While AI brings many advantages, like all technological capabilities, it also introduces a number of risks. The survey revealed varying levels of awareness of these potential pitfalls.
AI risk awareness
Defense risk: Poor quality and poorly implemented AI
With improved protection from cyber threats jointly at the top of the list of desired benefits from GenAI, it’s clear that reducing cybersecurity risk is a strong factor behind the adoption of AI-powered defense solutions.
However, poor quality and poorly implemented AI models can inadvertently introduce considerable cybersecurity risk of their own, and the adage “garbage in, garbage out” is particularly relevant to AI. Building effective AI models for cybersecurity requires extensive understanding of both threats and AI.
Organizations are largely alert to the risk of poorly developed and deployed AI in cybersecurity solutions. The vast majority (89%) of IT/cybersecurity professionals surveyed say they are concerned about the potential for flaws in cybersecurity tools’ generative AI capabilities to harm their organization, with 43% saying they are extremely concerned and 46% somewhat concerned.

It is therefore unsurprising that 99% (with rounding) of organizations say that when evaluating the GenAI capabilities in cybersecurity solutions, they assess the caliber of the cybersecurity processes and controls used in the development of the GenAI: 73% say they fully assess the caliber of the cybersecurity processes and controls and 27% say they partially assess the caliber of the cybersecurity processes and controls.
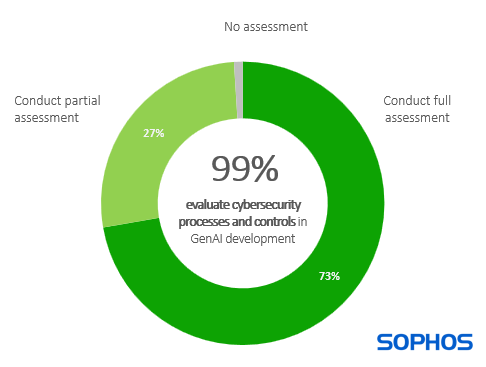
While the high percentage that report conducting a full assessment may initially appear encouraging, in reality it suggests that many organizations have a major blind spot in this area.
Assessing the processes and controls used to develop GenAI capabilities requires transparency from the vendor and a reasonable degree of AI knowledge by the assessor. Unfortunately, both are in short supply. Solution providers rarely make their full GenAI development roll-out processes easily available, and IT teams often have limited insights into AI development best practices. For many organizations, this finding suggests that they “don’t know what they don’t know”.
Financial risk: Poor return on investment
As previously seen, improved return on cybersecurity spend (ROI) also tops the list of benefits organizations are looking to achieve through GenAI.
High caliber GenAI capabilities in cybersecurity solutions are expensive to develop and maintain. IT and cybersecurity leaders across businesses of all sizes are alert to the consequences of this development expenditure, with 80% saying that they think GenAI will significantly increase the cost of their cybersecurity products.
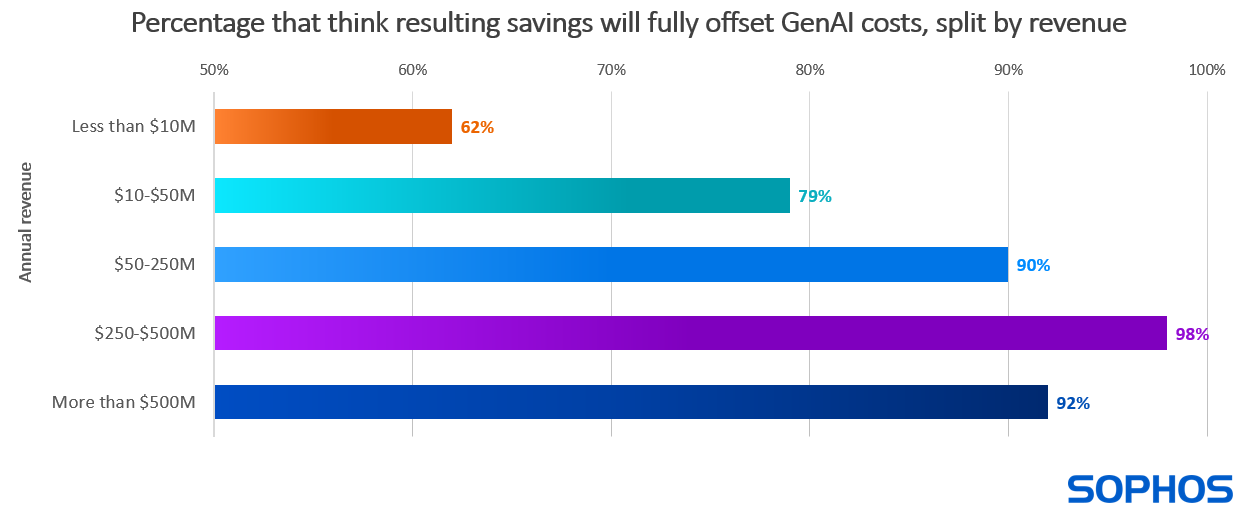
Despite these expectations of price increases, most organizations see GenAI as a path to lowering their overall cybersecurity expenditure, with 87% of respondents saying they are confident that the costs of GenAI in cybersecurity tools will be fully offset by the savings it delivers.
Diving deeper, we see that confidence in gaining positive return on investment increases with annual revenue, with the largest organizations ($500M+) 48% more likely to agree or strongly agree that the costs of generative AI in cybersecurity tools will be fully offset by the savings it delivers than the smallest (less than $10M).
