‘always on’ Internet connections thanks to fully integrated 4G LTE failover.
New Kaseya Business Services for European customers
Kaseya is also growing its Remote IT and Security Management (RITSM) training programme with a new Professional course. The new 40-hour certification course is designed to address the growing demand for tech talent, with modules covering critical MSP functions such as remote IT and security management, working in sandbox environments and customer service skills.
Key sessions at Kaseya DattoCon Europe included:
- Fred Voccola, CEO, Kaseya will deliver a keynote on the state of the MSP and SMB industry and opportunities ahead.
- Dr. Lior Zoref, Researcher, Advisor, TED Speaker, Former Vice President at Microsoft and author of the best-selling book, Mindsharing: The Art of Crowdsourcing Everything will delve into using collective intelligence to make better decisions and find new solutions to business challenges.
- Ranjan Singh, Chief Product Officer, Kaseya will give an overview of the latest Kaseya and Datto product innovations.
- Jason Manar, CISO, Kaseya will discuss the real threats that keep CISOs up at night.
- Nadir Merchant, General Manager and CTO, IT Glue will present integrated IT management with Kaseya One.
Source: Kaseya
Keeper Security has released its latest research, Password Management Report: Unifying Perception with Reality, which assesses the password habits of individuals across the United States and Europe.
For the report, Keeper surveyed over 8,000 people. The survey focuses on the differences between what people say they do to ensure their cybersecurity, and what they actually do. The survey revealed that many people are overconfident in their overall security health and that there is a clear disconnect between people’s actions and their perception. The report also found that older generations are more likely to practice good password security than their younger peers. Overall, cybersecurity and password best practices were revealed to be an enigma. Individuals think they are protected, but based on the actions those same individuals take, that confidence may be misplaced.
People Overestimate Their Security
The majority (51%) of respondents in the survey reported that “Cybersecurity is easy to understand.” Additionally, a full quarter of respondents reported that not only was cybersecurity an easy concept to grasp, but they actively take steps to protect themselves. Only 10% of all respondents admitted to feeling overwhelmed by cybersecurity. For anyone who works in the field, that may jump out as a shockingly low number. After all, new threat vectors are being exposed every day, major ransomware gangs dominate newscycle on a regular basis and the sheer number of breaches has grown at a seemingly exponential rate. How then, could people feel so confident in their security posture?
The answer, worryingly, could be simple ignorance. For example, the survey found that only 25% of people are using strong, unique passwords for all their accounts, which leaves 75% of individuals with dangerously weak password practices. A third of respondents (34%) use strong passwords but repeat variations of them (for example Hockeyfan123 and 123Hockeyfan), a practice which is vulnerable to credential-stuffing attacks. Finally, a jaw dropping 14% of all respondents use simple, repeated passwords across their accounts.
Creating and remembering hundreds of unique passwords is a mammoth task, and one most people neither have the time or energy to tackle. As a result, people tend to ignore advice from cybersecurity experts, government bodies and other experts, instead choosing to imagine that cyber risk does not apply to them.
Older Demographics Have Better Password Management
Not all individuals are hopelessly vulnerable, and contrary to popular belief, it is not the younger generation that has the best password management practices. In fact, 29% of Baby Boomers (aged 59-77 years) use strong, unique passwords versus only 20% of Gen Z (aged 16-26 years) respondents.
Older generations may be more in tune with the reality of sophisticated and ever present cyberthreats, or they may just have more to lose should a breach occur. Either way, we as an industry need to do more to educate users and improve their understanding of the tactics that can help people avoid a costly attack.
Bridging the Knowledge Gap
While advice on cybersecurity is abundant, Keeper’s survey reveals it is too overwhelming for over a third of people. Although respondents claim that strong passwords are the most effective way for personal cybersecurity, the majority do not follow the industry-recommended password protection practices in their day-to-day lives. Keeper’s findings show that three-quarters of people fail to follow password best practices, yet almost everyone considers cybersecurity to be easy to comprehend.
Cybersecurity is essential to effectively protect our increasingly dependent online presence, yet many ignore the value of proper digital safety protocols. People should confront their overconfidence, fear, and apathy to secure their devices, identities, and accounts. A first step is using a password manager like Keeper to create and store strong, unique passwords and passkeys for all of your accounts.
Source: Keeper Security
The SophosLabs Intelix portal is an excellent resource for staying informed about the latest cyber threats.
We are pleased to announce the launch of the SophosLabs Intelix portal, a web-based interface allowing anyone to submit suspicious threat artifacts for threat intelligence and classification. This free service is an excellent resource for individuals, researchers, and organizations looking to stay up to date with the latest cyber threats.
