As we approach the October 2024 deadline for EU Member States to enact the NIS 2 Directive, organizations that do business in Europe must prepare for the significant changes it brings to cybersecurity compliance.
This article aims to shed light on the NIS 2 Directive, its necessity, key updates from the original NIS Directive, and how businesses can prepare for compliance. For an even deeper dive on the directive, download the Sophos NIS 2 Directive whitepaper.
What is the NIS 2 Directive?
The NIS 2 Directive is an evolution of the original Network and Information Systems (NIS) Directive, implemented to bolster the cybersecurity posture of EU member states. The initial NIS Directive, enacted in 2016, established guidelines for improving cybersecurity resilience across the EU. However, with the increasing sophistication and frequency of cyber-attacks, especially during and after the Covid-19 pandemic, there was a clear need for more stringent and comprehensive regulations.
Cyber threats have escalated to an industrial scale, with ransomware attacks becoming particularly prevalent. In June 2024, a hacking group known as Qilin, with ties to the Kremlin, carried out an attack on Synnovis, which is a pathology lab used by the UK’s National Health Service (NHS). The hackers demanded a £40 million ransom, and when the NHS refused to pay, hackers released the stolen data on the dark web.
Additionally, geopolitical tensions, such as the Russian invasion of Ukraine, have underscored the necessity for robust cybersecurity measures. The NIS 2 Directive aims to address these challenges by enhancing the security and resilience of essential and important entities across the EU.
Implications for non-EU Companies
While primarily aimed at EU Member States, non-EU companies operating within the EU or providing services to EU entities will also be impacted. Many national regulations are currently not as wide-ranging as the NIS 2 Directive; however, it would be prudent to expect further changes to local law as the plans for the EU legislation are developed further.
By proactively addressing the challenges outlined below, non-EU companies can better protect themselves and their customers from evolving cyber threats while avoiding severe penalties for non-compliance.
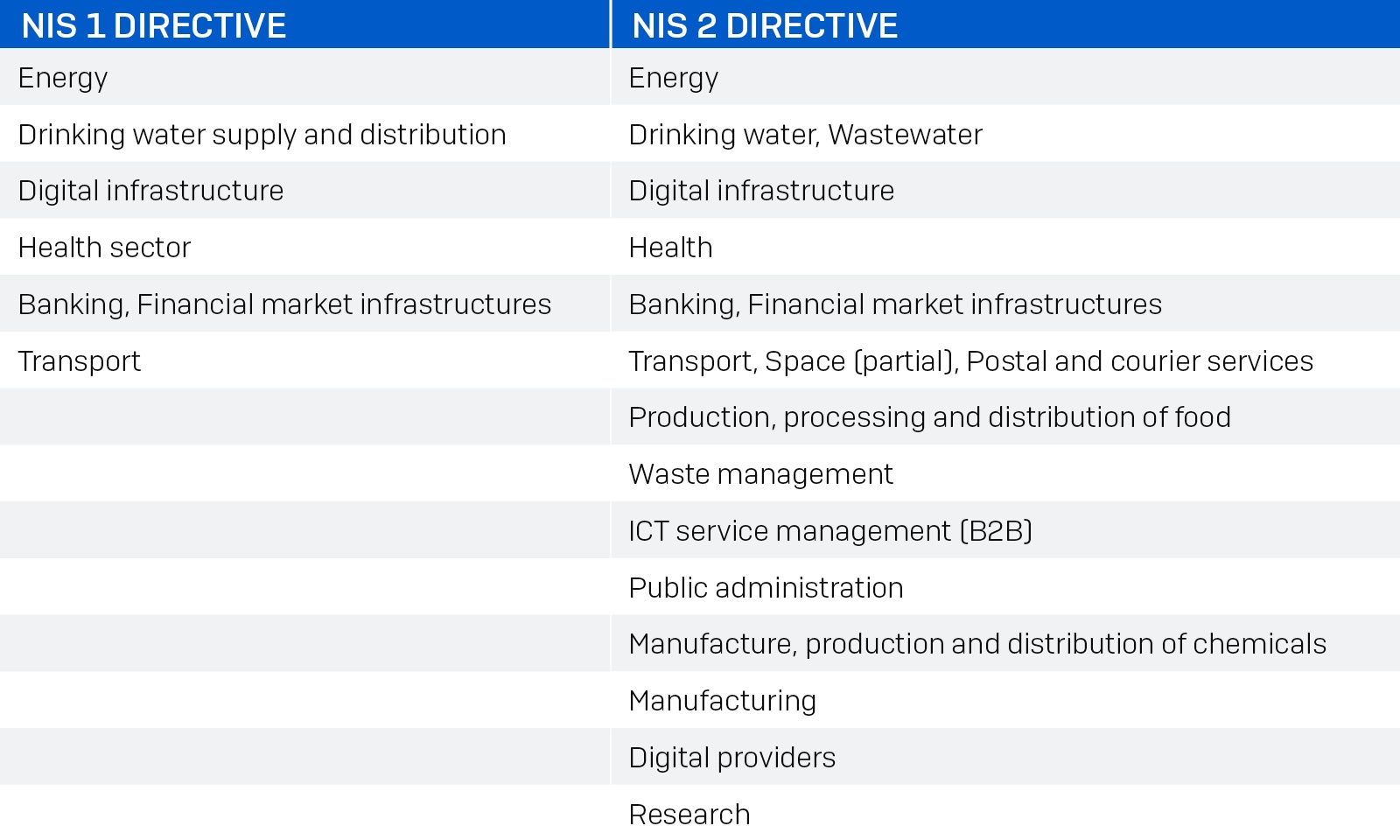
Key updates from NIS to NIS 2
The NIS 2 Directive introduces several critical updates and expansions from the original NIS Directive:
- Broader Scope of Covered Entities:
- Essential and Important Entities: NIS 2 categorizes entities into “essential” and “important” based on their sector and criticality. This expansion includes more sectors, such as wastewater, healthcare supply chains, postal and courier services, aerospace, public administration, and digital infrastructure.
- Supply Chain and Service Providers: Organizations involved in the supply chain and those providing critical support services are now explicitly covered, emphasizing the importance of securing interconnected networks.
- Enhanced Cybersecurity Standards:
- Mandatory Measures: Article 21 of the directive outlines mandatory cybersecurity measures, including basic cyber hygiene, vulnerability management, supply chain security, encryption, asset management, access control, and zero trust security.
- Incident Handling and Reporting: The directive mandates more rigorous incident reporting requirements, ensuring timely and consistent responses to cyber threats across the EU.
- Increased Accountability and Penalties:
- Senior Management Liability: Senior management can be held personally liable for non-compliance, underscoring the importance of executive involvement in cybersecurity governance.
- Fines and Sanctions: Organizations can face significant fines, up to €10 million or 2% of global turnover, for failing to comply with the directive.
The following 18 sectors are covered by the NIS 2 Directive:
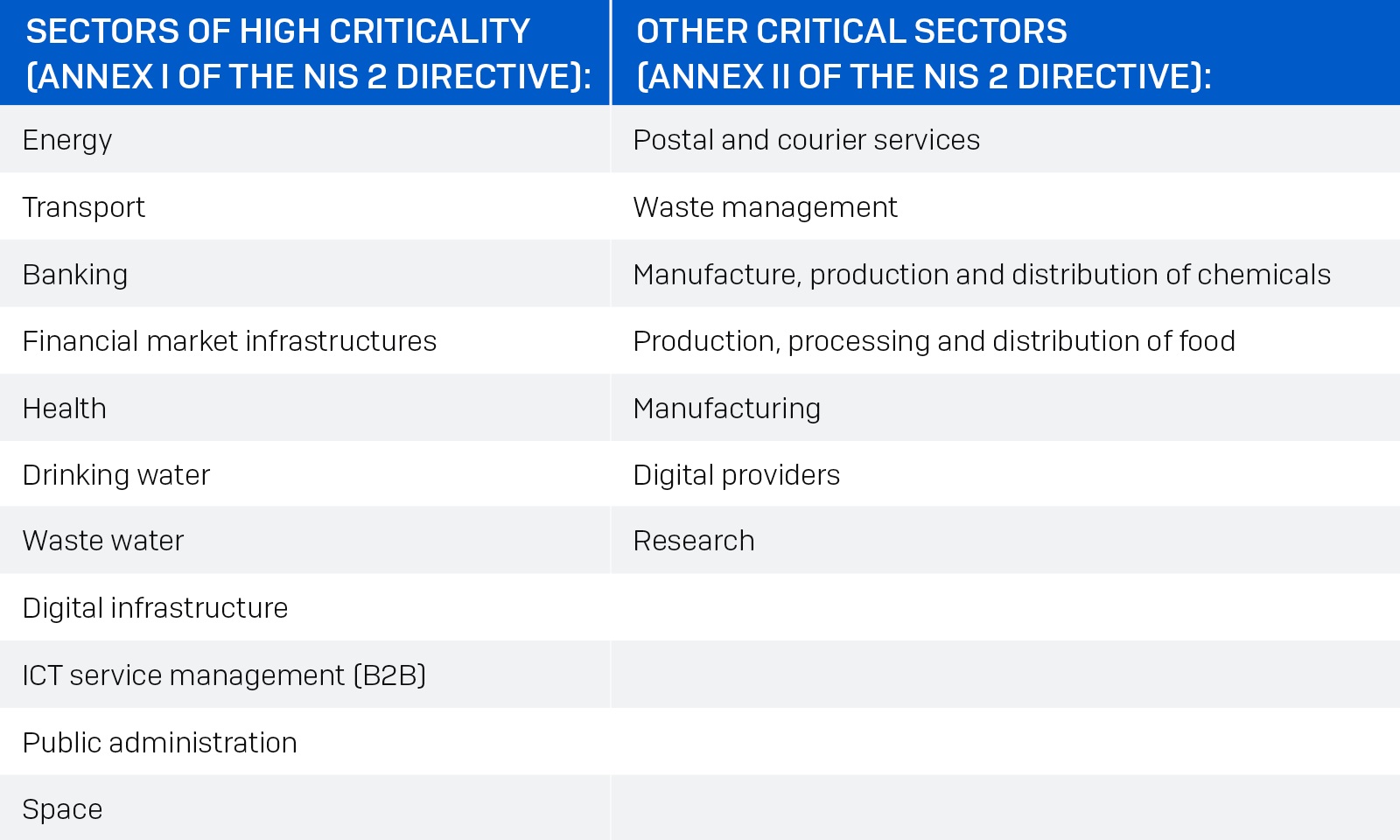
The following table illustrates the increase in sectors covered by the NIS 2 Directive as compared to the first NIS directive:
Impact on cybersecurity compliance
The NIS 2 Directive significantly impacts how organizations approach cybersecurity compliance. Businesses must adopt a proactive stance, integrating comprehensive risk management processes and ensuring adherence to the stringent standards set forth in the directive. The emphasis on mandatory measures and the potential for severe penalties necessitate a thorough review and enhancement of existing cybersecurity practices.
Organizations will need to allocate sufficient resources to meet these requirements. Estimates suggest that businesses already covered by the original NIS Directive may need to increase their cybersecurity budgets by up to 12%, while those newly covered could see budget increases of up to 22%, according to John Noble, former Director of the National Cyber Security Centre speaking on Sophos Spotlight: NIS2 Directive and Understanding Cybersecurity Compliance.