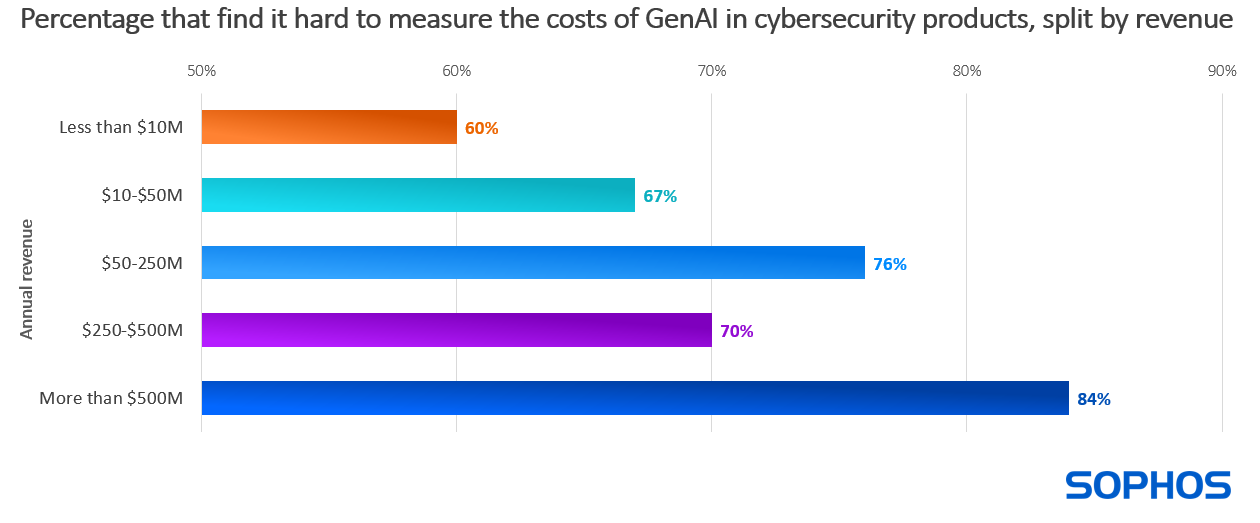
At the same time, organizations recognize that quantifying these costs is a challenge. GenAI expenses are typically built into the overall price of cybersecurity products and services, making it hard to identify how much organizations are spending on GenAI for cybersecurity. Reflecting this lack of visibility, 75% agree that these costs are hard to measure (39% strongly agree, 36% somewhat agree).
Broadly speaking, challenges in quantifying the costs also increase with revenue: organizations with $500M+ annual revenue are 40% more likely to find the costs difficult to quantify than those with less than $10M in revenue. This variation is likely due in part to the propensity for larger organizations to have more complex and extensive IT and cybersecurity infrastructures.
Without effective reporting, organizations risk not seeing the desired return on their investments in AI for cybersecurity or, worse, directing investments into AI that could have been more effectively spent elsewhere.
Operational risk: Over-reliance on AI
The pervasive nature of AI makes it easy to default too readily to AI, assume it is always correct, and take for granted that AI can do certain tasks better than people. Fortunately, most organizations are aware of and concerned about the cybersecurity consequences of over-reliance on AI:
- 84% are concerned about resulting pressure to reduce cybersecurity professional headcount (42% extremely concerned, 41% somewhat concerned)
- 87% are concerned about a resulting lack of cybersecurity accountability (37% extremely concerned, 50% somewhat concerned)
These concerns are broadly felt, with consistently high percentages reported by respondents across all size segments and industry sectors.
Recommendations
While AI brings risks, with a thoughtful approach, organizations can navigate them and safely, securely take advantage of AI to enhance their cyber defenses and overall business outcomes.
The recommendations provide a starting point to help organizations mitigate the risks explored in this report.
Ask vendors how they develop their AI capabilities
- Training data. What is the quality, quantity, and source of data on which the models are trained? Better inputs lead to better outputs.
- Development team. Find out about the people behind the models. What level of AI expertise do they have? How well do they know threats, adversary behaviors, and security operations?
- Product engineering and rollout process. What steps does the vendor go through when developing and deploying AI capabilities in their solutions? What checks and controls are in place?
Apply business rigor to AI investment decisions
- Set goals. Be clear, specific, and granular about the outcomes you want AI to deliver.
- Quantify benefits. Understand how much of a difference AI investments will make.
- Prioritize investments. AI can help in many ways; some will have a greater impact than others. Identify the important metrics for your organization – financial savings, staff attrition impact, exposure reduction, etc. – and compare how the different options rank.
- Measure impact. Be sure to see how actual performance relates to initial expectations. Use the insights to make any adjustments that are needed.
View AI through a human-first lens
- Maintain perspective. AI is just one item in the cyber defense toolkit. Use it, but make clear that cybersecurity accountability is ultimately a human responsibility.
- Don’t replace, accelerate. Focus on how AI can support your staff by taking care of many low-level, repetitive security operations tasks and providing guided insights.
About the survey
Sophos commissioned independent research specialist Vanson Bourne to survey 400 IT security decision makers in organizations with between 50 and 3,000 employees during November 2024. All respondents worked in the private or charity/not-for-profit sector and currently use endpoint security solutions from 19 separate vendors and 14 MDR providers.
Sophos’ AI-powered cyber defenses
Sophos has been pushing the boundaries of AI-driven cybersecurity for nearly a decade. AI technologies and human cybersecurity expertise work together to stop the broadest range of threats, wherever they run. AI capabilities are embedded across Sophos products and services and delivered through the largest AI-native platform in the industry. To learn more about Sophos’ AI-powered cyber defenses visit www.sophos.com/ai.
Source: Sophos