Intelix provides detailed, explainable, and proven threat intelligence, allowing people to make informed decisions. Submitted files and URLs undergo detailed threat analysis, including cloud lookups, static analysis, and dynamic analysis (cloud sandboxing).
From the rich reports generated, users can understand the verdict and the features and/or behaviors that led to the verdict.
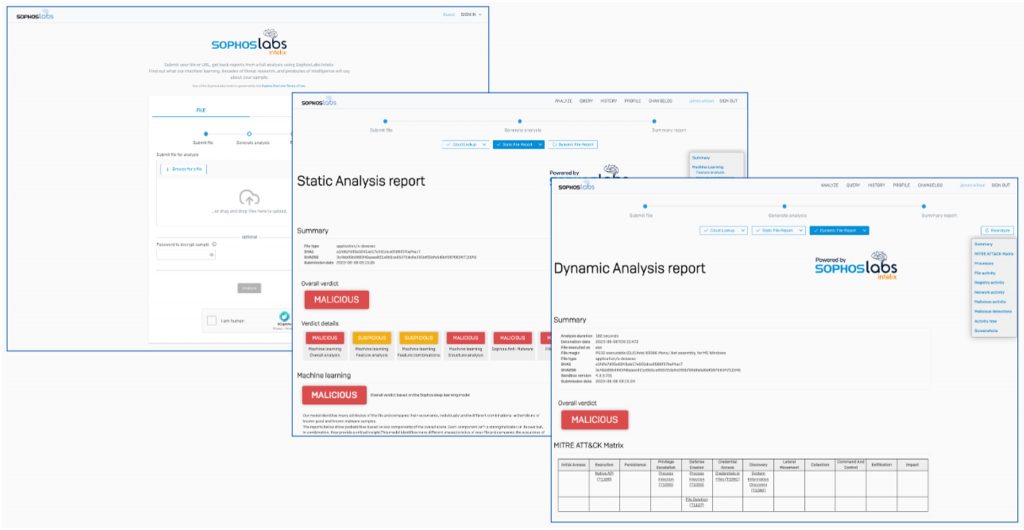
The Intelix portal showcases the power of the SophosLabs detection technologies and the Sophos X-Ops threat intelligence platform used by Sophos products.
If you’re a registered Sophos customer, the Intelix Portal offers additional features. By signing in with your Sophos ID, you can access the results of all previous analyses for up to one year. You can also instantly escalate an analysis to Sophos Support or SophosLabs for human review of the verdict.
The SophosLabs Intelix portal is an excellent resource for staying informed about the latest cyber threats. Whether you’re a researcher, an individual, or a business, the portal provides a wealth of information to help you stay one step ahead of cybercriminals. Intelix is also available in the AWS Marketplace and for OEM use cases.
Try it out today or visit Sophos.com/Intelix to learn more.
Source: Sophos
Cybercriminals often use phishing emails to get you to click on malicious links or attachments. Clicking on these scams can trigger a malware infection that places all your sensitive data at risk of becoming compromised. Before deciding to click on an attachment, you should make sure it’s safe to open.
You can check if an email attachment is safe by having antivirus software scan the attachments in your emails, double-checking who the sender is and not opening any attachments that are marked as spam. Keep reading to learn more about unsafe email attachments and how you can keep yourself from falling victim to them.
The Risks of Opening Unsafe Email Attachments
One of the biggest risks of opening unsafe email attachments is having your device become infected with malicious software called malware. When malware is successfully installed onto your computer, it can log your keystrokes, take screenshots of your activity and compromise your computer’s camera or microphone. All of this data is then sent to the cybercriminal who targeted your device.
Cybercriminals use malware to steal your sensitive data such as your account login information or credit card numbers. Depending on the type of malware that is installed on your computer, what the cybercriminal can get away with varies.
3 Tips To Check If an Email Attachment Is Safe
Here are tips you can use to check if an email attachment is safe.
Double-check who the sender is
Checking the sender’s email and name is a very important step to take before deciding to click on an email attachment. However, you cannot just rely on the sender’s name to verify an email. Many cybercriminals spoof the names of senders to make it look like they’re coming from a trusted source, when in reality, they’re not. Even if you use an email provider like Gmail, which released an update that shows a blue checkmark next to “verified” senders, don’t trust it fully. Cybercriminals have already found a way to exploit Gmail’s blue checkmark verification.
Instead, rather than clicking on the attachment, contact the sender yourself through another communication method to confirm that it is really the person or organization who sent it.
Don’t open any email attachments that are marked as spam
Many email providers flag spam emails and automatically place them into your spam folder. If your email provider does this, ensure you don’t open any attachments from those flagged emails as they’re likely to be phishing attempts.