Preparing for NIS 2 compliance
To ensure compliance with the NIS 2 Directive, organizations should take the following steps:
- Assess Applicability:
- Determine whether your organization falls under the categories of essential or important entities. This involves evaluating your sector, the criticality of your services, and your operational footprint within the EU.
- Understand Jurisdiction:
- Identify which EU member states have jurisdiction over your operations for NIS 2 purposes. This is crucial for understanding specific national requirements and reporting obligations.
- Implement Cybersecurity Risk Management:
- Conduct a comprehensive risk analysis to identify potential cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities.
- Implement the mandatory measures outlined in Article 21, mapping them against an appropriate security framework such as ISO 27001 or the NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
- Strengthen Supply Chain Security:
- Focus on mitigating risks within your supply chain, particularly concerning software and service providers. This includes ensuring that third-party vendors comply with NIS 2 standards.
- Develop an Incident Response Plan:
- Formalize an incident response plan that includes clear protocols for reporting cyber incidents to relevant national authorities. Ensure that significant incidents are reported within the 24-hour timeframe specified by the directive.
- Engage Senior Management:
- Secure formal high-level management sign-off on your compliance strategy. Senior management involvement is critical for demonstrating a commitment to cybersecurity and ensuring that necessary resources are allocated.
The NIS2 Directive represents a significant step forward in enhancing the cybersecurity resilience of organizations across Europe. By understanding the key updates and taking proactive measures to ensure compliance, businesses can better protect themselves against the growing threat of cyber-attacks.
As the October deadline approaches, it is imperative for senior management and IT security professionals to prioritize NIS 2 compliance, leveraging resources such as the Sophos whitepaper to guide their efforts.
Source: Sophos