Use antivirus software to scan attachments
Antivirus software is a type of program you install on your computer that detects, isolates and removes viruses and other malware before cybercriminals can successfully infect your computer. An added benefit to some antivirus software is that it can also scan the attachments in your email to check if they’re safe. If they’re not safe, your antivirus software will let you know.
Which Email Attachments Are Generally Safe To Open?
Some email attachments that are considered generally safe to open are:
- .JPEG
- .JPG
- .PNG
- .GIF
- .TIF
- .TIFF
- .MPEG
- .MPG
- .MP3
- .MP4
- .WAV
- .MOV
While these types of attachments are considered safe, we still recommend being cautious about clicking them, especially when they’re unsolicited or from an unknown sender.
Which email attachments are less safe to open?
Some email attachments that are considered less safe to open include:
- .EXE
- .DOC
- .DOCX
- .XLS
- .XLSX
- .PPT
- .DMG
- .ZIP
- .RAR
- .HTML
Before deciding to click on these types of attachments, we recommend taking precautions such as using antivirus software and confirming the sender. If it’s a file from a sender you were expecting, there’s most likely nothing to worry about.
What To Do If You Click an Unsafe Email Attachment
Here are the steps you can take if you accidentally click on an unsafe email attachment.
1. Disconnect your device from the internet
One of the first things you need to do is disconnect your device from the internet. Malware can spread through your WiFi and infect other devices connected to the same network if it remains connected. Disconnecting your device from the internet can also lessen the amount of damage the malware causes.
2. Change your passwords and enable MFA
After disconnecting your device from the internet, you should use a different device to change the passwords for all of your accounts, most importantly, your email. You can use a password manager to help you change the passwords quickly. Keeper Password Manager offers a free 30-day trial that you can start using right away. A password manager will help you create strong, unique passwords for each of your accounts and securely store them so you never forget them.
Along with changing your passwords, enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). MFA adds an extra layer of security to your account to prevent anyone but you from being able to access it. An added benefit to using a password manager is that it can also store your 2FA codes and autofill them when you log in.
3. Scan your device for viruses and other malware
Most antivirus software programs work without having to be connected to the internet. If you already have antivirus installed on your infected computer, run a scan so the malware is removed from your device. If you don’t already have antivirus software, you’ll need to connect to the internet and download an antivirus program.
Some malware and viruses may prevent you from being able to download antivirus software. If this is the case, you’ll need the help of a professional. If you already have everything on your device backed up, another approach you can take is completely wiping your computer. Remember, wiping your computer will remove everything from it, including your files, pictures and other data, so only take this approach if you know all of your data is backed up.
4. Keep an eye out for suspicious activity
After taking the steps above, it’s important to keep an eye on your accounts. You never know what the cybercriminal could have gotten away with in a short period of time. Watch out for any suspicious activity such as purchases you didn’t make or unusual login attempts on any of your accounts.
Protect Yourself From Unsafe Email Attachments
One of the best ways you can stay safe from falling victim to phishing email scams is by knowing how to spot them. This means knowing the red flags to look for, like unsolicited email attachments. As a preventative measure, always use strong passwords on each of your accounts and always have MFA enabled. The stronger your cyber hygiene is, the safer you and your data will be, even if you accidentally fall for a scam and click on an unsafe email attachment or link.
Start a free 30-day trial of Keeper Password Manager today to start protecting your accounts and data from cybercriminals.
Source: Keeper
Sophos rated 4.7/5 in Network Firewalls. Customers have recognized Sophos for the second consecutive year.
Over the last two years, customers have recognized Sophos with an average overall rating of 4.7/5 based on 462 reviews, as of March 31, 2023. What’s more, Sophos is the only vendor to be named a Customers’ Choice for BOTH the 2021 Endpoint Protection Platforms and 2023 Network Firewalls market categories. In addition, we are the only vendor to be named a Customers’ Choice for the Network Firewalls Public Sector, Gov’t, Edu segment.
Based solely on independent customer reviews that have been rigorously evaluated by Gartner, we believe this recognition is a testament to the unparalleled value that Sophos Firewall delivers thanks to its industry leading protection, superior visibility, and easier management.
Access the full report here.
Gartner Peer Insights shares the independent voices of verified enterprise customers. Recent feedback on Sophos Firewall includes:

These are just a few of the hundreds of Sophos network firewall customer reviews available on the Gartner Peer Insights site. I would like to take this opportunity to thank our customers who have shared their feedback; we truly appreciate your time and your trust.
Sophos Firewall optimizes your network protection
Sophos Firewall delivers the ultimate value for your network security investment by providing powerful protection and performance for even the most demanding network environments, with benefits you just can’t get with any other firewall:
Expose hidden risks – Sophos Firewall does a far better job exposing hidden risks than other solutions through a visual dashboard, rich on-box and cloud reporting, and unique risk insights.
Block unknown threats – Sophos Firewall makes blocking unknown threats faster, easier, and more effective than other firewalls with advanced high-performance TLS inspection and a full suite of advanced protection capabilities that are very easy to set up and manage.
Automatically respond to incidents – Sophos Firewall with Synchronized Security automatically responds to incidents on the network thanks to Sophos Security Heartbeat, which shares real-time intelligence between your Sophos endpoints and your firewall.
Sophos Firewall is just part of the best cybersecurity ecosystem
Sophos Firewall is tightly integrated with our full line of secure access network security products, including Sophos Switches, Wireless, SD-RED and ZTNA – along with the rest of the Sophos cybersecurity ecosystem of endpoint, XDR, MDR, and messaging security solutions.
Whether you want to manage it yourself with our easy and integrated Sophos Central cloud manager, or have us manage it for you with our 24/7 managed threat detection and response service, we’ve got you covered.
Source: Sophos
Many organizations know they need to improve their approach to cybersecurity or grow their security ecosystem, but they don’t know where to begin. If this sounds familiar, you’re in the right place. Getting started with cybersecurity or bolstering your existing infrastructure can often be an arduous process. We’re here to help.
Fortra Offers a Comprehensive Approach to Cybersecurity
Fortra is ready to support your organization’s unique needs as you work to enhance your security posture on multiple fronts. We offer a robust security portfolio that spans both infrastructure and data protection to provide a comprehensive approach from a single trusted partner.
Vulnerability Management
Identify, evaluate, prioritize, and report on security weaknesses that may be putting your organization at risk. Easy to deploy, simple to use, and scalable, these solutions help streamline your security efforts in these areas:
- Vulnerability Management
- Web Application Scanning
- Application Security Testing
Offensive Security
Prioritize the risks that truly pose the biggest threat to your infrastructure. Monitor for weaknesses in the infrastructure and defensive processes of your organization with tools that help you evaluate the potential consequences of cyberattacks:
- Automated Pen Testing
- Adversary Simulations
- Red Team Operations
Data Protection
Protect sensitive information and comply with regulatory requirements. Identify and classify data and root out policy violations by leveraging:
- Data Classification
- Rights Management
- Endpoint DLP
Digital Risk Protection
Safeguard critical digital assets through expert-curated threat intelligence and complete mitigation against brand impersonation, data leakage, social media threats, account takeover, and other digital risks in one complete solution. This encompasses:
- Account Takeover Protection
- Social Media Protection
Secure File Transfer
Simplify, secure, and automate enterprise file transfer through a single intuitive interface that enables employees, partners, and customers to move data easily without the need for programming skills. Solutions span:
- Managed File Transfer
- Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
- File Acceleration
Email Security
Keep emails, brands, and data protected with minimal disruption. Reduce the chance of cyberattacks starting with inbound email as well as outbound data loss prevention with these capabilities:
- Brand Protection
- Business Email Compromise (BEC)
- Secure Email Gateway
Source: Fortra
While some people have returned to working in an office, it seems that the majority have not. Looking back, the pandemic will likely have been a turning point for many things around the world, and the rhythms of office-centered worklife will be something that will never return to the old ways.
With this increased flexibility employees are not just working from home behind consumer-grade Wi-Fi routers; they are also spending part of the day at the park or coffee shop, or perhaps even having a “working holiday.” Those in charge of protecting enterprise assets have to assume these endpoints are always in hostile territory.
Even before the pandemic, organizations working toward improving their security maturity were often trying to “push left.” What is pushing left? At its most basic level it means moving things closer to the start. It originates from software development where the stages of the development process are conceptualized from left to right, left being the beginning. In applied security we also use the term “pushing left,” but rather than referring to the software development process we are referring to the attack chain, which moves from reconnaissance on the left through action (exfiltration or other attacker goal) on the right.
For many years, the most comprehensive security strategies have involved defense in depth. The idea is that not all technologies are suitable for detecting a given threat type, so it is best to deploy them in layers. These layers often directly correspond to how far “left” something is in the attack chain. If you can detect something at the network border through your firewall, email, or web filters, you have contained the threat before it has any negative impact on operations.
Ideally you want to detect and block an attacker as far left as possible, i.e., as early as possible. Pushing detections left also alerts security analysts that an intrusion may be underway, initiating more focused threat hunting to anticipate gaps in defenses your attacker may be attempting to exploit.
For employees at the office, you can centralize control of these defenses and provide optimum protection. The question is, are you able to provide the same protection for remote workers regardless of their location? Can you monitor and respond to threats being detected on those assets when they are out of the office? As many have observed, this did not work as well as we would have liked when we all went into lockdown, many of us without a plan.
While there are still many benefits to monitoring the network when you have control of it, including reduced endpoint overhead and the ability to keep threats at a distance from sensitive assets, we need to ensure we can take as much of this protection as possible with us when we are out and about.
We must ensure not only that protection is optimized, but also that we don’t lose our ability to monitor, detect, and respond to attacks targeting these remote assets. Most organizations have moved to utilizing EDR/XDR solutions (or plan to in the very near future) , which is a great start, but not all solutions are comprehensive.
In the remote-work era, insufficiently protected remote users can encounter plenty of issues – malicious URLs and downloads, and networks attacks, to name only the most mundane – that in the Before Times would have been handled by machines guarding the corporate “fort.” The biggest missing components when users are “outside the fort” are HTTPS filtering and web content inspection of the sort that is typically implemented within next-generation firewalls. When you add these technologies to pre-execution protection, behavioral detection, machine learning models, client firewalls, DLP, application control, and XDR, you are starting to look at a comprehensive stack of defenses for attackers to overcome – even if the endpoints themselves are now free-range.
For initiatives like zero trust network access (ZTNA) to be effective, we must not only wrap the applications we interact with, but we must also wrap the endpoints that connect to them. Simple checks like whether the OS up-to-date and whether it has security software installed may be a good start, but not all protection is created equal.
With most devices being connected to the internet whenever they’re in use, we can leverage the power of the cloud to help provide ubiquitous protection and monitoring. Modern security solutions must assume the endpoint device or phone is in a hostile environment at all times. The old idea of inside and outside is not only outdated, it’s downright dangerous.
Source: Sophos
These Apps -Known as Fleeceware- Take Advantage of App Store Policy Loopholes and Coercive Tactics to Overcharge Users for AI Assistants.
Sophos, a global leader in innovating and delivering cybersecurity as a service, today announced that it had uncovered multiple apps masquerading as legitimate, ChatGPT-based chatbots to overcharge users and bring in thousands of dollars a month. As detailed in Sophos X-Ops’ latest report, “FleeceGPT’ Mobile Apps Target AI-Curious to Rake in Cash,” these apps have popped up in both the Google Play and Apple App Store, and, because the free versions have near-zero functionality and constant ads, they coerce unsuspecting users into signing up for a subscription that can cost hundreds of dollars a year.
“Scammers have and always will use the latest trends or technology to line their pockets. ChatGPT is no exception. With interest in AI and chatbots arguably at an all-time high, users are turning to the Apple App and Google Play Stores to download anything that resembles ChatGPT. These types of scam apps—what Sophos has dubbed ‘fleeceware’—often bombard users with ads until they sign up for a subscription. They’re banking on the fact that users won’t pay attention to the cost or simply forget that they have this subscription. They’re specifically designed so that they may not get much use after the free trial ends, so users delete the app without realizing they’re still on the hook for a monthly or weekly payment,” said Sean Gallagher, principal threat researcher, Sophos.
In total, Sophos X-Ops investigated five of these ChatGPT fleeceware apps, all of which claimed to be based on ChatGPT’s algorithm. In some cases, as with the app “Chat GBT,” the developers played off the ChatGPT name to improve their app’s ranking in the Google Play or App Store. While OpenAI offers the basic functionality of ChatGPT to users for free online, these apps were charging anything from $10 a month to $70.00 a year. The iOS version of “Chat GBT,” called Ask AI Assistant, charges $6 a week—or $312 a year—after the three-day free trial; it netted the developers $10,000 in March alone. Another fleeceware-like app, called Genie, which encourages users to sign up for a $7 weekly or $70 annual subscription, brought in $1 million over the past month.
The key characteristics of so-called fleeceware apps, first discovered by Sophos in 2019, are overcharging users for functionality that is already free elsewhere, as well as using social engineering and coercive tactics to convince users to sign up for a recurring subscription payment. Usually, the apps offer a free trial but with so many ads and restrictions, they’re barely useable until a subscription is paid. These apps are often poorly written and implemented, meaning app function is often less than ideal even after users switch to the paid version. They also inflate their ratings in the app stores through fake reviews and persistent requests of users to rate the app before it’s even been used or the free trial ends.
“Fleeceware apps are specifically designed to stay on the edge of what’s allowed by Google and Apple in terms of service, and they don’t flout the security or privacy rules, so they are hardly ever rejected by these stores during review. While Google and Apple have implemented new guidelines to curb fleeceware since we reported on such apps in 2019, developers are finding ways around these policies, such as severely limiting app usage and functionality unless users pay up. While some of the ChatGPT fleeceware apps included in this report have already been taken down, more continue to pop up—and it’s likely more will appear. The best protection is education. Users need to be aware that these apps exist and always be sure to read the fine print whenever hitting ‘subscribe.’ Users can also report apps to Apple and Google if they think the developers are using unethical means to profit,” said Gallagher.
All apps included in the report have been reported to Apple and Google. For users who have already downloaded these apps, they should follow the App or Google Play store’s guidelines on how to “unsubscribe.” Simply deleting the fleeceware app will not void the subscription.
Learn more about these scam ChatGPT apps and how to avoid them in ’FleeceGPT’ Mobile Apps Target AI-Curious to Rake in Cash on Sophos.com.
Source: Sophos
With the threat landscape expanding and criminals taking advantage of security gaps, organizations are turning to controls that can help them limit their exposure. Among other controls, penetration testing stands out because it simulates attackers’ malicious activities and tactics to identify security gaps in business systems or applications. A penetration test aims to understand what vulnerabilities are in business systems, how they could be exploited, and the potential impact if an attacker were successful. Because pen tests thoroughly investigate vulnerabilities, the scope of each pen test must be limited and may differ from test to test. Pen tests take on two different types of perspectives: internal and external. In this blog, we will examine what internal and external penetration testing is, who conducts these tests, and why organizations need both.
Getting Past the Perimeter: External Pen Testing

The 2023 Pen Testing Report revealed that 77% of security professionals pen test their external infrastructure. Essentially, external networks encompass all public-facing assets—including the internet at large. Additionally, many organizational applications, like mail servers, websites, or even customer portals maintain a connection to these external networks and can also provide a doorway from which a threat actor can pivot.
External penetration tests are typically what people think of when they hear about pen testing. These tests use the same techniques as adversaries to attempt to exploit weaknesses in an organization’s front facing perimeter or attempt to bypass them altogether with strategies like a phishing campaign or other social engineering methods.
Thinking Beyond the Initial Breach: Internal Penetration Testing
This year’s report also showed that 73% of security professionals pen test their external infrastructure. Internal penetration tests take on the role of an adversary who has already gained a foothold within the corporate network and is looking to elevate privileges to move laterally, gain further control and cause more damage. These assumed breach scenarios also deal with security gaps that such an attacker could exploit.
Internal attacks can originate from malicious insiders or compromised users like careless employees, insecure third-party vendors, and even clients or customers. Internal threats can be anything from bad hygiene habits, like weak passwords and poor access controls, to system and app misconfigurations and insecure endpoints. The Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report indicates that human errors are responsible for 13% of data breaches.
Though many think pen tests concentrate on an initial breach, it’s just as important to deploy tests that focus on what happens once someone is already inside the perimeter. Since such attacks start with internal access, they may attempt to achieve more high-value objectives including acquiring high-level privileges, compromising the Domain, or accessing other valuable assets and/or information. Because of this, it is crucial to identify and prioritize these threat vectors.
Who Should Be Conducting These Pen Tests?
Though it’s easy to think that in-house teams would handle all internal tests and external/third party teams would handle external tests, this is not the case. Both teams can conduct internal and external pen tests.
The one exception may be physical pen tests. These external tests involve attempting to gain entry to a physical facility, system, or network by exploiting weaknesses like doors, locks, cameras, or other access controls. Third parties tend to be the only teams that complete such assessments. 36% of respondents to the pen test report used third-parties for such services.
Otherwise, using both types of teams simply provides the capability to conduct more tests. Internal teams can conduct routine tests more often, while third-party services are solicited to provide a fresh prospective and different skill sets.
Creating a Holistic Pen Testing Strategy
Though organizations have to make tough choices when deciding what tests they have the time and resources to run, one of the most important criteria to consider is whether you’re balancing internal and external tests.
Only testing externally overlooks vulnerabilities that can be exploited by a malicious insider or a compromised account. With strategies like phishing more popular than ever, it’s critical to remember how easily insider access can be attained. However, only testing internally can inadvertently leave a door wide open for an attacker to get in without much difficulty.
Ultimately, by conducting both internal and external pen testing, organizations can gain full visibility into their security posture and ensure that they are adequately protected. The pen test report showed that in 2022, internal environments were regularly tested 14% less than external environments. With a gap of only 4% in 2023, it’s encouraging that this year’s pen testing report show that organizations are better understanding this balance.
Source: Core Security
Security adviser Roger Grimes once famously wrote, “To beat hackers, you have to think like them.” Grimes explained that security professionals should step into the attackers’ shoes and seek how to break into corporate systems, discover weaknesses, and create robust security countermeasures. Walking the walk of an attacker is what penetration testing is all about.
What is In-House Pen Testing?
In-house pen testing is, quite simply, when any pen testing efforts are deployed from within an organization. Instead of (or in addition to) hiring a third-party service, businesses can run their own pen tests to assess the state of their security.
Though some think a full, dedicated in-house pen testing team is needed in order to run a successful pen testing program, organizations can start small, with just one employee or security teams taking on pen testing duties. Organizations can utilize penetration testing tools that have automated features which can be used by security team members who may not have an extensive pen testing background. These tools can be used for tests that are easy to run, but essential to perform regularly, like validating vulnerability scans, network information gathering, privilege escalation, or phishing simulations.
According to the 2023 Penetration Testing Report, it’s clear organizations realize the importance of internal penetration testing since 48% of the 2023 Penetration Testing survey respondents have in-house teams. This percentage marks a 7% increase compared to the 2022 results.
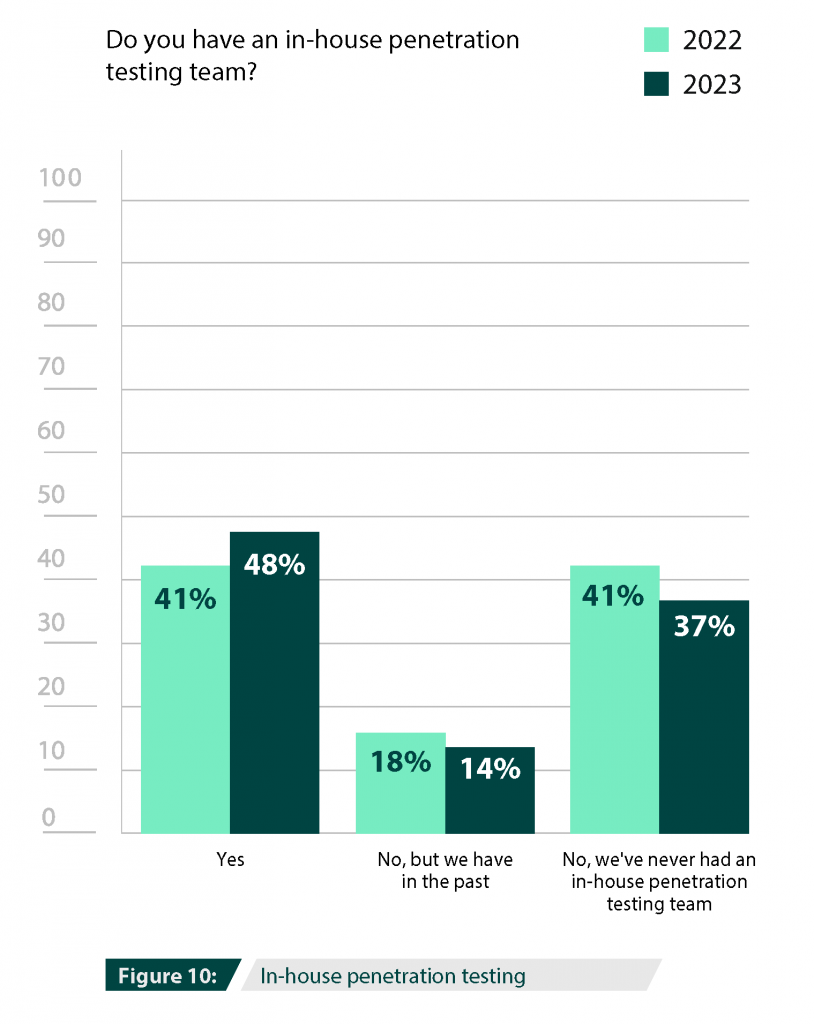
Why Do Organizations Have In-House Pen Testing?
Having in-house pen-testing capabilities can quickly expand efforts, allowing for more frequent tests and coverage of a broader scope of the IT infrastructure. It also ensures that changes to the infrastructure are more efficiently assessed to ensure new security gaps aren’t created.
According to the report, organizations conduct penetration testing for multiple reasons. 69% report that they perform pen tests for risk assessment and remediation prioritization. By having internal knowledge of the organization, teams can tailor remediation plans knowing what the available resources are and their limitations. They can outline the best and most effective changes that are also achievable and help implement them.
58% reported using in-house pen testing for regulatory compliance mandates and 40% for company policy requirements. Having an in-house pen testing capabilities ensures that these standards will be met and won’t fall through the cracks. With continuous testing, organizations can far exceed the bare minimum conditions of a mandate or regulation.
Reasons for Penetration Testing
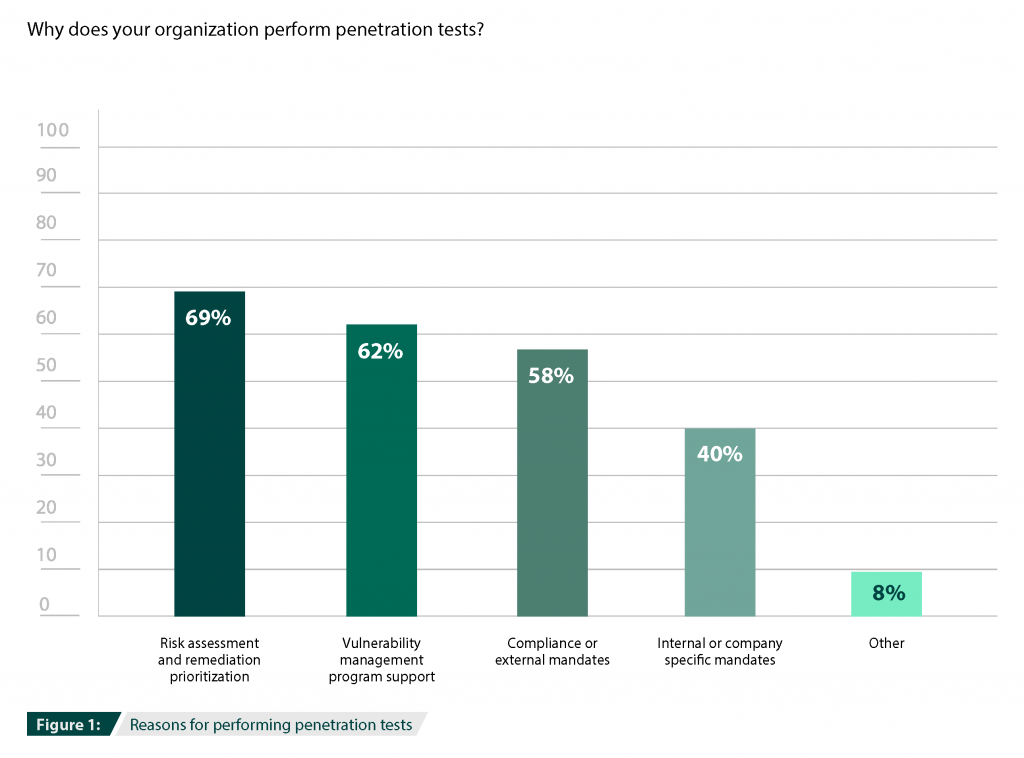
No matter the driving reason, it is essential not to pen test to check a box. Businesses should take the next step forward and take all necessary steps to mitigate identified weaknesses. A pen test program does not end with discovering vulnerabilities; a formalized program can help organizations achieve maximum coverage and impact.
Every pen test involves several steps, from scoping and intelligence gathering to threat modeling, analysis, and reporting. However, the specific goals, methodology, conditions, and targets can differ quite a bit depending on whether the organization chooses in-house or external penetration testing.
The Challenges of In-House Pen Testing
While in-house pen testing appears to be on the rise, 52% of organizations do not have an in-house penetration testing team. Many factors contribute to this finding, the most important being the lack of required talent.
The skills gap is a persistent issue in the cybersecurity industry, affecting the establishment and staffing of penetration testing teams. In fact, according to the (ISC)² 2022 Cybersecurity Workforce Study, the cybersecurity workforce gap has grown more than twice as much as the workforce, with a 26.2% year-over-year increase.
In addition, the tech and cybersecurity sectors have been massively affected by The Great Reshuffle, which created further challenges in retaining staff. In a field with so many job openings, there wouldn’t be uncommon to be more turnover and instability in any team building.
Other factors affecting the organization’s ability (or decision) to maintain a pen-testing capacity are the lack of leadership buy-in and the consequent lack of required funding. These findings, coupled with the response that there is insufficient need, may indicate a lack of perception and prioritization.
Using Tools to Deploy In-House Pen Tests
Using pen testing solutions can help organizations overcome many of these challenges. While the skills gap may prevent an organization from being able to find and hire advanced testers, security or IT professionals don’t need have much experience with pen testing if they’re aided by effective tools. An automated commercial pen testing tool, like Core Impact, can guide them through routine tests and techniques. These tools can also be deployed without adding to your headcount, making them a cost-effective way to show the benefits of in-house pen testing efforts.
Source: Core Security


























